日期函数
(1)时间戳转换
日期格式转换时间戳
unix_timestamp(date,dateformat)不加参数获取当前的时间戳
select unix_timestamp() as time_stamp,unix_timestamp('2018-09-26 9:13:26','yyyy-MM-ddHH:mm:ss') as time_stamp1 from dual; time_stamp time_stamp1 1538054001 1537924406
时间戳转换日期格式
from_unixtime(timestamp,dateformat)
select from_unixtime(unix_timestamp(),'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss') asdate_time,from_unixtime(1537924406,'yyyy-MM-dd') as date_time1 from dual; date_time date_time1 2018-09-27 21:16:13 2018-09-26
(2)日期格式化
date_format(string/date,dateformat)把字符串或者日期转成指定格式的日期
select date_format('2018-09-12','yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss') as date_time,date_format('2018-09-12','yyyyMMdd') as date_time1 from dual; date_time date_time1 2018-09-12 00:00:00 20180912
to_date(date)返回yyyy-MM-dd日期格式
3、日期加减/月份加减(位移)
对日期进行加减法,date_add函数参数n是正数往后推n天,如果是负数往前推n天,date_sub函数相反
对月份进行加减,add_months 函数参数m是正数往后推m个月,如果是负数往前推m个月
date_add(date,n)
date_sub(date,n)
select date_add('2018-09-27',2) as date1,date_add('2018-09-27',-2) as date2 from dual;
date1 date2
2018-09-29 2018-09-25
add_months(date,m)
select add_months('2018-09-27',1) as month1,add_months('2018-09-27',-1) as month2 from dual;
month1 month2
2018-10-27 2018-08-27
4、日期差/月份差
日期差计算两个日期之间相差多少天,前面的日期减去后面的日期
月份差计算前面的日期减去后面的日期计算月份差,这个结果是按照天数占月分的比值计算得到的,是一个小数,可以自己取整
datediff(date,date1)
select datediff('2018-09-22','2018-08-02') as day_diff,datediff('2018-08-02','2018-09-22') as day_diff1 from dual;
day_diff day_diff1
51 -51
months_between(date,date1)
select months_between('2018-09-22','2018-08-02') as mon_diff,round(months_between('2018-09-22','2018-08-02')) as mon_diff1 from dual;
mon_diff mon_diff1
1.64516129 2.0
5、获取月末、月初、年初、当前日期下个星期X的日期
获取月末最后一天
last_day(date)
select last_day('2018-09-30') as date_time,last_day('2018-09-27 21:16:13') as date_time1 from dual;
date_time date_time1
2018-09-30 2018-09-30
获取月初、年初
trunc(date,format) format:MONTH/MON/MM, YEAR/YYYY/YY
select trunc('2018-09-27','YY') as date_time,trunc('2018-09-27 21:16:13','MM') as date_time1 from dual;
date_time date_time1
2018-01-01 2018-09-01
当前日期下个星期X的日期
next_day(date,formate) format:英文星期几的缩写或者全拼
select next_day('2018-09-27','TH') as date_time,next_day('2018-09-27 21:16:13','TU') as date_time1 from dual;
date_time date_time1
2018-10-04 2018-10-02
hive条件函数
(1)if函数:if(条件表达式,结果1,结果2)
hive> select if(1=2,100,200) from lxw_dual; 200 hive> select if(1=1,100,200) from lxw_dual; 100
(2)coalesce函数:返回参数中的第一个非空值;如果所有值都为null,那么返回null
hive> select COALESCE(null,'100','50′) from lxw_dual; 100
(3)case when函数:
- CASE a WHEN b THEN c [WHENd THEN e]* [ELSE f] END
- 如果a等于b,那么返回c;如果a等于d,那么返回e;否则返回f
hive> Select case 100 when 50 then 'tom' when 100 then 'mary' else 'tim' end from lxw_dual; mary hive> Select case 200 when 50 then 'tom' when 100 then 'mary' else 'tim' end from lxw_dual; tim
- CASE WHEN a THEN b [WHEN cTHEN d]* [ELSE e] END
- 如果a为TRUE,则返回b;如果c为TRUE,则返回d;否则返回e
hive> select case when 1=2 then 'tom' when 2=2 then 'mary' else 'tim' end from lxw_dual; mary hive> select case when 1=1 then 'tom' when 2=2 then 'mary' else 'tim' end from lxw_dual; tom
count函数
count(*):所有行进行统计,包括null行
count(1):所有行进行统计,包括null行
count(columc)与count(if(条件)):都是对column中非null进行统计,来一条就统计一条,不关心怎样进行分类
count(distinct column):去重统计也会排除字段为null的值
使用group by代替distinct
count(case when plat=1 then u else null end)
count(distinct case when plat=1 then u else null end)
count(case when (type=2 OR type=6) then u else null end)
count(distinct case when (type=2 OR type=6) then u else null end)
create table t1( a int); insert into t1 (a) values (1); insert into t1 (a) values (2); insert into t1 (a) values (3); insert into t1 (a) values (NULL); select count(*) from t1; 4 select count(1) from t1; 4 select count(a) from t1; 3 select count(a>1) from t1; 3 select count(distinct a) from t1; 3 select count(distinct case when a>1 then a else NULL end) from t1 2
count(if)与count(distinct if)小案例:
表名: user_active_day (用户日活表)
表内容:
user_id(用户id) user_is_new(是否新用户 1:新增用户 0:老用户) location_city(用户所在地区) partition_date(日期分区)
需求:
找出20180901至今的xxx地区的用户日活量以及新增用户量
思路:
筛选日期分区和地区,统计user_id的数量为用户日活量,统计user_is_new = 1的数量为新增用户量.
最开始写的hql语句
select partition_date,count(user_id), count(if(user_is_new = 1, user_id, 0)) --注意新增用户量的统计 from dw.nice_live_dw_user_active_day where location_city like '%xxx%' and partition_date >= 20180901 group by partition_date;
我们使用count(if())来进行筛选统计,但是效果并没有达到,出现的结果如下
20180901 16737 16737
根本就没有达到筛选的目的,为什么?
这就要从count的机制说起
首先count()是对数据进行计数,说白了就是你来一条数据我计数一条,我不关心你怎么分类,我只对数据计数
每条数据从if()函数出来,还是一条数据,所以count+1
所以count(user_id)跟count(if(user_id))没有任何的区别.
我们稍做修改
select partition_date,count(user_id), count(distinct if(user_is_new = 1, user_id, 0)) --注意新增用户量的统计,加了distinct去重 from dw.nice_live_dw_user_active_day where location_city like '%xxx%' and partition_date >= 20180901 group by partition_date;
结果如下
20180901 16737 261
这次看着就像是对了吧,我们加了distinct进行去重
每次来一条数据先过if()然后再进行去重最后统计.但是实际上结果依旧是错误的.
我们来模拟一下筛选统计的过程
我们有这样四条数据
user_id user_is_new
1 1
2 0
3 1
4 0
表中的数据是一条一条遍历的,
(1)当user_id = 1的数据过来的时候,我们先过if函数 user_is_new = 1 ==> count(distinct user_id = 1),
然后我们把user_id = 1进行重复判断,我们用一个模拟容器来模拟去重,
从容器里找user_id = 1的数据,发现没有,不重复,所以通过我们把count+1,然后把user_id = 1的数据放入,用于下条去重
(2)当user_id = 2的数据过来的时候,我们先过if函数 user_is_new = 0 ==> count(distinct 0),
然后我们把0进行重复判断,
从容器里找0的数据,发现没有,不重复,所以通过我们把count+1,然后把0的数据放入,用于下条去重
(3)当user_id = 3的数据过来的时候,我们先过if函数 user_is_new = 1 ==> count(distinct user_id = 3),
然后我们把user_id = 3进行重复判断,
从容器里找user_id = 3的数据,发现没有,不重复,所以通过我们把count+1,然后把user_id = 3的数据放入,用于下条去重
(4)当user_id = 4的数据过来的时候,我们先过if函数 user_is_new = 0 ==> count(distinct 0),
然后我们把0进行重复判断,
从容器里找0的数据,发现重复,是之前user_id = 2的时候过if()转化成0的那条数据,所以count不执行
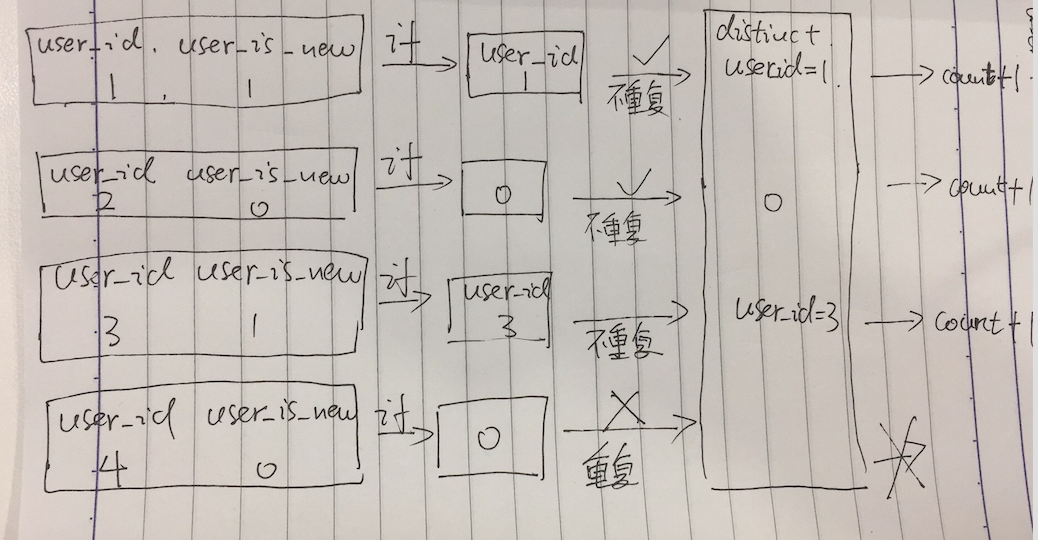
我们通过模拟count(distinct if)过程发现,在count的时候我们把不符合条件的最开始的那条语句也count进去了一次
导致最终结果比正确结果多了1.
我们在原基础语句上再减去1就是正确的hql语句
其实在日常中我们做分类筛选统计的时候一般是用sum来完成的,符合条件sum+1,不符合条件sum+0
select partition_date,count(user_id), sum(if(user_is_new = 1, 1, 0)) --用sum进行筛选统计 from dw.nice_live_dw_user_active_day where location_city like '%xxx%' and partition_date >= 20180901 group by partition_date;
结果如下
20180901 16737 260
sum(if)只试用于单个条件判断,如果筛选条件很多,我们可以用sum(case when then else end)来进行多条件筛选
注意,hive中并没有sum(distinct col1)这种使用方式,我们可以使用sum(col) group by col来达到相同效果.