单主机架构
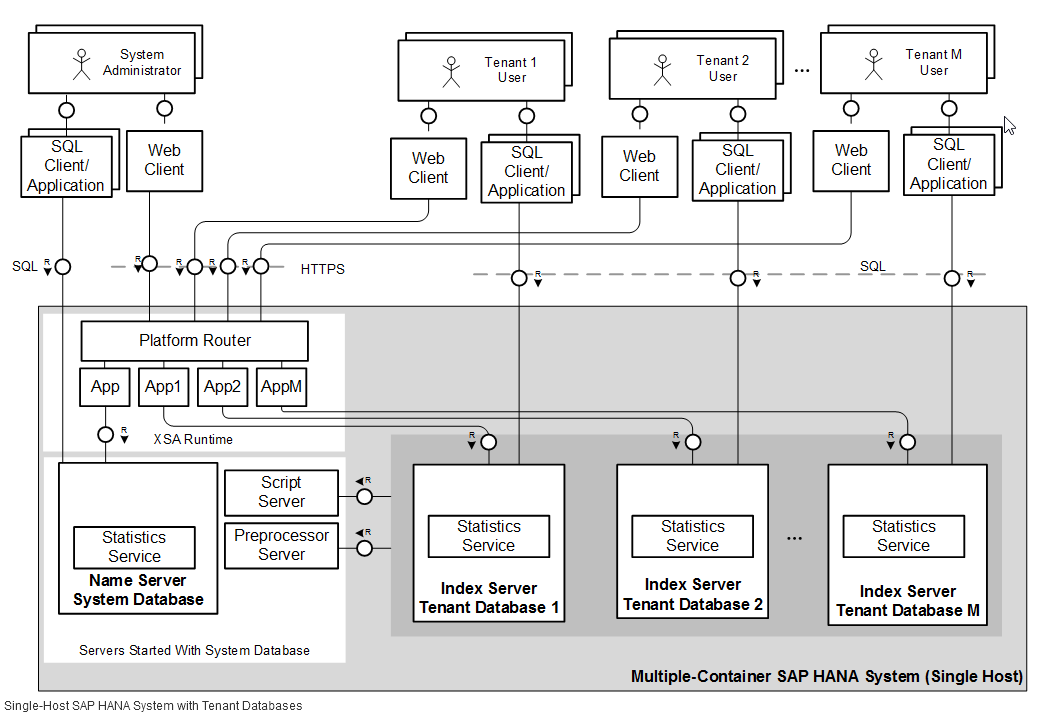
System Database
- The system database does not have the same functionality as a tenant database.
- The system database is not a database with full SQL support.
- The system database cannot be distributed across multiple hosts, in other words, scale-out is not possible.
- If you need a full-featured SAP HANA database, you always have to create at least one tenant database.
- The system database does not support Application Function Libraries (AFL) and SAP liveCache applications.
- Cross-database access between the system database and a tenant database is not possible. The system database can show monitoring data from tenant databases (views in the schema SYS_DATABASES) but can never show actual content from tenant databases.
- The system database cannot be copied or moved to another host.
- SAP HANA options can only run in tenant databases.
- Tenant-specific configurations cannot be set in the system database. Only global settings are allowed.
- Features can only be restricted or disabled at high level for tenant databases.
Tenant Databases:(Database-related topology information is stored in the relevant tenant database catalog.)
- Set of database users
- Database catalog
- Repository
- Persistence
- Backups
- Traces and logs
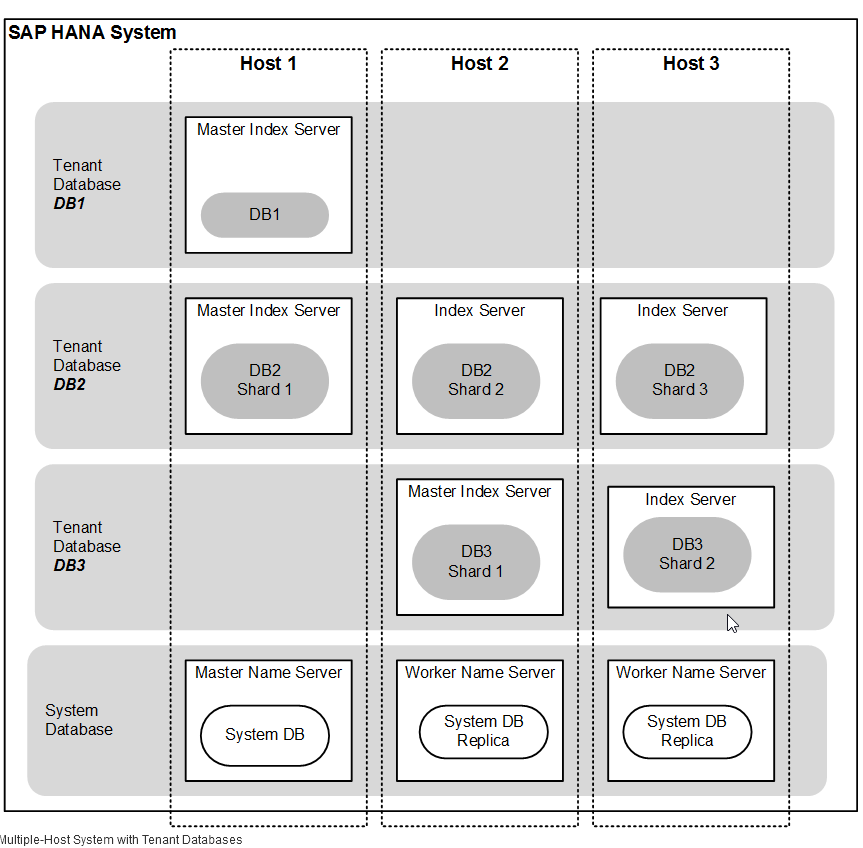
Scale-Out Recommendations
When planning your SAP HANA deployment with tenant databases, various options exist with regard to scale-up versus scale-out.
In general, scaling up offers some performance advantages over scaling out, as memory access is local and minor overhead associated with inter-node network communication is avoided.
Note the following with regard to scale-out:
- It is possible to distribute tenant databases across several hosts in a scale-out system.
- The primary reason to distribute tenant databases generally is when their size is larger than the capacity of a single host. However, other reasons for distributing tenant database may exist, for example, a large SAP Business Warehouse (BW) system requires a scale-out configuration in accordance with its sizing rules.
- If tenant databases are distributed in a scale-out configuration due to sizing requirements, caution is advised when deploying additional tenant databases on the same host as a distributed tenant database shard. The rationale is this: Workload in distributed scenarios can be somewhat volatile and less predictable. Therefore in many cases, it can be advantageous to dedicate maximum resources of the host to the distributed tenant database shard in order to maintain expected performance.
- In certain cases, more than one distributed tenant database shard may share the same host. In these cases, in order to dedicate maximum resources for a master node (for performance reasons), it is advisable to avoid deploying other tenant databases on the master node. For example, the following deployment should offer performance advantages:
- Host 1: Master for tenant database 1
- Host 2: Worker for tenant database 1 and worker for tenant database 2
- Host 3: Master for tenant database 2
- Host 4: Standby host for failover

During the installation of a multiple-host system with SAP HANA XS advanced, additional host roles are assigned for XS advanced. By default all worker hosts are configured to act as XS worker hosts; that is, they are additionally assigned the role xs_worker. However, it is also possible to configure dedicated hosts for XS advanced during installation.Additionally, the XS advanced runtime can be set up behind a reverse proxy (for example, a load balancer).
Failover Configuration

refer to https://help.sap.com/viewer/6b94445c94ae495c83a19646e7c3fd56/2.0.04/en-US/f9aba40d6c4c4ae48cce461db4d42d88.html