进程间通信方式主要分为 管道、SystemV IPC、 POSIX IPC三大类,管道作为进程间通信的一大重要方式,平时应用当中十分广泛。于是这里就先简单整理了一些关于管道的用法和注意事项。
匿名管道
管道是UNIX中最古老的进程间通信形式。通常将一个进程连接到另一个进程的一个数据流称为一个 “管道”。它本质上其实就是内核的一块缓存。
管道的限制:
* 大小有限制(一般是65536)
*半双工 (数据只能向一个方向流动)
*在有亲缘关系的进程间使用(父进程创建一个管道,两个子进程通过管道进行通信也行)
如何创建管道?
使用 int pipe(int fds[2]) 函数创建一个无名管道 //fds[0]代表读; fds[1] 代表写 ; 函数成功返回0, 错误返回错误代码
比如来创建一个管道来用于父子进程间通信:

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <unistd.h> 5 6 //父子进程间通信 7 int main(void) 8 { 9 int fds[2]; 10 //创建一个无名管道 11 if(pipe(fds) == -1){ 12 perror("make pipe");exit(1); 13 } 14 15 pid_t pid = fork(); 16 if(pid == 0) 17 { //子进程写 18 close(fds[0]); //关闭读 19 //sleep(1); 20 write(fds[1], "change world!", 14); 21 close(fds[1]); 22 } 23 else 24 { //父进程读 25 close(fds[1]); //关闭写 26 char buf [100] = {}; 27 int r = read(fds[0], buf, 100); //返回读取的字节数 28 printf("r= %d, buf=%s ", r, buf); 29 close(fds[0]); 30 } 31 32 }过关到
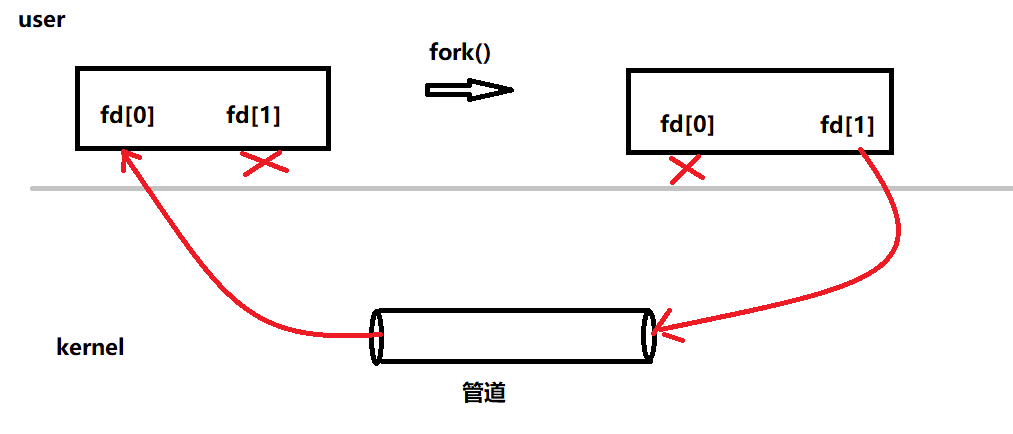
再来分析分析 ls -l | wc -l 这种采用了管道的命令,假定子进程实现ls,父进程实现wc。ls命令正常执行将结果集写出到stdout,但dup后,现在会写入管道的写端;wc –l 正常应该从stdin读取数据,dup后会从管道的fd[0]读。
来代码:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(void) { int fds[2]; if(pipe(fds) < 0){
perror("make pipe");exit(1);
}; pid_t pid = fork(); if(pid == 0) { //子进程写进管道 执行ls -l close(1); close(fds[0]); dup(fds[1]); //让stdout指向fds[1]指向的file表 execlp("ls", "ls", "-l", NULL); //实现将ls -l的结果写入管道 close(fds[1]); exit(1); } else { //父进程从管道读 执行wc -l close(0); close(fds[1]); dup(fds[0]); //让stdin指向fds[0]指向file表 close(fds[0]); execlp("wc", "wc", "-l", NULL); //从管道接收数据,执行wc -l命令 exit(1); } }

注意:不能让父进程执行 ls -l ,子进程执行 wc -l 。这是因为程序的子进程将stdin重定向给管道,父进程执行ls -l 的结果集将通过管道写给子进程。若父进程在子进程打印wc的结果到屏幕之前被shell调用wait回收,shell就会先输出$提示符,最后程序都执行结束,shell还在阻塞等待用户输入。
总结:
(1) 读管道:
1.管道中有数据,read返回实际读到的字节数。
2.管道中无数据:
①管道写端被全部关闭,read返回0 (好像读到文件结尾)
② 写端没有全部被关闭,read阻塞等待(不久的将来可能有数据抵达,此时会让出cpu资源)
(2) 写管道:
1. 管道读端全部被关闭, 进程异常终止 (操作系统发出SIGPIPE信号)
2. 管道读端没有全部关闭:
①管道已满,write阻塞。
②管道未满,write将数据写入,并返回实际写入的字节数。
命名管道
命名管道可在同一台计算机的不同进程之间或在跨越一个网络的不同计算机的不同进程之间,支持可靠的、单向或双向的数据通信。
不同于匿名管道的是:命名管道可以在不相关的进程之间和不同计算机之间使用,服务器建立命名管道时给它指定一个名字,任何进程都可以通过该名字打开管道的另一端,根据给定的权限和服务器来进程通信。使通过网络传输数据并不比同一计算机上两进程之间通信更困难,不过如果要同时和多个进程通信它就力不从心了。
如何创建?
int mkfifo(const char* pathname, mode_t mod)

//命名管道创建 #include <stdio.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> int main(void) { if(mkfifo("fifo_pipe", 0777) == -1) { perror("make pipe"); exit(1); } return 0; }
read.c

#include<stdio.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<fcntl.h> int main(void) { int fd; char buf[80]; fd = open("fifo_pipe", O_RDONLY); while(1) { read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)); //读到buf里 printf("%s ", buf); sleep(1); } return 0; }
write.c

1 #include<sys/types.h> 2 #include<sys/stat.h> 3 #include<stdio.h> 4 #include<unistd.h> 5 #include<fcntl.h> 6 7 int main(void) 8 { 9 int fd; 10 char s[]="I am from write.c"; 11 fd=open("fifo_pipe", O_WRONLY); 12 13 while(1) 14 { 15 write(fd, s, sizeof(s)); 16 sleep(1); 17 } 18 19 return 0; 20 } ~
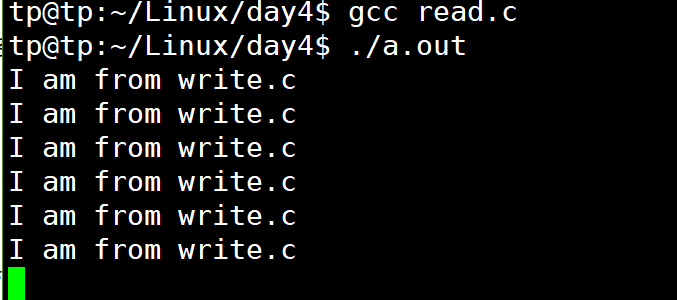
注意:一旦建立起联系,删掉管道名称文件进程间的通信也不会出现问题。
