redis中对象都使用redisObjec结构,字符串对象ptr指向sdshdr结构
1 /* 2 * 保存字符串对象的结构 3 */ 4 struct sdshdr { 5 6 // buf 中已占用空间的长度 7 int len; 8 9 // buf 中剩余可用空间的长度 10 int free; 11 12 // 数据空间 13 char buf[]; 14 };
字符串对象的编码可以是int、raw或者embstr。
如果一个字符串对象保存的是整数值,那么字符串对象会将整数值保存在字符串对象结构的ptr属性里面,
并且将字符串对象的编码设置为int
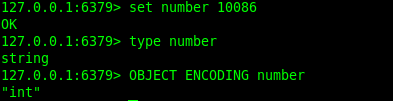
这时对象结构如下
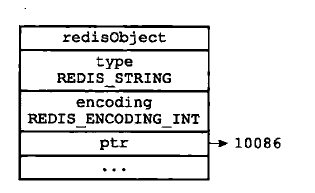
如果字符串对象保存的是一个字符串值,并且这个字符串的长度大于39(redis 4.0.1 是44)字节,那么
字符串对象将使用一个简单动态字符串(SDS)来保存这个字符串值,并将对象的编码设置为raw。
如果字符串对象保存的是一个字符串值,并且小于等于32字节,那么字符串对象将使用embstr编码的
方式来保存这个字符串值
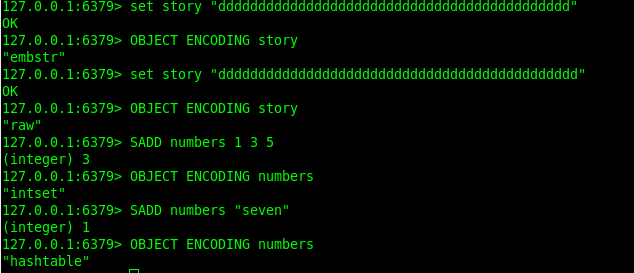
embstr编码是专门用于保存短字符串的一种优化编码方式,这种编码和raw编码一样,都使用redis-
Object结构和sdshdr结构来表示字符串对象,但raw编码会调用两次内存分配函数来分别创建redisObject
结构和sdshdr结构,而embstr编码则通过调用一次内存分配函数来分配一块连续的空间,空间中依次包含
redisObject和sdshdr两个结构
embstr编码的字符串对象的所有数据都保存在一块连续的内存里面,所以这种编码的字符串对象比起
raw编码的字符串对象能够更好的利用缓存带来的优势
另外,浮点数据也可以通过字符串对象保存,编码是embstr或者raw
embstr字符串是只读的,如果修改(例如append命令)编码会变成raw
创建字符串对象入口

1 /* Create a string object with EMBSTR encoding if it is smaller than 2 * REIDS_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT, otherwise the RAW encoding is 3 * used. 4 * 5 * The current limit of 39 is chosen so that the biggest string object 6 * we allocate as EMBSTR will still fit into the 64 byte arena of jemalloc. */ 7 #define REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT 39 8 robj *createStringObject(char *ptr, size_t len) { 9 if (len <= REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT) 10 return createEmbeddedStringObject(ptr,len); 11 else 12 return createRawStringObject(ptr,len); 13 }
embstr编码String

1 /* Create a string object with encoding REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR, that is 2 * an object where the sds string is actually an unmodifiable string 3 * allocated in the same chunk as the object itself. */ 4 // 创建一个 REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR 编码的字符对象 5 // 这个字符串对象中的 sds 会和字符串对象的 redisObject 结构一起分配 6 // 因此这个字符也是不可修改的 7 robj *createEmbeddedStringObject(char *ptr, size_t len) { 8 robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(robj)+sizeof(struct sdshdr)+len+1); 9 struct sdshdr *sh = (void*)(o+1); 10 11 o->type = REDIS_STRING; 12 o->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_EMBSTR; 13 o->ptr = sh+1; 14 o->refcount = 1; 15 o->lru = LRU_CLOCK(); 16 17 sh->len = len; 18 sh->free = 0; 19 if (ptr) { 20 memcpy(sh->buf,ptr,len); 21 sh->buf[len] = '�'; 22 } else { 23 memset(sh->buf,0,len+1); 24 } 25 return o; 26 }
raw编码String

1 /* Create a string object with encoding REDIS_ENCODING_RAW, that is a plain 2 * string object where o->ptr points to a proper sds string. */ 3 // 创建一个 REDIS_ENCODING_RAW 编码的字符对象 4 // 对象的指针指向一个 sds 结构 5 robj *createRawStringObject(char *ptr, size_t len) { 6 return createObject(REDIS_STRING,sdsnewlen(ptr,len)); 7 } 8 9 10 /* 11 * 创建一个新 robj 对象 12 */ 13 robj *createObject(int type, void *ptr) { 14 15 robj *o = zmalloc(sizeof(*o)); 16 17 o->type = type; 18 o->encoding = REDIS_ENCODING_RAW; 19 o->ptr = ptr; 20 o->refcount = 1; 21 22 /* Set the LRU to the current lruclock (minutes resolution). */ 23 o->lru = LRU_CLOCK(); 24 return o; 25 } 26 27 28 /* 29 * 根据给定的初始化字符串 init 和字符串长度 initlen 30 * 创建一个新的 sds 31 * 32 * 参数 33 * init :初始化字符串指针 34 * initlen :初始化字符串的长度 35 * 36 * 返回值 37 * sds :创建成功返回 sdshdr 相对应的 sds 38 * 创建失败返回 NULL 39 * 40 * 复杂度 41 * T = O(N) 42 */ 43 /* Create a new sds string with the content specified by the 'init' pointer 44 * and 'initlen'. 45 * If NULL is used for 'init' the string is initialized with zero bytes. 46 * 47 * The string is always null-termined (all the sds strings are, always) so 48 * even if you create an sds string with: 49 * 50 * mystring = sdsnewlen("abc",3"); 51 * 52 * You can print the string with printf() as there is an implicit � at the 53 * end of the string. However the string is binary safe and can contain 54 * � characters in the middle, as the length is stored in the sds header. */ 55 sds sdsnewlen(const void *init, size_t initlen) { 56 57 struct sdshdr *sh; 58 59 // 根据是否有初始化内容,选择适当的内存分配方式 60 // T = O(N) 61 if (init) { 62 // zmalloc 不初始化所分配的内存 63 sh = zmalloc(sizeof(struct sdshdr)+initlen+1); 64 } else { 65 // zcalloc 将分配的内存全部初始化为 0 66 sh = zcalloc(sizeof(struct sdshdr)+initlen+1); 67 } 68 69 // 内存分配失败,返回 70 if (sh == NULL) return NULL; 71 72 // 设置初始化长度 73 sh->len = initlen; 74 // 新 sds 不预留任何空间 75 sh->free = 0; 76 // 如果有指定初始化内容,将它们复制到 sdshdr 的 buf 中 77 // T = O(N) 78 if (initlen && init) 79 memcpy(sh->buf, init, initlen); 80 // 以 � 结尾 81 sh->buf[initlen] = '�'; 82 83 // 返回 buf 部分,而不是整个 sdshdr 84 return (char*)sh->buf; 85 }
