写在最前
因为这一内容的东西实在是太多了,能更一点是一点,最初的更新可能没有什么学习顺序,后续内容逐渐完整后会重新排版
本文暂时停止更新 对话编辑器的代码放在了Github
其他和编辑器有关的代码也可以翻此项目,虽然个人感觉有点臭,日后再优化
自定义Inspector窗口
自定义编辑器脚本的创建
- 编辑器脚本需要置于Editor文件夹下方,类似资源读取的文件需要存放在Resources下方
- 编辑器脚本的命名规则一般为:
所编辑类名 + Editor,例如当我需要自定义类StateMachine的Inspector窗口时,我将在Editor目录下创建StateMachineEditor.cs - 添加Attribute:
[CustomEditor(typeof(T))]。目的是告知编辑器类该编辑器所针对的运行时类型,此例中,需要告诉编辑器我们想要修改类StateMachine的Inspector窗口,故T为StateMachine - 使类
StateMachineEditor继承类Editor
// StateMachineEditor.cs
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
[CustomEditor(typeof(StateMachine))]
public class StateMachineEditor : Editor
{
public override void OnEnable() {}
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
base.OnInspectorGUI();
}
}
OnEnable()函数将在每次查看对应的Inspector时被调用,故可用来初始化编辑器所需要的变量。常用的有两种类型的变量
private StateMachine selectMachine;
private SerializedProperty property1;
private SerializedProperty property2;
// ...
本例中selectMachine用于存取编辑器获得的需要编辑的类
private void OnEnable()
{
selectMachine = target as StateMachine;
if (selectMachine == null)
{
Debug.LogError("Editor Error: Can not translate selectMachine");
}
}
target是继承的Editor类中的一个字段(get)。本身为Object类型,在拆箱后可以转换成上文Attribute:CustomEditor中的T,用来显示类中原本不会被绘制到Inspector窗口的信息,达到自定义的功能
public override void OnInspectorGUI()
{
// 之前
base.OnInspectorGUI();
// 之后
}
base.OnInspectorGUI()会执行默认Inspector信息的绘制,若去除Inspector面板将空无一物。可以根据项目需求,选择将自定义代码写在”之前“或”之后“的位置,本例中将代码写在”之后“,也就是说新自定义添加的属性,将在Inspector的底部被绘制
若要完全自定义Inspector面板,通常会选择不调用基类的函数,直接重写整个面板的绘制代码
初级API - EditorGUILayout
EditorGUILayout用于在Inspector面板上绘制信息
EditorGUILayout.Space();
用于在面板中生成一小段间隙,功能可以类比Attribute:[Space]
EditorGUILayout.LabelField("");
用于在面板中生成一串文字
EditorGUILayout.BeginHorizontal();
// Codes...
EditorGUILayout.EndHorizontal();
在上述代码范围内开启一段水平空间,在此范围内的信息将被绘制在同一行
EditorGUILayout.BeginVertical();
// Codes...
EditorGUILayout.EndVertical();
在上述代码范围内开启一段垂直空间,在此范围内的信息将被绘制在同一列
更多相关API参考:EditorGUILayout
完整效果
// StateMachineEditor.csusing UnityEngine;using UnityEditor;[CustomEditor(typeof(StateMachine))]public class StateMachineEditor : Editor{ public override void OnEnable() { selectMachine = target as StateMachine; if (selectMachine == null) { Debug.LogError("Editor Error: Can not translate selectMachine"); } } public override void OnInspectorGUI() { base.OnInspectorGUI(); EditorGUILayout.Space(); EditorGUILayout.BeginHorizontal(); EditorGUILayout.LabelField("Current StateName:"); EditorGUILayout.LabelField(selectMachine.CurrentState.StateName); EditorGUILayout.EndHorizontal(); }}
成果如下,在底部生成了一串文字标签,显示当前状态的名字(当前无状态,故为Null)

漫漫谈
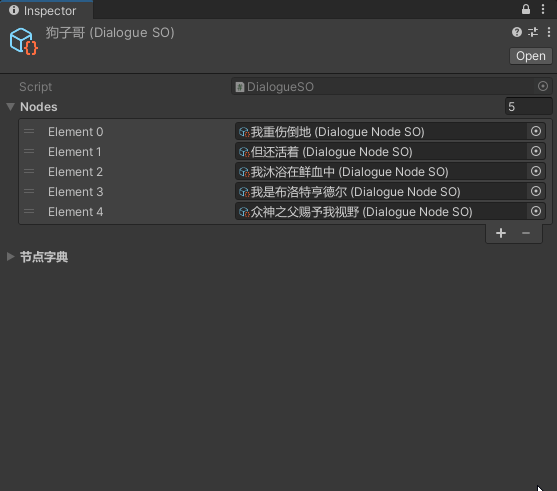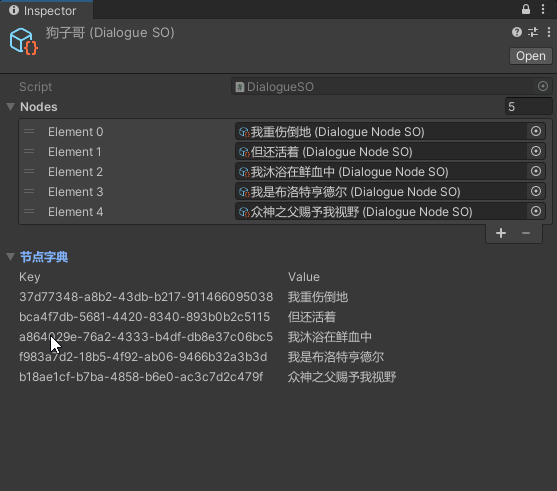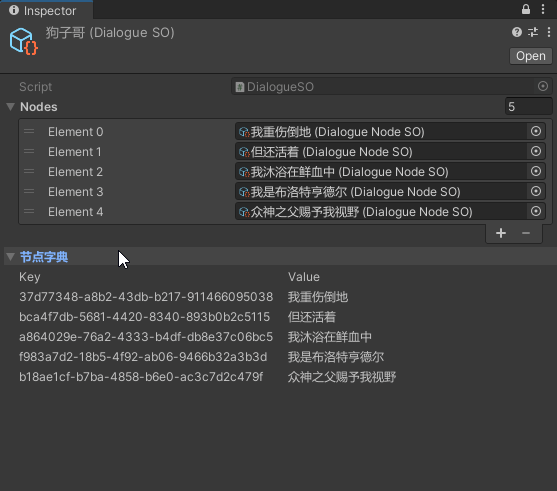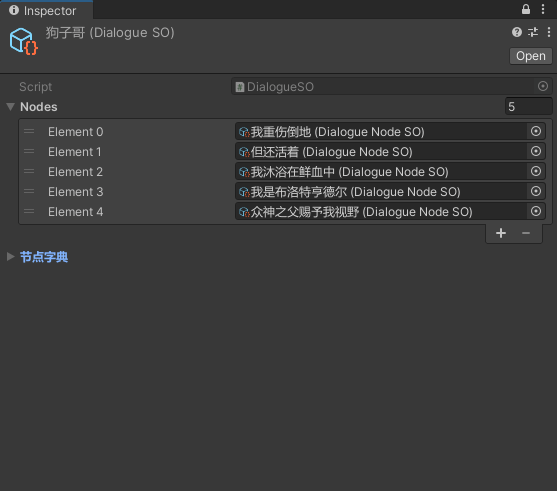
众所周知,Dictionary是无法被序列化显示在Inspector面板中的。直接上编辑器代码,简陋的显示字典的Key和Value
using UnityEditor;[CustomEditor(typeof(DialogueSO))]public class DialogueSOEditor : Editor{ private DialogueSO _selectSO; private bool _showDictionary = true; private string _statusStr = "节点字典"; private void OnEnable() { _selectSO = target as DialogueSO; } public override void OnInspectorGUI() { base.OnInspectorGUI(); // 开启可折叠区域 _showDictionary = EditorGUILayout.BeginFoldoutHeaderGroup(_showDictionary, _statusStr); // 若打开折叠 if (_showDictionary) { HorizontalLabel("Key", "Value"); // 遍历字典 显示Key与Value foreach (var nodePair in _selectSO.NodeDic) { HorizontalLabel(nodePair.Key, nodePair.Value.Content); } } // 结束可折叠区域 EditorGUILayout.EndFoldoutHeaderGroup(); } private void HorizontalLabel(string leftStr, string rightStr) { EditorGUILayout.BeginHorizontal(); EditorGUILayout.LabelField(leftStr); EditorGUILayout.LabelField(rightStr); EditorGUILayout.EndHorizontal(); }}
实现效果
自定义EditorWindow
为讲GraphView做铺垫,这里先说一下如何创建EditorWindow
创建窗口
写代码前应该先明确应该实现什么功能
- 在上拉菜单中创建选项,点击可以打开编辑窗口
- 双击Project文件目录中对应的资源文件时也能打开编辑窗口
using UnityEditor;public class DialogueEditorWindow : EditorWindow{ [MenuItem("Window/Dialogue")] public static void ShowDialogueEditorWindow() { // 打开或创建窗口 命名为DialogueWindow GetWindow<DialogueEditorWindow>(false, "DialogueWindow"); } [OnOpenAsset(1)] public static bool OnDoubleClickDialogueAsset(int instanceID, int line) { // 检测打开资源 DialogueSO openAsset = EditorUtility.InstanceIDToObject(instanceID) as DialogueSO; // 打开资源则打开编辑窗口 if (openAsset) { ShowDialogueEditorWindow(); return true; } return false; }}
GetWindow函数为EditorWindow里的一个静态成员函数,它接收两个参数:bool,string,执行后会检测窗口是否已经存在(若不存在则创建)然后将其返回
-
第一个参数决定此窗口是浮动窗口(true)或是正常窗口(false)。若要创建像是Scene,Game,Inspector这种类型的窗口,则设置为false。若设置为true,窗口看上去便像是一个应用程序(参照项目以小窗模式Build后的样式)
浮动窗口 ↓
正常窗口 ↓
-
第二个参数决定窗口的名字,如上述截图窗口的左上角
Attribute:[OnOpenAsset(X)],用于打开Unity中的某个资源的回调,回调需要满足两个条件
- 为静态函数
- 返回值为
bool,函数参数为两个int类型的参数(有一个三参数的版本,但几乎没用过,所以不介绍)
回调函数的用法可以参照之前的代码,这里需要注意的是属性中的X(在上面的代码中为1)。这里的X其实是执行顺序的意思
[OnOpenAsset(1)]public static bool OnDoubleClickDialogueAssetOne(int instanceID, int line) {}[OnOpenAsset(2)]public static bool OnDoubleClickDialogueAssetTwo(int instanceID, int line) {}[OnOpenAsset(3)]public static bool OnDoubleClickDialogueAssetThree(int instanceID, int line) {}// 当双击资源文件时,函数的执行顺序为OnDoubleClickDialogueAssetOne -> OnDoubleClickDialogueAssetTwo -> OnDoubleClickDialogueAssetThree// 若执行中有任意一个返回了true,则在其顺序之后的回调函数都不会被执行
而返回值bool,代表我们是否已经处理了资源的打开操作,若已处理则返回true。举个例子,当我们双击的是.txt格式的文件时,若我们代码返回true,等同于告诉Unity:我们已经完成相应的处理了,你不需要执行什么打开操作;相反若返回false,则相当于把资源处理权交给Unity —— 结果是该.txt文件在你的代码编辑器中被打开(Rider,VSC...)
自定义GraphView
UIElements
有句话是这么说的
Use the new UI Toolkit to create UIElements with the UI Builder
这里扔几篇学习博客和官方文档
- Unity Documentation - UI Toolkit
- UIElements渲染细节 比NGUI/UGUI/FairyGUI好在哪?
- What's new with UIElements in 2019.1
- Building UI for games with the new UI Builder - Unite Copenhagen
因为UI Toolkit是2020新推出的编辑UI的工具,目前我仍未能搞懂他们之间的关联,故先从UIElements开始学起
按照Unity以往的逻辑,在runtime时使用的时NGUI,UGUI,FairyGUI等,在编辑器中用IMGUI。在2019年的时候,UIElements主要用于解决拓展编辑器的问题,欲以保留模式代替IMGUI的即时模式。现如今,随着UI Toolkit的推出,UIElements也适用于runtime环境。官方曾说:UIElement将成为UI未来主要的工作方式,但短时间内UGUI仍会保持更新(Unity 2019.1 - In its current form, it’s a tool that makes it easier for you to extend the Unity Editor. In-game support and visual authoring will come in future releases.)本篇文章暂时专注于将UIElements在编辑器的运用
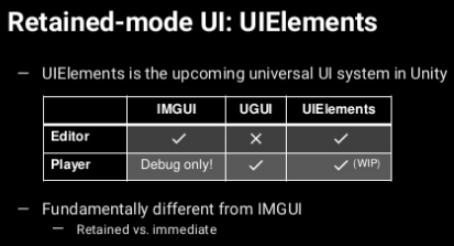
在后续的代码中会不断的介绍UIElements的入门使用
创建节点编辑器窗口
根据之前自定义编辑器窗口的经验,先写出窗口创建的代码,代码不长,下面会分析部分新出现的API
using UnityEngine;using UnityEditor;using UnityEditor.Callbacks;using UnityEditor.UIElements;using UnityEngine.UIElements;namespace RPG.DialogueSystem.Graph{ public class DialogueGraphEditorWindow : EditorWindow { private DialogueGraphSO _selectSO; // 对话SO private DialogueGraphView _selectView; // 对话节点编辑器窗口 private Label _selectSONameLabel; // 当前对话SO显示标签 [MenuItem("Window/DialogueGraph")] private static DialogueGraphEditorWindow ShowDialogueGraphWindow() { DialogueGraphEditorWindow window = GetWindow<DialogueGraphEditorWindow>(false, "DialogueGraph"); window.minSize = new Vector2(400, 300); return window; } /// <summary> /// 双击打开资源 /// </summary> /// <param name="instanceID">资源ID</param> /// <param name="line"></param> /// <returns>处理结果</returns> [OnOpenAsset(0)] private static bool OnDoubleClickAsset(int instanceID, int line) { DialogueGraphSO selectSO = EditorUtility.InstanceIDToObject(instanceID) as DialogueGraphSO; if (selectSO == null) return false; DialogueGraphEditorWindow window = ShowDialogueGraphWindow(); // OnOpenAsset回调不包含Selection Change window.Load(selectSO); return true; } /// <summary> /// 单击资源 /// </summary> private void OnClickAsset() { // 重新绘制编辑器界面 Load(Selection.activeObject as DialogueGraphSO); } /// <summary> /// 加载对话SO /// </summary> /// <param name="selectSO">对话SO</param> private void Load(DialogueGraphSO selectSO) { if (selectSO == null) return; _selectSO = selectSO; // 刷新窗口上端Label显示 _selectSONameLabel.text = _selectSO == null ? "当前无选择物体" : $"所选物体为: {_selectSO.name}"; } private void OnEnable() { // 添加单击资源监听 Selection.selectionChanged += OnClickAsset; // 先创建窗口组件(Toolbar) CreateWindowComponents(); // 再创建对话节点编辑器界面 CreateDialogueGraphView(); } private void OnDisable() { // 移除单击资源监听 Selection.selectionChanged -= OnClickAsset; } private void CreateWindowComponents() { // 创建各个组件 Toolbar windowToolbar = new Toolbar(); Button saveButton = new Button(); _selectSONameLabel = new Label(); // 传统艺能 saveButton.text = "Save"; saveButton.clicked += delegate { Debug.Log("Save Button Clicked"); }; // 设置顶部信息显示栏Style StyleSheet styleSheet = AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath<StyleSheet>("XX/DialogueGraphViewSheet.uss"); rootVisualElement.styleSheets.Add(styleSheet); // 将Button加入Toolbar中 windowToolbar.Add(saveButton); // 将Label加入Toolbar中 windowToolbar.Add(_selectSONameLabel); // 将Toolbar加入窗口绘制中 rootVisualElement.Add(windowToolbar); } private void CreateDialogueGraphView() { // 往窗口中添加GraphView _selectView = new DialogueGraphView(this) { style = {flexGrow = 1} }; // 将节点编辑器加入窗口绘制中 rootVisualElement.Add(_selectView); } }}
保留模式
在代码中使用到的Label,Button, Toolbar都是UIElement,这些元素都是VisualElement的派生类。整个UIElements的基本构建块都是VisualElement。各个VisualElement以使用者规定的顺序排列,组成一定的UI层级结构(通过Add,Insert等操作完成),最后布局,样式等系统会遍历这个层次结构,然后将UI绘制到屏幕上
在EditorWindow中,有一个类成员rootVisualElement,它代表窗口的根VisualElement,我们需要将需要绘制的元素添加至此父根。在上述代码中,根节点的子元素为Toolbar与GraphView;Toolbar的子元素为Button,Label。上述UI的创建都是在OnEnable()中进行的,若以传统IMGUI的工作方式来制作,需要在OnGUI()也就是每帧绘制中去指定UI的绘制,这代表UI层级结构需要在每帧中被指定或者被修改,不仅系统难以优化,性能也降低了。从上述例子应该能大概体会到保留模式和即使模式的区别
style与styleSheets


上述例子中提到了两种样式的设置方法:对DialogueGraphView采用C#对属性进行赋值的方式,对窗口的rootVisualElement采用了静态设置的方法(读取USS),两种方法效果相同,但由于大多数UI的样式都是静态的,不需要运行时赋值(或设置),因此推荐使用解析USS资源文件的方式来设置UI样式(UIBuilder也是通过写入USS文件来改变样式)。UIElements将.uss的资源文件解析为StyleSheet类,通过一系列添加操作加入到应用为UI样式
USS的语法与CSS相同,若不知道属性的名称以及功能,可以百度查看CSS的语法或查看UIElements.IStyle,下面先介绍USS的简单配置
styleSheets - 使用C#格式设置
Label{ -unity-text-align: middle-center; // 字体格式居中对齐 color: white; // 字体颜色为白色}
// 通过Label类型直接进行设置 style应用到rootVisualElement下的所有子Label组件StyleSheet styleSheet = AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath<StyleSheet>("XX/DialogueGraphViewSheet.uss"); rootVisualElement.styleSheets.Add(styleSheet);
styleSheets - 使用类名设置
._selectSONameLabelSheet{ -unity-text-align: middle-center; // 字体格式居中对齐 color: white; // 字体颜色为白色}
// 通过类名进行设置 只有进行AddToClassList操作的组件才会应用此style
StyleSheet styleSheet = AssetDatabase.LoadAssetAtPath<StyleSheet>("XX/DialogueGraphViewSheet.uss");
rootVisualElement.styleSheets.Add(styleSheet);
_selectSONameLabel.AddToClassList("_selectSONameLabelSheet");
styleSheets - 使用Element Name设置
不会,下次一定
style直接设置(不推荐)
// 居中对齐
_selectSONameLabel.style.unityTextAlign = new StyleEnum<TextAnchor>(TextAnchor.MiddleCenter);
// 文字颜色为白色
_selectSONameLabel.style.color = new StyleColor(Color.white);
UI样式的应用
上文说过,用USS和直接设置style的效果相同。UI的最终样式(m_Element)由二者决定
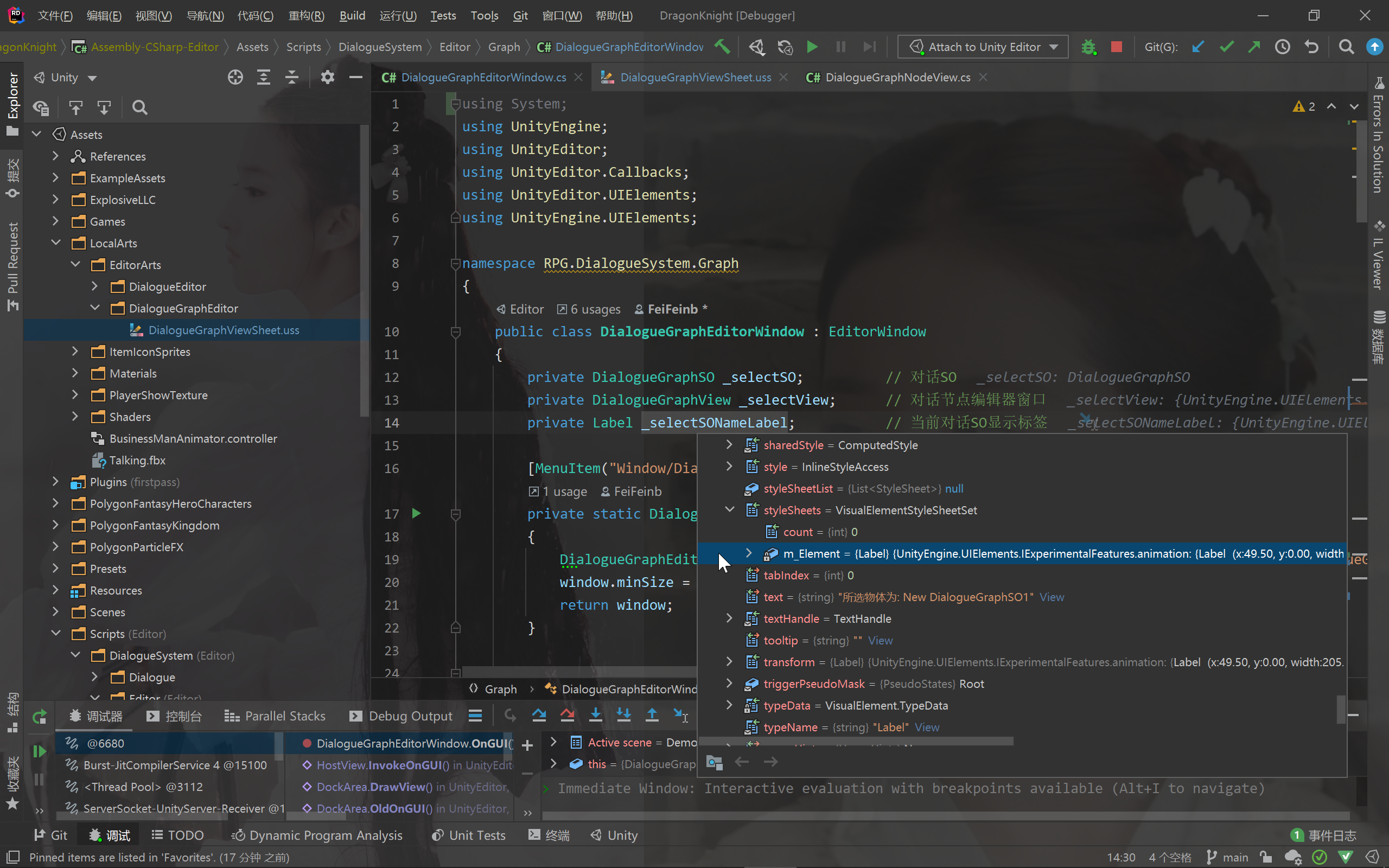
从下图可以看出,UI的对齐方式被设置为MiddleCenter(居中对齐)
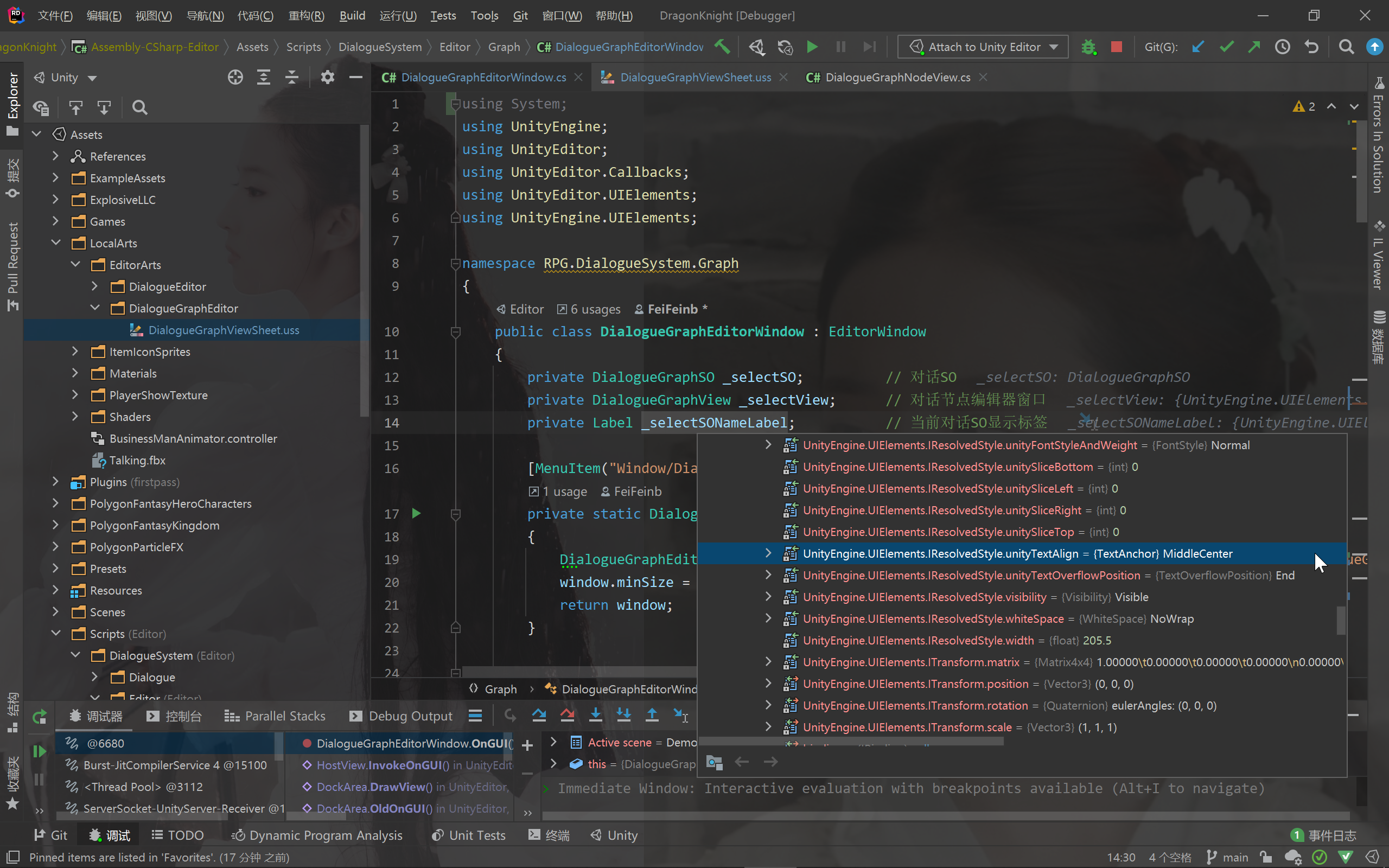
需要注意,m_Element中的UI样式并不是立即被赋值
- 若通过
style更改,在更改结束后m_Element也会同步更改 - 若通过
styleSheets(本例中是在OnEnable()中更改),则m_Element的值将会被延迟到OnEnable()后的第一次OnGUI()被更改
故,不管是USS还是赋值style,他们都是最终都是更改到m_Element中的UI样式,然后绘制到屏幕上。暂时就先说这么多,更多内容可以查看相关博客或查阅后续代码
额外补充
在创建对话节点编辑器的时候,选择了设置flexGrow = 1
IStyle.flexGrow - Specifies how much the item will grow relative to the rest of the flexible items inside the same container.
大概意思就是指定该元素能够在窗口剩下的空间内的填充比例
private void CreateDialogueGraphView(){ // 往窗口中添加GraphView _selectView = new DialogueGraphView(this) { style = {flexGrow = 1}, }; // _selectView.StretchToParentSize(); // 将节点编辑器加入窗口绘制中 rootVisualElement.Add(_selectView);}
指定flexGrow为1与0.5的区别见下图

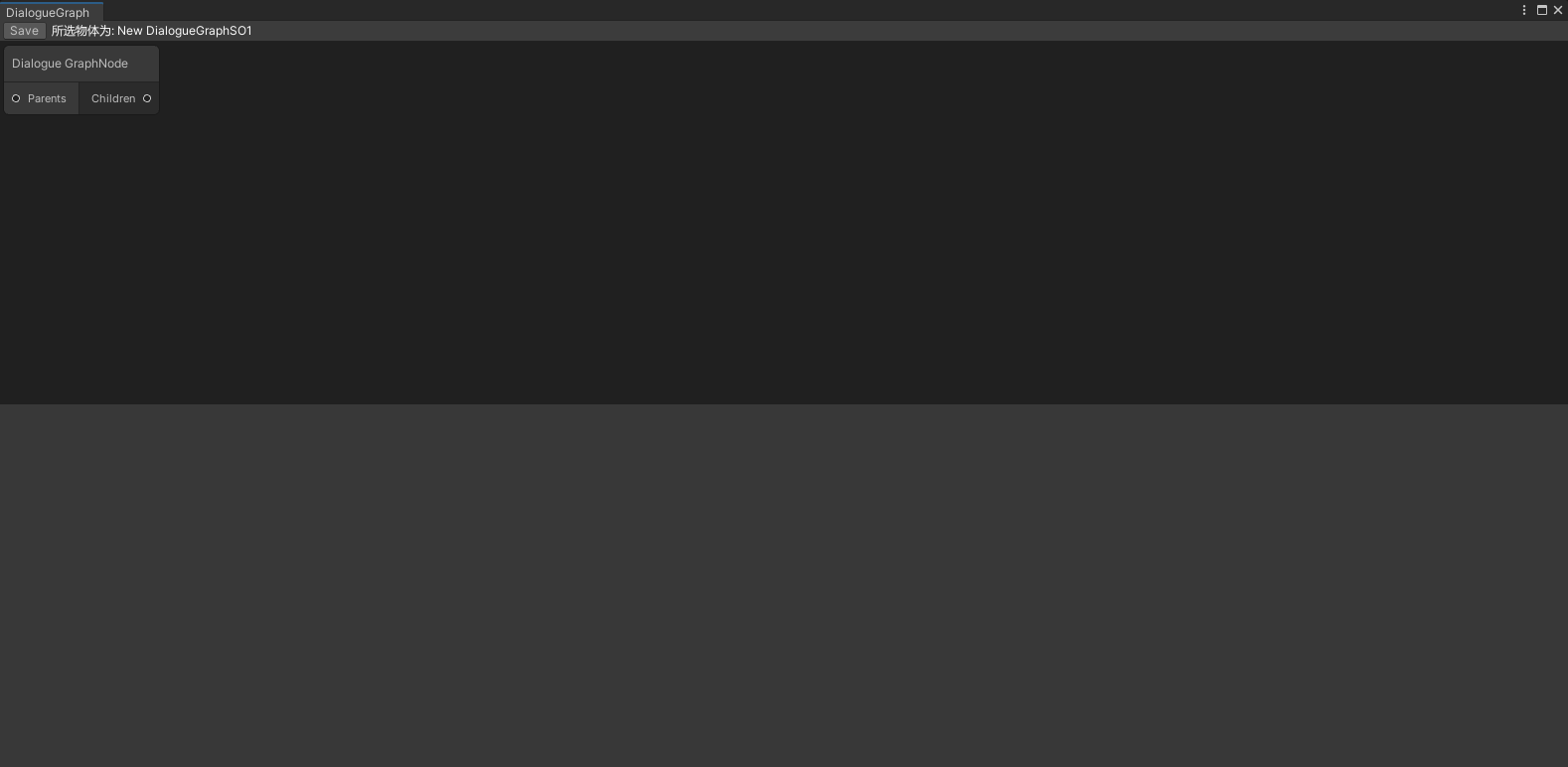
若使用StretchToParentSize()强制缩放至父类大小,节点编辑器则会填充至整个窗口(这是将会根据节点编辑器窗口与Toolbar的绘制先后顺序,造成UI层级的遮挡),而非排在Toolbar下方
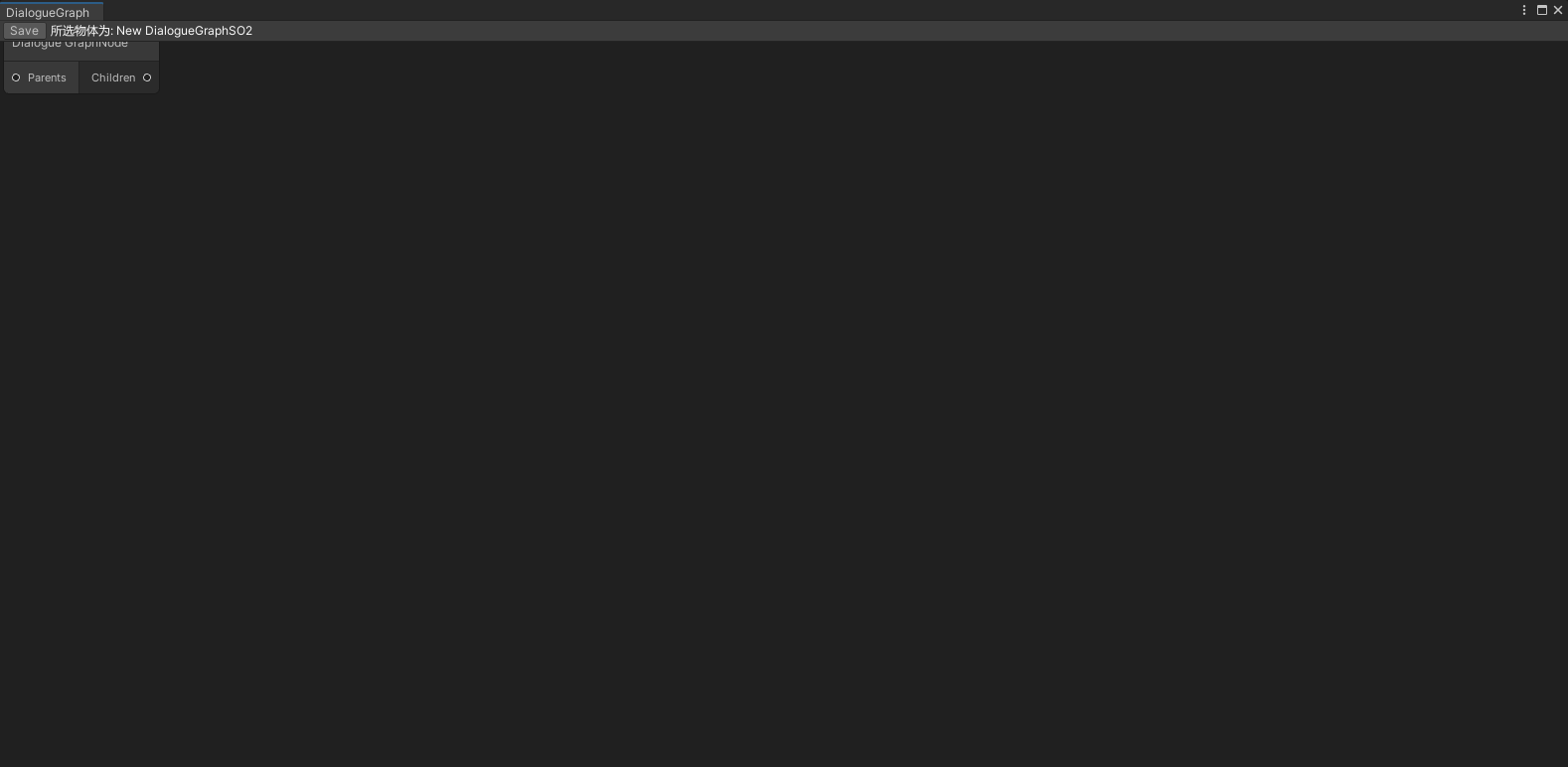
创建对话节点编辑器
using UnityEditor.Experimental.GraphView;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UIElements;
namespace RPG.DialogueSystem.Graph
{
public class DialogueGraphView : GraphView
{
private DialogueGraphEditorWindow _editorWindow;
public DialogueGraphView(DialogueGraphEditorWindow editorWindow)
{
_editorWindow = editorWindow;
// 设置节点拖拽
var dragger = new SelectionDragger()
{
// 不允许拖出边缘
clampToParentEdges = true
};
// 其他按键触发节点拖拽
dragger.activators.Add(new ManipulatorActivationFilter()
{
button = MouseButton.RightMouse,
clickCount = 1,
modifiers = EventModifiers.Alt
});
// 添加节点拖拽
this.AddManipulator(dragger);
// 设置界面缩放
SetupZoom(ContentZoomer.DefaultMinScale, 2);
// this.AddManipulator(new ContentZoomer());
// 设置创建节点回调
nodeCreationRequest += (info) =>
{
AddElement(new DialogueGraphNodeView());
};
// 添加界面移动
this.AddManipulator(new ContentDragger());
// 添加举行选择框
this.AddManipulator(new RectangleSelector());
// 创建背景
Insert(0, new GridBackground());
}
}
}
添加操控器
通过拓展API:AddManipulator(UIElements.IManipulator manipulator)来添加操控器。常见的有:节点拖拽,界面移动以及界面缩放。更多操控器及功能可以查阅相关文档
// 其他按键触发节点拖拽
dragger.activators.Add(new ManipulatorActivationFilter()
{
button = MouseButton.RightMouse,
clickCount = 1,
modifiers = EventModifiers.Alt
});
操控器还可以设置其他的键位触发,例如除了鼠标左键单击外,我再设置 Alt+鼠标右键单击 拖拽节点
添加背景
用Insert而不用Add的原因是:背景应位于UI元素的最底层,若通过Add操作,则会将背景生成在对话节点编辑器之上,导致背景遮挡住了节点编辑器上的所有元素(注意区分Add与AddElement的层级关系,前者是VisualElement,后者是GraphElement,后者是位于GraphView上的)
// 创建背景
Insert(0, new GridBackground());
增加右键面板菜单选项
添加类型为Action<NodeCreationContext>的回调,至于NodeCreationContext类型有啥用,我暂时还没搞清楚,不过目前不需要用到那就先这样吧
// 设置创建节点回调
nodeCreationRequest += (info) =>
{
AddElement(new DialogueGraphNodeView());
};
通过AddElement(GraphElement graphElement)来往对话节点编辑器中添加元素,这里添加的是node

创建对话节点
using UnityEditor.Experimental.GraphView;
namespace RPG.DialogueSystem.Graph
{
public class DialogueGraphNodeView : Node
{
public DialogueGraphNodeView()
{
// 节点标题
title = "Dialogue GraphNode";
// 创建入连接口
var inputPort = Port.Create<Edge>(Orientation.Horizontal, Direction.Input, Port.Capacity.Single, typeof(Port));
inputPort.portName = "Parents";
inputContainer.Add(inputPort);
// 创建出连接口
var outputPort = Port.Create<Edge>(Orientation.Horizontal, Direction.Output, Port.Capacity.Single, typeof(Port));
outputPort.portName = "Children";
outputContainer.Add(outputPort);
}
}
}
摸了
Undo坑点
Undo只能记录能被序列化的变量
一般的来讲,和变量能否被序列化挂钩的有两个Attribute:[System.Serializable]和[SerializeField]
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
[System.Serializable]
public class Person
{
public int age;
public int height;
}
public class Children : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializeField] private Person p1;
private Person p2;
[ContextMenu("UndoTest")]
private void UndoTest()
{
Undo.RecordObject(this, "Change Info");
// 赋值操作
p1.age = 100;
p1.height = 1000;
p2.age = 200;
p2.height = 2000;
}
}
当完成赋值操作后,按下Ctrl + Z进行撤销:只有p1的属性被还原为修改前的状态,而p2保持不变
继承自UnityEngine.Object的对象都是可序列化的
像是ScriptableObject或者是各种Unity自带的组件,又或是继承MonoBehaviour的类等,都可用于Undo记录撤销操作。
当写在ScriptableObject或MonoBehaviour类中的变量,记录撤销操作时:
// 节点数列
[SerializeField] private List<DialogueNodeSO> nodes = new List<DialogueNodeSO>();
// 节点ID字典
private Dictionary<string, DialogueNodeSO> nodeDic = new Dictionary<string, DialogueNodeSO>();
// Codes...
Undo.RecordObject(this, "Change Info");
// Codes...
由于字典是不可被序列化的(即使他添加了[SerializeField]),故在执行撤销操作后,能够恢复的只有nodes,而nodeDic则保持更改不变。