之前已经介绍过了迷宫生成算法中的深度优先算法,这次让我来解析下迷宫生成之一的prim算法。
代码来源:https://blog.csdn.net/juzihongle1/article/details/73135920?spm=1001.2014.3001.5506
1. 我理解的迷宫生成算法之一的prim算法:
从起点开始对图形进行分析,并把当前所在的格子和走过的格子标记为1,从起始格子出发,找到当前格子下一步能走的路径,然后随机选择一个能走的路径走,直到没有路径可走,那么就返回可以选择其他路径的单元格,继续探索可以的方法,直到把所有的单元格都走完了,迷宫就生成完毕。
2. 储备知识
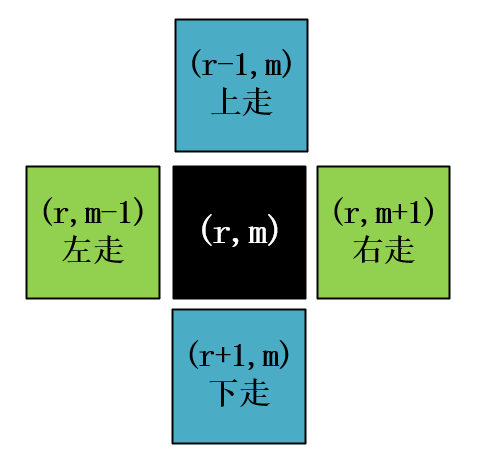
(1)row表示行,缩写是 r;col表示列,缩写是 c
(2)每个单元格有 上 下 左 右 四个的方向可以走,它们的表示方式如下图所示,理解:水平方向上行数是相同的,越往左边列数越小,越往右边列数越大。垂直方向上列数是相同的,越往上行数越小,越往下行数越大。
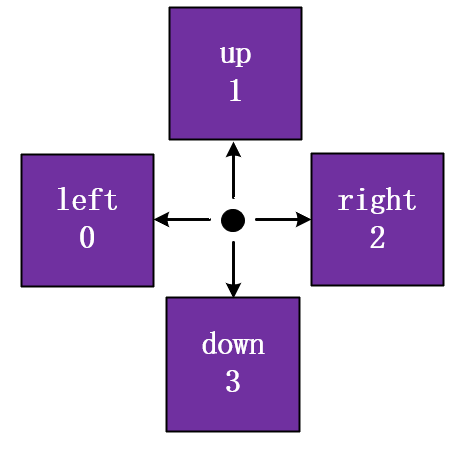
(3)在M变量中,第三维存储的5个值得含义 (LEFT, UP, RIGHT, DOWN, CHECK_IF_VISITED),要理解代码,最好记住每个数字表示得方向,最后一个参数就是表示是否被访问过,如果被访问那么就为1,否则为0
3. 帮助看懂的代码(如果你觉得 print 太多,那你可以从代码来源中复制过来看会比较干净点):
1 import random
2 import numpy as np
3 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
4 import matplotlib.cm as cm
5
6 # num_rows = int(input("Rows: ")) # number of rows
7 # num_cols = int(input("Columns: ")) # number of columns
8 num_rows = 4
9 num_cols = 5
10
11 # The array M is going to hold the array information for each cell.
12 # The first four coordinates tell if walls exist on those sides
13 # and the fifth indicates if the cell has been visited in the search.
14 # M(LEFT, UP, RIGHT, DOWN, CHECK_IF_VISITED)
15 M = np.zeros((num_rows, num_cols, 5), dtype=np.uint8)
16
17 # The array image is going to be the output image to display
18 image = np.zeros((num_rows * 10, num_cols * 10), dtype=np.uint8)
19
20 # Set starting row and column
21 r = 0
22 c = 0
23 history = [(r, c)] # The history is the stack of visited locations
24
25 # Trace a path though the cells of the maze and open walls along the path.
26 # We do this with a while loop, repeating the loop until there is no history,
27 # which would mean we backtracked to the initial start.
28 trend = []
29 while history:
30 print("==================================================")
31 # random choose a candidata cell from the cell set histroy
32 r, c = random.choice(history)
33 print("r = ", r)
34 print("c = ", c)
35 M[r, c, 4] = 1 # designate this location as visited
36 history.remove((r, c))
37 check = []
38 # If the randomly chosen cell has multiple edges
39 # that connect it to the existing maze,
40 # c 大于0才有 左方向
41 if c > 0:
42 print("c > 0")
43 print([r, c - 1, 4], M[r, c - 1, 4])
44 # 等于1表示被访问过,找到已经被访问过的路径进行添加
45 if M[r, c - 1, 4] == 1:
46 check.append('L')
47 # 等于0表示没有被访问过,那么就添加到需要访问history列表中,标记成2表示在history中将要被访问的,该值要与0和1不同,被访问后就会变成1。
48 # 添加临近的单元格
49 elif M[r, c - 1, 4] == 0:
50 history.append((r, c - 1))
51 M[r, c - 1, 4] = 2
52 # r 大于0才有 上方向
53 if r > 0:
54 print("r > 0")
55 print([r-1, c, 4], M[r-1, c, 4])
56 if M[r - 1, c, 4] == 1:
57 check.append('U')
58 elif M[r - 1, c, 4] == 0:
59 history.append((r - 1, c))
60 M[r - 1, c, 4] = 2
61 # c 小于 num_cols-1 才有 右方向
62 if c < num_cols - 1:
63 print("c < num_cols - 1")
64 print([r, c + 1, 4], M[r, c + 1, 4])
65 if M[r, c + 1, 4] == 1:
66 check.append('R')
67 elif M[r, c + 1, 4] == 0:
68 history.append((r, c + 1))
69 M[r, c + 1, 4] = 2
70 # r 小于 num_rows-1 才有 下方向
71 if r < num_rows - 1:
72 print("r < num_rows - 1")
73 print([r+1, c, 4], M[r+1, c, 4])
74 if M[r + 1, c, 4] == 1:
75 check.append('D')
76 elif M[r + 1, c, 4] == 0:
77 history.append((r + 1, c))
78 M[r + 1, c, 4] = 2
79
80 print("check = ", check)
81
82 # select one of these edges at random.
83 if len(check):
84 move_direction = random.choice(check)
85 print("move_direction = ", move_direction)
86 trend.append([r, c, move_direction])
87 if move_direction == 'L':
88 # 如果是往左走就标记index[0]=1,并且列数-1,然后标记右边被堵
89 M[r, c, 0] = 1
90 c = c - 1
91 M[r, c, 2] = 1
92 if move_direction == 'U':
93 # 如果是往上走就标记index[1]=1,并且行数-1,然后标记下方被堵
94 M[r, c, 1] = 1
95 r = r - 1
96 M[r, c, 3] = 1
97 if move_direction == 'R':
98 # 如果是往右走就标记index[2]=1,并且列数+1,然后标记左方被堵
99 M[r, c, 2] = 1
100 c = c + 1
101 M[r, c, 0] = 1
102 if move_direction == 'D':
103 # 如果是往下走就标记index[3]=1,并且行数+1,然后标记上方被堵
104 M[r, c, 3] = 1
105 r = r + 1
106 M[r, c, 1] = 1
107
108 # Open the walls at the start and finish
109 M[0, 0, 0] = 1
110 M[num_rows - 1, num_cols - 1, 2] = 1
111 print(M)
112 # Generate the image for display
113 for row in range(0, num_rows):
114 for col in range(0, num_cols):
115 cell_data = M[row, col]
116 for i in range(10 * row + 2, 10 * row + 8):
117 image[i, range(10 * col + 2, 10 * col + 8)] = 255
118 if cell_data[0] == 1:
119 image[range(10 * row + 2, 10 * row + 8), 10 * col] = 255
120 image[range(10 * row + 2, 10 * row + 8), 10 * col + 1] = 255
121 if cell_data[1] == 1:
122 image[10 * row, range(10 * col + 2, 10 * col + 8)] = 255
123 image[10 * row + 1, range(10 * col + 2, 10 * col + 8)] = 255
124 if cell_data[2] == 1:
125 image[range(10 * row + 2, 10 * row + 8), 10 * col + 9] = 255
126 image[range(10 * row + 2, 10 * row + 8), 10 * col + 8] = 255
127 if cell_data[3] == 1:
128 image[10 * row + 9, range(10 * col + 2, 10 * col + 8)] = 255
129 image[10 * row + 8, range(10 * col + 2, 10 * col + 8)] = 255
130
131 # Display the image
132 plt.imshow(image, cmap=cm.Greys_r, interpolation='none')
133 plt.show()
134 pass
4. 代码理解图
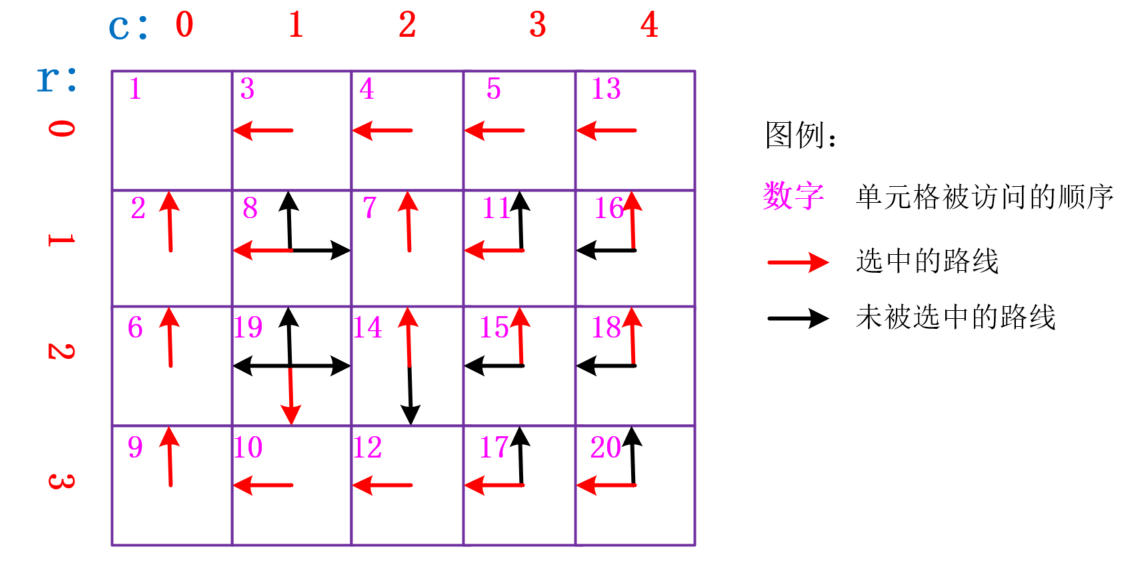
理解:
(1)首先设置了(r, c)=(0, 0)作为起始点添加到history中,也就是数字为1的位置,每次被选中的单元格的 index[4] 会被标记为1,接下来因为它满足 c<num_cols-1 和 r<num_rows-1 中的 M[r, c + 1, 4] == 0 和 M[r + 1, c, 4] == 0 ,所以history中添加 (0, 1) 和 (1,0)两个路径,即(0, 0)邻近的但是没有被访问过的单元格,并且把它标记成2,表示已经被添加到history中了。
(2)接下来,在history中随机抽取一个值,这里抽到了(1, 0),看代码可以发现,只有标记为1的数 check 才会添加方向,所以对于 (1, 0)来说,和它邻近的毕竟被访问过的只有(0,0),所以只有向上的方向可以选择,所以 check=['U'],即move_direction="U",所以就标记当下单元格的上方(index=1)和上一个单元格(r=r-1)的下方(index=3)为1。
(3)以此规律继续重复,重 history 随机抽取再判断能走的方向,再随机选择方向,直到所有的单元格都被选过,index[4]=1,这样就不会执行 history.append( ) 语句,等 history=[] 时就结束循环。
5. 生成的迷宫图
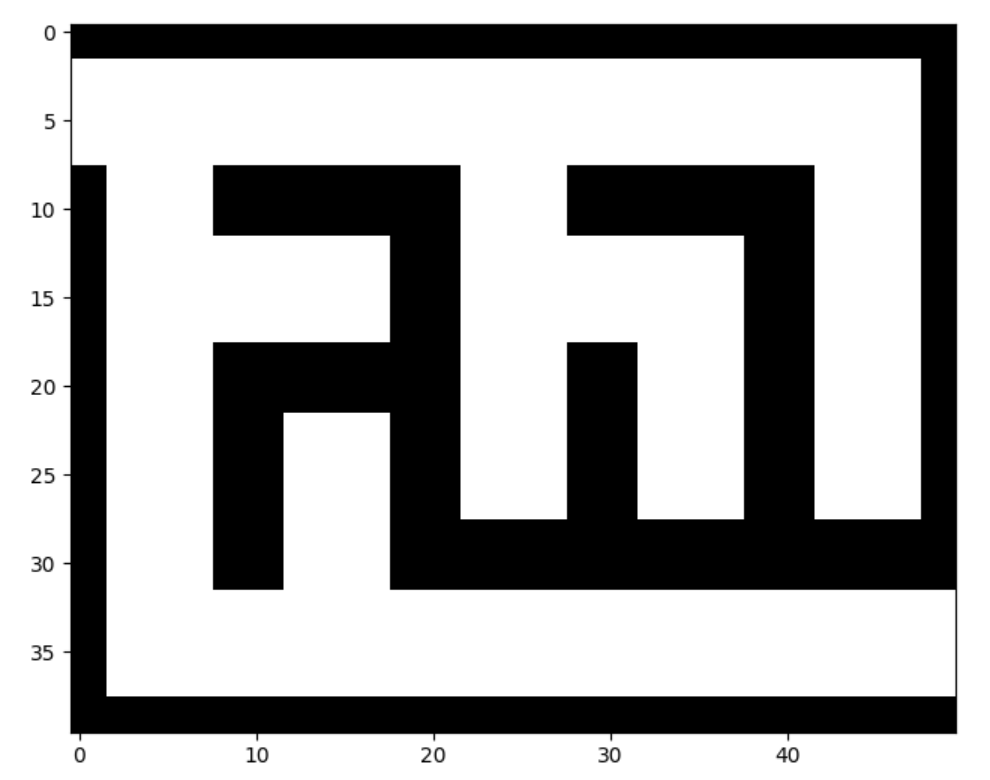
把生成图和理解图的红色箭头对照着看,你就能更好的理解迷宫的生成原理啦。
6. M 值
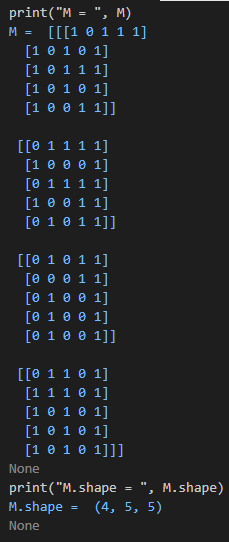
可以看到, 最后的画出迷宫完全就是根据 M 值来画的,那么我们来看看 M 值到底是怎么样的。
(1)首先 M 矩阵的大小是 4 * 5 * 5, 即有4个5*5的矩阵,4表示的是4行,第1个5表示的是5列的数据,第2个5表示的是 (LEFT, UP, RIGHT, DOWN, CHECK_IF_VISITED) 这5个的选择。
(2)我们可以看到所有 5*5 的数组最后一个值都是1,表示每个格子都被访问过。
(3)我们看看第一行的值 [ [1 0 1 1 1], [1 0 1 0 1], [1 0 1 1 1], [1 0 1 0 1], [1 0 0 1 1] ],
其中 [1 0 1 1 1] 表示第一行第一列的情况:我们看1的值,1表示就是可以走的打通的区域,我们只看前4个值,即 [1 0 1 1],首先,第一个1是 M[0, 0, 0] = 1 这条语句添加的,表示添加上路口,左边是通的,其次,看索引2的位置的1,它表示的是right,那么对照着迷宫途中就是第一个(0,0)和(0,1)左右相连,再看索引3的位置1,表示的是down,即(0,0)和(1,0)是相通的。
其中 [1 0 1 0 1] 表示的是第一行第二列的情况:1的位置出现在 index=0 (left)和 index=2(right)(不用管index=4),那么此单元格是左通和右通的
其中 [1 0 1 1 1] 表示的是第一行第三列的情况:1的位置出现在 index=0(left)和 index=2 (right)和 index=3 (down),那么此单元格就是左通,右通,下通
其中 [1 0 1 0 1] 表示的是第一行第四列的情况:1的位置出现在 index=0 (left)和 index=2(right),那么此单元格就是左通和右通
其中 [1 0 0 1 1] 表示的是第一行第五列的情况:1的位置出现在 index=0 (left) 和 index=3(down),那么此单元格就是左通和下通
以上就是我的理解,如果右什么不当的地方,欢迎大家指正!