from keras.layers import LeakyReLU from keras.layers import BatchNormalization from keras.optimizers import RMSprop import math def build_generator(inputs, image_size): ''' 生成者网络与编解码网络中的解码器如出一辙,输入给它的一维随机向量相当于输入解码器网络的编码向量, 解码器网络将一维向量反向构造成图片所对应的二维向量,这也是生成者要做的工作,所以下面代码与我们做过 的解码器网络几乎一模一样 ''' image_resize = image_size // 4 kernel_size = 5 layer_filters = [128, 64, 32, 1] x = Dense(image_resize * image_resize * layer_filters[0])(inputs) x = Reshape((image_resize, image_resize, layer_filters[0]))(x) #构造三层反卷积网络 for filters in layer_filters: if filters > layer_filters[-2]: strides = 2 else: strides = 1 #使用batch normalization将输入反卷积网络的向量做预处理,没有这一步GAN的训练就会失败 x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) x = Conv2DTranspose(filters = filters, kernel_size = kernel_size, strides = strides, padding = 'same')(x) x = Activation('sigmoid')(x) generator = Model(inputs, x, name = 'generator') return generator
def build_discriminator(inputs): ''' 识别者网络与编码器很像,它使用三层卷积网络从图片中抽取信息,最后使用sigmoid函数输出 图片是否为真的概率 ''' kernel_size = 5 layer_filters = [32, 64, 128, 256] x = inputs for filters in layer_filters: if filters == layer_filters[-1]: strides = 1 else: strides = 2 x = LeakyReLU(alpha = 0.2)(x) x = Conv2D(filters=filters, kernel_size=kernel_size , strides = strides, padding = 'same')(x) x = Flatten()(x) x = Dense(1)(x) x = Activation('sigmoid')(x) discriminator = Model(inputs, x, name='discriminator') return discriminator
def build_and_train_models(): ''' 将生成者和识别者连城一个网络进行训练 ''' (x_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data() image_size = x_train.shape[1] x_train = np.reshape(x_train, [-1, image_size, image_size, 1]) x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255 #设置训练相关的参数 model_name = '/content/gdrive/My Drive/dcgan_mnist' latent_size = 100 batch_size = 64 train_steps = 40000 lr = 2e-4 decay = 6e-8 input_shape = (image_size, image_size, 1) #构建识别者网络 inputs = Input(shape = input_shape, name = 'discriminator_input') discriminator = build_discriminator(inputs) optimizer = RMSprop(lr = lr, decay = decay) discriminator.compile(loss = 'binary_crossentropy', optimizer = optimizer, metrics = ['accuracy']) #构建生成者网络 input_shape = (latent_size, ) inputs = Input(shape = input_shape, name = 'z_input') generator = build_generator(inputs, image_size) optimizer = RMSprop(lr = lr * 0.5, decay = decay * 0.5) #将生成者和识别者连接成一个网络时要冻结识别者,因为训练生成者时识别者网络要保持不变 discriminator.trainable = False adversarial = Model(inputs, discriminator(generator(inputs)), name = model_name) adversarial.compile(loss = 'binary_crossentropy', optimizer = optimizer, metrics = ['accuracy']) models = (generator, discriminator, adversarial) params = (batch_size, latent_size, train_steps, model_name) train(models, x_train, params)
def train(models, x_train, params): ''' 训练时需要遵守的步骤是,先冻结生成者网络,把真实图片输入到识别者网络,训练识别者网络识别真实图片。 然后冻结识别者网络,让生成者网络构造图片输入给识别者网络识别,根据识别结果来改进生成者网络 ''' #先获得生成者,识别者,以及两者的结合体 generator, discriminator, adversarial = models batch_size, latent_size , train_steps, model_name = params save_interval = 500 #构造给生成者网络的一维随机向量 noise_input = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, size = [16, latent_size]) train_size = x_train.shape[0] for i in range(train_steps): #先训练识别者网络,将真实图片和伪造图片同时输入识别者,让识别者学会区分真假图片 rand_indexes = np.random.randint(0, train_size, size = batch_size) real_images = x_train[rand_indexes] noise = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, size = [batch_size, latent_size]) #让生成者构造虚假图片 fake_images = generator.predict(noise) x = np.concatenate((real_images, fake_images)) y = np.ones([2 * batch_size, 1]) #真实图片对应标签1,虚假图片对应标签0 y[batch_size : , :] = 0.0 loss, acc = discriminator.train_on_batch(x, y) log = "%d: [discriminator loss: %f, acc: %f]" % (i, loss, acc) #冻结识别者,让生成者构造一系列图片输入识别者,根据识别者识别结果改进生成者网络 noise = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, size = [batch_size, latent_size]) y = np.ones([batch_size, 1]) #训练生成者时需要使用到识别者返回的结果,因此我们从两者连接后的网络进行训练 loss, acc = adversarial.train_on_batch(noise, y) log = "%s [adversarial loss: %f, acc: %f]" % (log, loss, acc) print(log) if (i + 1) % save_interval == 0: if (i + 1) == train_steps: show = True else: show = False #将生成者构造的图片绘制出来 plot_images(generator, noise_input = noise_input, show = show, step = (i + 1), model_name = model_name) #将生成者当前的网络参数存储成文件 generator.save(model_name + ".h5")
def plot_images(generator, noise_input, show = False, step = 0, model_name = ''): os.makedirs(model_name, exist_ok = True) filename = os.path.join(model_name, "%05d.png" % step) images = generator.predict(noise_input) plt.figure(figsize = (2.2, 2.2)) num_images = images.shape[0] image_size = images.shape[1] rows = int(math.sqrt(noise_input.shape[0])) for i in range(num_images): plt.subplot(rows, rows, i + 1) image = np.reshape(images[i], [image_size, image_size]) plt.imshow(image, cmap= 'gray') plt.axis('off') plt.savefig(filename) if show: plt.show() else: plt.close('all')
from google.colab import drive drive.mount('/content/gdrive')
from keras.datasets import mnist from keras.layers import LeakyReLU from keras.layers import Activation from keras.optimizers import RMSprop import os build_and_train_models()
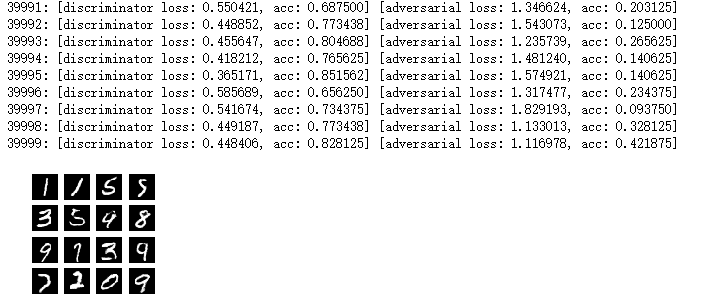
from keras.models import load_model import os generator = load_model('/content/gdrive/My Drive/dcgan_mnist.h5') #构造一批随机初始化的一维向量让生成者网络创造图片 noise = np.random.randint(-1.0, 1.0, size=[16, 100]) plot_images(generator, noise_input = noise, show = True, model_name="test_image")

from keras.layers.merge import concatenate from keras.utils import to_categorical def build_cgan_discriminator(inputs, y_labels, image_size): ''' 识别图片,并将图片与输入的one-hot-vector关联起来 ''' kernel_size = 5 layer_filters = [32, 64, 128, 256] x = inputs y = Dense(image_size * image_size)(y_labels) y = Reshape((image_size, image_size, 1))(y) #把图片数据与one-hot-vector拼接起来,这里是唯一与前面代码不同之处 x = concatenate([x, y]) for filters in layer_filters: if filters == layer_filters[-1]: strides = 1 else: strides = 2 x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(x) x = Conv2D(filters = filters, kernel_size = kernel_size, strides = strides, padding = 'same')(x) x = Flatten()(x) x = Dense(1)(x) x = Activation('sigmoid')(x) discriminator = Model([inputs, y_labels], x , name = 'discriminator') return discriminator
def build_cgan_generator(inputs, y_labels, image_size): ''' 生成者网络在构造图片时,需要将输入向量与对应的one-hot-vector结合在一起考虑 ''' image_resize = image_size // 4 kernel_size = 5 layer_filters = [128, 64, 32, 1] #将输入向量与One-hot-vector结合在一起 x = concatenate([inputs, y_labels], axis = 1) x = Dense(image_resize * image_resize * layer_filters[0])(x) x = Reshape((image_resize, image_resize, layer_filters[0]))(x) for filters in layer_filters: if filters > layer_filters[-2]: strides = 2 else: strides = 1 x = BatchNormalization()(x) x = Activation('relu')(x) x = Conv2DTranspose(filters = filters, kernel_size = kernel_size, strides = strides, padding = 'same')(x) x = Activation('sigmoid')(x) generator = Model([inputs, y_labels], x, name='generator') return generator
def train_cgan(models, data, params): generator, discriminator, adversarial = models #获取图片数据以及图片对应数字的one-hot-vector x_train, y_train = data batch_size, latent_size, train_steps, num_labels, model_name = params save_interval = 500 noise_input = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, size=[16, latent_size]) ''' np.eye产生对角矩阵,例如np.eye(3) = [[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]], 于是np.eye(3)[2, 3, 1] = [[0,1,0], [0,0,1], [1,0,0]] ''' noise_class = np.eye(num_labels)[np.arange(0, 16) % num_labels] train_size = x_train.shape[0] print(model_name, "Labels for generated images: ", np.argmax(noise_class, 1)) for i in range(train_steps): rand_indexes = np.random.randint(0, train_size, size = batch_size) real_images = x_train[rand_indexes] #增加图片对应的one-hot-vector real_labels = y_train[rand_indexes] noise = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, size = [batch_size, latent_size]) #增加构造图片对应的one-hot-vector fake_labels = np.eye(num_labels)[np.random.choice(num_labels, batch_size)] fake_images = generator.predict([noise, fake_labels]) #把真实图片和虚假图片连接起来 x = np.concatenate((real_images, fake_images)) #将真实图片对应的one-hot-vecotr和虚假图片对应的One-hot-vector连接起来 y_labels = np.concatenate((real_labels, fake_labels)) y = np.ones([2 * batch_size, 1]) #上半部分图片为真,下半部分图片为假 y[batch_size:, :] = 0.0 #先训练识别者网络,这里需要将图片及对应的one-hot-vector输入 loss, acc = discriminator.train_on_batch([x, y_labels], y) log = "%d: [discriminator loss : %f, acc: %f]" % (i, loss, acc) ''' 冻结识别者网络,构造随机一维向量以及指定数字的one-hot-vector输入生成者 网络进行训练 ''' noise = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, size=[batch_size, latent_size]) fake_labels = np.eye(num_labels)[np.random.choice(num_labels, batch_size)] y = np.ones([batch_size, 1]) loss, acc = adversarial.train_on_batch([noise, fake_labels], y) log = "%s [adversarial loss :%f, acc: %f]" % (log, loss, acc) if (i + 1) % save_interval == 0: print(log) if (i+1) == train_steps: show = True else: show = False plot_images_cgan(generator, noise_input = noise_input, noise_class = noise_class, show = show, step = (i+1), model_name = model_name) generator.save(model_name + ".h5")
def build_and_train_models_cgan(): (x_train, y_train), (_,_) = mnist.load_data() image_size = x_train.shape[1] x_train = np.reshape(x_train, [-1, image_size, image_size, 1]) x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255 #获得要生成数字的最大值 num_labels = np.amax(y_train) + 1 #转换为one-hot-vector y_train = to_categorical(y_train) model_name = "/content/gdrive/My Drive/cgan_mnist" latent_size = 100 batch_size = 64 train_steps = 40000 lr = 2e-4 decay = 6e-8 input_shape = (image_size, image_size, 1) label_shape = (num_labels, ) inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='discriminator_input') labels = Input(shape=label_shape, name = 'class_labels') #构建识别者网络时要传入图片对应的One-hot-vector discriminator = build_cgan_discriminator(inputs, labels, image_size) optimizer = RMSprop(lr=lr, decay = decay) discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer, metrics = ['accuracy']) input_shape = (latent_size,) inputs = Input(shape=input_shape, name='z_input') #构造生成者时也要传入one-hot-vector generator = build_cgan_generator(inputs, labels, image_size) optimizer = RMSprop(lr = lr*0.5, decay = decay * 0.5) #将生成者和识别者连接起来时要冻结识别者 discriminator.trainable = False outputs = discriminator([generator([inputs, labels]), labels]) adversarial = Model([inputs, labels], outputs, name = model_name) adversarial.compile(loss ='binary_crossentropy', optimizer = optimizer, metrics = ['accuracy']) models = (generator, discriminator, adversarial) data = (x_train, y_train) params = (batch_size, latent_size, train_steps, num_labels, model_name) train_cgan(models, data, params)
def plot_images_cgan(generator, noise_input, noise_class, show = False, step = 0, model_name = ''): os.makedirs(model_name, exist_ok = True) filename = os.path.join(model_name, "%05d.png" % step) images = generator.predict([noise_input, noise_class]) print(model_name, "labels for generated images: ", np.argmax(noise_class, axis =1)) plt.figure(figsize = (2.2, 2.2)) num_images = images.shape[0] image_size = images.shape[1] rows = int(math.sqrt(noise_input.shape[0])) for i in range(num_images): plt.subplot(rows, rows, i + 1) image = np.reshape(images[i], [image_size, image_size]) plt.imshow(image, cmap= 'gray') plt.axis('off') plt.savefig(filename) if show: plt.show() else: plt.close('all')
from keras.layers import LeakyReLU from keras.layers import BatchNormalization from keras.optimizers import RMSprop import math from keras.layers import Activation, Dense, Input build_and_train_models_cgan()
