import sys import codecs import tensorflow as tf # 1.参数设置。 # 读取checkpoint的路径。9000表示是训练程序在第9000步保存的checkpoint。 CHECKPOINT_PATH = "F:\temp\seq2seq_ckpt-9000" # 模型参数。必须与训练时的模型参数保持一致。 HIDDEN_SIZE = 1024 # LSTM的隐藏层规模。 NUM_LAYERS = 2 # 深层循环神经网络中LSTM结构的层数。 SRC_VOCAB_SIZE = 10000 # 源语言词汇表大小。 TRG_VOCAB_SIZE = 4000 # 目标语言词汇表大小。 SHARE_EMB_AND_SOFTMAX = True # 在Softmax层和词向量层之间共享参数。 # 词汇表文件 SRC_VOCAB = "F:\TensorFlowGoogle\201806-github\TensorFlowGoogleCode\Chapter09\en.vocab" TRG_VOCAB = "F:\TensorFlowGoogle\201806-github\TensorFlowGoogleCode\Chapter09\zh.vocab" # 词汇表中<sos>和<eos>的ID。在解码过程中需要用<sos>作为第一步的输入,并将检查 # 是否是<eos>,因此需要知道这两个符号的ID。 SOS_ID = 1 EOS_ID = 2
# 2.定义NMT模型和解码步骤。 # 定义NMTModel类来描述模型。 class NMTModel(object): # 在模型的初始化函数中定义模型要用到的变量。 def __init__(self): # 定义编码器和解码器所使用的LSTM结构。 self.enc_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(HIDDEN_SIZE)for _ in range(NUM_LAYERS)]) self.dec_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(HIDDEN_SIZE) for _ in range(NUM_LAYERS)]) # 为源语言和目标语言分别定义词向量。 self.src_embedding = tf.get_variable("src_emb", [SRC_VOCAB_SIZE, HIDDEN_SIZE]) self.trg_embedding = tf.get_variable("trg_emb", [TRG_VOCAB_SIZE, HIDDEN_SIZE]) # 定义softmax层的变量 if SHARE_EMB_AND_SOFTMAX: self.softmax_weight = tf.transpose(self.trg_embedding) else: self.softmax_weight = tf.get_variable("weight", [HIDDEN_SIZE, TRG_VOCAB_SIZE]) self.softmax_bias = tf.get_variable("softmax_bias", [TRG_VOCAB_SIZE]) def inference(self, src_input): # 虽然输入只有一个句子,但因为dynamic_rnn要求输入是batch的形式,因此这里 # 将输入句子整理为大小为1的batch。 src_size = tf.convert_to_tensor([len(src_input)], dtype=tf.int32) src_input = tf.convert_to_tensor([src_input], dtype=tf.int32) src_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.src_embedding, src_input) # 使用dynamic_rnn构造编码器。这一步与训练时相同。 with tf.variable_scope("encoder"): enc_outputs, enc_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(self.enc_cell, src_emb, src_size, dtype=tf.float32) # 设置解码的最大步数。这是为了避免在极端情况出现无限循环的问题。 MAX_DEC_LEN=100 with tf.variable_scope("decoder/rnn/multi_rnn_cell"): # 使用一个变长的TensorArray来存储生成的句子。 init_array = tf.TensorArray(dtype=tf.int32, size=0,dynamic_size=True, clear_after_read=False) # 填入第一个单词<sos>作为解码器的输入。 init_array = init_array.write(0, SOS_ID) # 构建初始的循环状态。循环状态包含循环神经网络的隐藏状态,保存生成句子的 # TensorArray,以及记录解码步数的一个整数step。 init_loop_var = (enc_state, init_array, 0) # tf.while_loop的循环条件: # 循环直到解码器输出<eos>,或者达到最大步数为止。 def continue_loop_condition(state, trg_ids, step): return tf.reduce_all(tf.logical_and(tf.not_equal(trg_ids.read(step), EOS_ID),tf.less(step, MAX_DEC_LEN-1))) def loop_body(state, trg_ids, step): # 读取最后一步输出的单词,并读取其词向量。 trg_input = [trg_ids.read(step)] trg_emb = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.trg_embedding,trg_input) # 这里不使用dynamic_rnn,而是直接调用dec_cell向前计算一步。 dec_outputs, next_state = self.dec_cell.call(state=state, inputs=trg_emb) # 计算每个可能的输出单词对应的logit,并选取logit值最大的单词作为 # 这一步的而输出。 output = tf.reshape(dec_outputs, [-1, HIDDEN_SIZE]) logits = (tf.matmul(output, self.softmax_weight)+ self.softmax_bias) next_id = tf.argmax(logits, axis=1, output_type=tf.int32) # 将这一步输出的单词写入循环状态的trg_ids中。 trg_ids = trg_ids.write(step+1, next_id[0]) return next_state, trg_ids, step+1 # 执行tf.while_loop,返回最终状态。 state, trg_ids, step = tf.while_loop(continue_loop_condition, loop_body, init_loop_var) return trg_ids.stack()
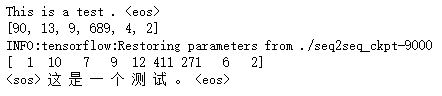
def main(): # 定义训练用的循环神经网络模型。 with tf.variable_scope("nmt_model", reuse=None): model = NMTModel() # 定义个测试句子。 test_en_text = "This is a test . <eos>" print(test_en_text) # 根据英文词汇表,将测试句子转为单词ID。 with codecs.open(SRC_VOCAB, "r", "utf-8") as f_vocab: src_vocab = [w.strip() for w in f_vocab.readlines()] src_id_dict = dict((src_vocab[x], x) for x in range(len(src_vocab))) test_en_ids = [(src_id_dict[token] if token in src_id_dict else src_id_dict['<unk>']) for token in test_en_text.split()] print(test_en_ids) # 建立解码所需的计算图。 output_op = model.inference(test_en_ids) sess = tf.Session() saver = tf.train.Saver() saver.restore(sess, CHECKPOINT_PATH) # 读取翻译结果。 output_ids = sess.run(output_op) print(output_ids) # 根据中文词汇表,将翻译结果转换为中文文字。 with codecs.open(TRG_VOCAB, "r", "utf-8") as f_vocab: trg_vocab = [w.strip() for w in f_vocab.readlines()] output_text = ''.join([trg_vocab[x] for x in output_ids]) # 输出翻译结果。 print(output_text.encode('utf8').decode(sys.stdout.encoding)) sess.close() if __name__ == "__main__": main()