import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 定义RNN的参数。 HIDDEN_SIZE = 30 # LSTM中隐藏节点的个数。 NUM_LAYERS = 2 # LSTM的层数。 TIMESTEPS = 10 # 循环神经网络的训练序列长度。 TRAINING_STEPS = 10000 # 训练轮数。 BATCH_SIZE = 32 # batch大小。 TRAINING_EXAMPLES = 10000 # 训练数据个数。 TESTING_EXAMPLES = 1000 # 测试数据个数。 SAMPLE_GAP = 0.01 # 采样间隔。
# 产生正弦数据。 def generate_data(seq): X = [] y = [] # 序列的第i项和后面的TIMESTEPS-1项合在一起作为输入;第i + TIMESTEPS项作为输 # 出。即用sin函数前面的TIMESTEPS个点的信息,预测第i + TIMESTEPS个点的函数值。 for i in range(len(seq) - TIMESTEPS): X.append([seq[i: i + TIMESTEPS]]) y.append([seq[i + TIMESTEPS]]) return np.array(X, dtype=np.float32), np.array(y, dtype=np.float32) # 用正弦函数生成训练和测试数据集合。 test_start = (TRAINING_EXAMPLES + TIMESTEPS) * SAMPLE_GAP test_end = test_start + (TESTING_EXAMPLES + TIMESTEPS) * SAMPLE_GAP train_X, train_y = generate_data(np.sin(np.linspace(0, test_start, TRAINING_EXAMPLES + TIMESTEPS, dtype=np.float32))) test_X, test_y = generate_data(np.sin(np.linspace(test_start, test_end, TESTING_EXAMPLES + TIMESTEPS, dtype=np.float32)))
# 定义网络结构和优化步骤。 def lstm_model(X, y, is_training): # 使用多层的LSTM结构。 cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(HIDDEN_SIZE) for _ in range(NUM_LAYERS)]) # 使用TensorFlow接口将多层的LSTM结构连接成RNN网络并计算其前向传播结果。 outputs, _ = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, X, dtype=tf.float32) output = outputs[:, -1, :] # 对LSTM网络的输出再做加一层全链接层并计算损失。注意这里默认的损失为平均 # 平方差损失函数。 predictions = tf.contrib.layers.fully_connected(output, 1, activation_fn=None) # 只在训练时计算损失函数和优化步骤。测试时直接返回预测结果。 if not is_training: return predictions, None, None # 计算损失函数。 loss = tf.losses.mean_squared_error(labels=y, predictions=predictions) # 创建模型优化器并得到优化步骤。 train_op = tf.contrib.layers.optimize_loss(loss, tf.train.get_global_step(),optimizer="Adagrad", learning_rate=0.1) return predictions, loss, train_op
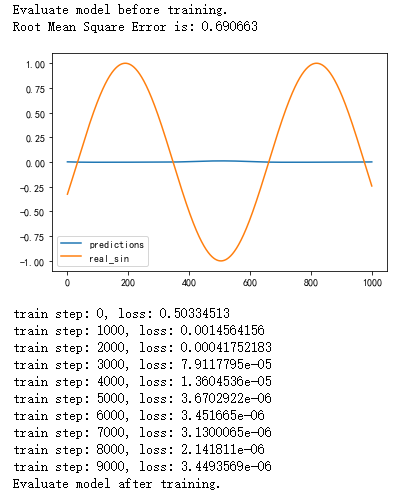
# 定义测试方法。 def run_eval(sess, test_X, test_y): # 将测试数据以数据集的方式提供给计算图。 ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((test_X, test_y)) ds = ds.batch(1) X, y = ds.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next() # 调用模型得到计算结果。这里不需要输入真实的y值。 with tf.variable_scope("model", reuse=True): prediction, _, _ = lstm_model(X, [0.0], False) # 将预测结果存入一个数组。 predictions = [] labels = [] for i in range(TESTING_EXAMPLES): p, l = sess.run([prediction, y]) predictions.append(p) labels.append(l) # 计算rmse作为评价指标。 predictions = np.array(predictions).squeeze() labels = np.array(labels).squeeze() rmse = np.sqrt(((predictions - labels) ** 2).mean(axis=0)) print("Root Mean Square Error is: %f" % rmse) #对预测的sin函数曲线进行绘图。 plt.figure() plt.plot(predictions, label='predictions') plt.plot(labels, label='real_sin') plt.legend() plt.show()
# 执行训练和测试。 # 将训练数据以数据集的方式提供给计算图。 ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((train_X, train_y)) ds = ds.repeat().shuffle(1000).batch(BATCH_SIZE) X, y = ds.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next() # 定义模型,得到预测结果、损失函数,和训练操作。 with tf.variable_scope("model"): _, loss, train_op = lstm_model(X, y, True) with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # 测试在训练之前的模型效果。 print("Evaluate model before training.") run_eval(sess, test_X, test_y) # 训练模型。 for i in range(TRAINING_STEPS): _, l = sess.run([train_op, loss]) if i % 1000 == 0: print("train step: " + str(i) + ", loss: " + str(l)) # 使用训练好的模型对测试数据进行预测。 print("Evaluate model after training.") run_eval(sess, test_X, test_y)