
使用除法来缩减数字,使用余数法来计算个数。

class Solution: def hammingWeight(self, n: int) -> int: count = 0 while True : s = n // 2 y = n % 2 if y == 1: count += 1 if s == 0 : break n = s return count
移位运算:
如果求余数结果为一,则计数然后右移一位,否者直接右移一位。以此类推:直到输入的数字递减为0,退出。

class Solution: def hammingWeight(self, n: int) -> int: res = 0 while n: if not n % 2: n = n >> 1 continue res += 1 n = n >> 1 return res
如果输入1,这输出1-9的数字。
如果输入2,则输出1-99的数字。
使用循环的方式直接取出:

class Solution: def printNumbers(self, n: int) -> List[int]: newList = list() for _ in range(1,10**n): newList.append(_) return newList
使用列表解析:

class Solution: def printNumbers(self, n: int) -> List[int]: return [i for i in range(1,10**n)]
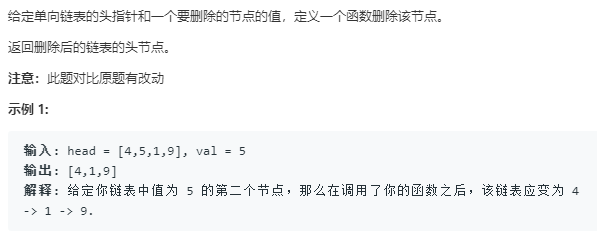

# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def deleteNode(self, head: ListNode, val: int) -> ListNode: if head.val == val: return head.next pre, cur = head, head.next while cur and cur.val != val: pre, cur = cur, cur.next pre.next = cur.next return head
