创建三个线程按顺序输出1-60,每个线程输出5个数
public class ThreadStart { public static void main(String[] args) { Thread t1 = new ThreadA(); Thread t2 = new ThreadB(); Thread t3 = new ThreadC(); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } } class ThreadA extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); for (int i =1; i <=4 ; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(95); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.print("A: "); for(int j=15*(i-1)+1;j<(15*(i-1)+6);j++){ if(j!=15*(i-1)+5) System.out.print(j+" "); else System.out.print(j); } System.out.println(""); } } } class ThreadB extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); for (int i =1; i <=4 ; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.print("B: "); for(int j=15*(i-1)+6;j<15*(i-1)+11;j++){ if(j!=15*(i-1)+10) System.out.print(j+" "); else System.out.print(j); } System.out.println(""); } } } class ThreadC extends Thread { @Override public void run() { super.run(); for (int i =1; i <=4 ; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(105); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.print("C: "); for(int j=15*(i-1)+11;j<15*i+1;j++){ if(j!=15*i) System.out.print(j+" "); else System.out.print(j); } System.out.println(""); } } }
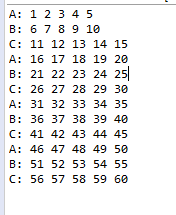
2019-11-05更新简便方法,之前写的太啰嗦了
方法一 利用synchronized:同一时刻,只有一个线程可以执行某个方法或某个代码块
public class Main01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ProcessingThread pt = new ProcessingThread(); Thread t1 = new Thread(pt,"A"); Thread t2 = new Thread(pt,"B"); Thread t3 = new Thread(pt,"C"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } } class ProcessingThread implements Runnable { private int count; @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) { processSomething(i); synchronized(this){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"|"); for(int c=0;c<4;c++){ System.out.print(++count+","); } System.out.println(++count); } } } public synchronized int getCount() { // return count.get(); return count; } private void processSomething(int i) { // processing some job try { Thread.sleep(i * 800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
利用AtomicInteger原子操作
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class Main01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ProcessingThread pt = new ProcessingThread(); Thread t1 = new Thread(pt,"A"); Thread t2 = new Thread(pt,"B"); Thread t3 = new Thread(pt,"C"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } } class ProcessingThread implements Runnable { private AtomicInteger count =new AtomicInteger(); @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) { processSomething(i); synchronized(this){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"|"); for(int c=0;c<4;c++){ System.out.print(count.incrementAndGet()+","); } System.out.println(count.incrementAndGet()); } } } public synchronized int getCount() { return count.get(); } private void processSomething(int i) { try { Thread.sleep(i * 800); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
结果
