在讲解这些属性之前,假如我们项目的目录的结构如下:
### 目录结构如下: demo1 # 工程名 | |--- dist # 打包后生成的目录文件 | |--- node_modules # 所有的依赖包 | |--- app | | |---index | | | |-- views # 存放所有vue页面文件 | | | | |-- parent.vue # 父组件 | | | | |-- child.vue # 子组件 | | | | |-- index.vue | | | |-- components # 存放vue公用的组件 | | | |-- js # 存放js文件的 | | | |-- store # store仓库 | | | | |--- actions.js | | | | |--- mutations.js | | | | |--- state.js | | | | |--- mutations-types.js | | | | |--- index.js | | | |-- app.js # vue入口配置文件 | | | |-- router.js # 路由配置文件 | |--- views | | |-- index.html # html文件 | |--- webpack.config.js # webpack配置文件 | |--- .gitignore | |--- README.md | |--- package.json | |--- .babelrc # babel转码文件
具体理解vuex的项目构建可以看这篇文章(https://www.cnblogs.com/tugenhua0707/p/9763177.html). 下面讲解的也是在这篇文章项目结构基础之上进行讲解的。当然如果你对 vuex熟悉的话,就不用看了,直接跳过即可。
注意:下面的代码都是在 webpack+vue+route+vuex 中构建的,可以把下面的代码 复制到该项目中运行即可。
一:理解mapState的使用
当我们的组件需要获取多个状态的时候,将这些状态都声明为计算属性会有些重复和冗余,为了解决这个问题,我们可以使用mapState的辅助函数来帮助我们生成计算属性。
mapState函数返回的是一个对象,我们需要使用一个工具函数将多个对象合并为一个,这样就可以使我们将最终对象传给computed属性。
上面的表述可能会有些模糊,下面我们来做个简单的demo来演示一下:
项目架构如上面示意图所示,先看看 app/index/store/state.js 代码如下:
export default { add: 0, errors: '', counts: 0 };
app/index/store/mutations.js 代码如下:
import * as types from './mutations-types'; export default { [types.ADD] (state, payload) { state.add = payload; }, [types.SETERROR] (state, payload) { state.errors = payload; }, [types.COUNTASYNC] (state, payload) { state.counts = payload; } }
app/index/store/mutations-types.js 代码如下:
// 新增list export const ADD = 'ADD'; // 设置错误提示 export const SETERROR = 'SETERROR'; // 异步操作count export const COUNTASYNC = 'COUNTASYNC';
app/index/store/index.js 代码如下:
import Vue from 'vue'; import Vuex from 'vuex'; import state from './state'; import mutations from './mutations'; import actions from './actions'; Vue.use(Vuex); Vue.config.devtools = true; export default new Vuex.Store({ state, mutations, actions });
app/index/store/actions.js 代码请看github
如上代码所示,现在我们在 app/index/views/parent.vue 这个路由下,在mounted生命周期打印一下 console.log(this);这句代码的时候,如下代码:
<template> <div></div> </template> <script type="text/javascript"> export default { data() { return { } }, methods: { }, mounted() { console.log(this); } } </script>
在浏览器运行后,如下图所示:
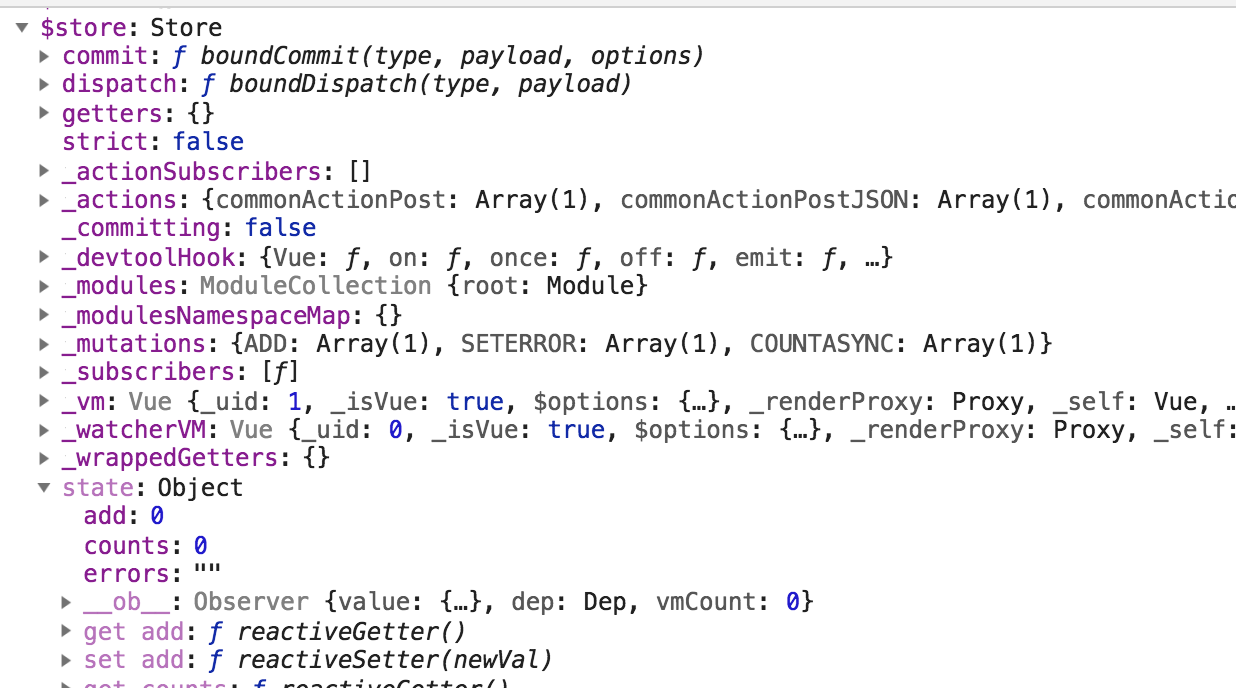
如果我们想获取add,或 count的时候,我们需要使用 this.$store.state.add 或 this.$store.state.count 这样的。
现在我们使用 mapState的话,代码就变成如下了:
<template>
<div>
</div>
</template>
<script type="text/javascript">
import { mapState } from 'vuex';
export default {
data() {
return {
}
},
methods: {
},
computed: {
...mapState({
add: state => state.add,
counts: state => state.counts
})
},
mounted() {
console.log(this.add); // 打印出 0
console.log(this.counts); // 打印 0
}
}
</script>
如上代码,我们使用 mapState工具函数会将store中的state映射到局部计算属性中。
我们在mounted方法内,直接使用 this.xx 即可使用到对应computed中对应的属性了。也就是 我们使用 this.add 就直接映射到 this.$store.state.add 了 。
当然mapState也可以接受一个数组,如下简单代码:
computed: { /* ...mapState({ add: state => state.add, counts: state => state.counts }) */ ...mapState([ 'add', 'counts' ]) }, mounted() { console.log(this); }
然后我们再在控制台查看输出的this的值,如下:
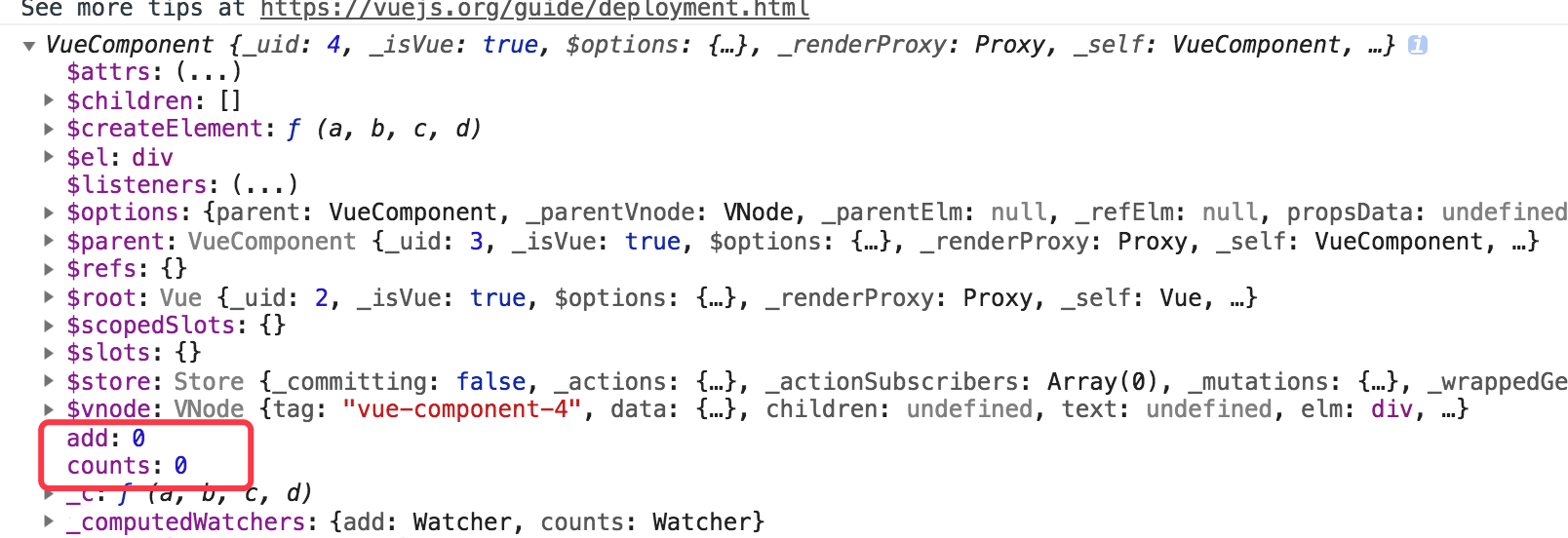
可以看到,接受数组也是可以的,在mounted生命周期内,我们直接可以使用 this.add 或 this.counts 可以获取到值了。
切记:mapState的属性的时候,一定要和state的属性值相对应,也就是说 state中定义的属性值叫add,那么mapState就叫add,如果我们改成add2的话,就获取不到add的值了,并且add2的值也是 undefined,如下所示: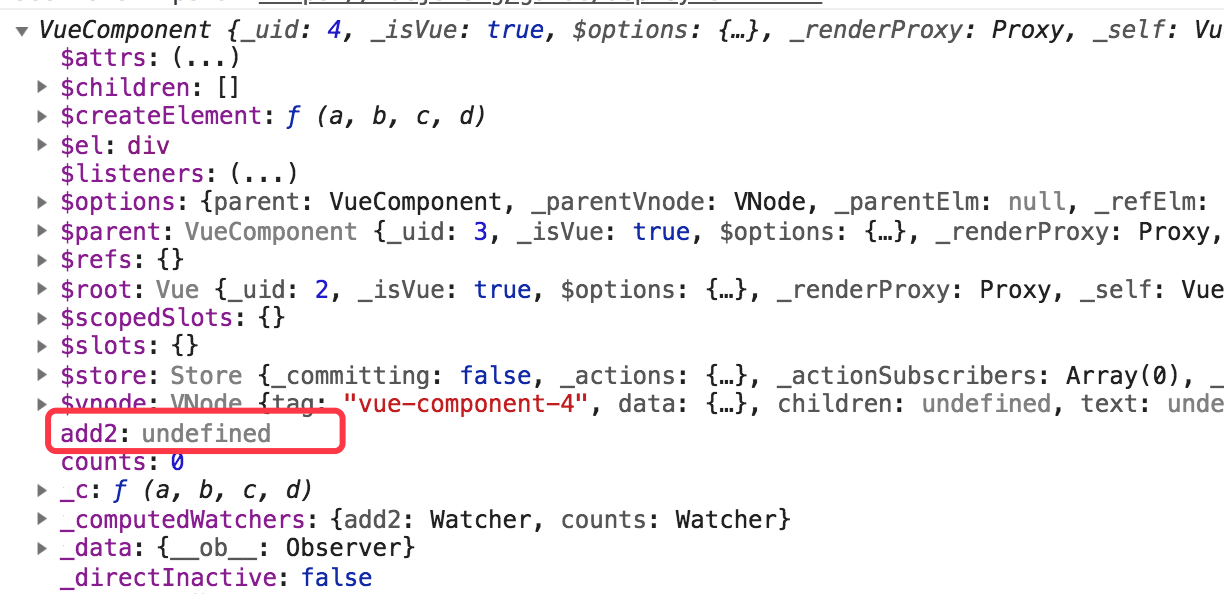
二:理解mapActions的使用
mapActions 的思想 和 mapState 一样的,下面我们直接看代码的使用方法哦,如下代码:
如果我们不使用 mapActions 的话,我们调用某个方法需要如下代码所示:
<template> <div></div> </template> <script type="text/javascript"> export default { data() { return { } }, created() { this.test(); }, methods: { test() { // 调用action 需要时使用 this.$store.dispatch 这样的 Promise.all([this.$store.dispatch('commonActionGet', ['getPower', {}])]).then((res) =>{ }); } }, computed: { }, mounted() { } } </script>
下面我们使用 mapActions的话,代码如下所示:
<template> <div> </div> </template> <script type="text/javascript"> import { mapActions } from 'vuex'; export default { data() { return { } }, created() { this.test(); }, methods: { test() { // 调用 Promise.all([this.commonActionGet(['getPower', {}])]).then((res) => { }); }, // mapActions 使用方法一 将 this.commonActionGet() 映射为 this.$store.dispatch('commonActionGet') ...mapActions(['commonActionGet', 'commonActionGetJSON', 'commonActionPost', 'commonActionPostJSON']) /* // 第二种方式 ...mapActions({ 'commonActionGet': 'commonActionGet', 'commonActionGetJSON': 'commonActionGetJSON', 'commonActionPost': 'commonActionPost', 'commonActionPostJSON': 'commonActionPostJSON' }) */ } } </script>
三:理解 mapMutations 的使用。
首先我们不使用 mapMutations的话,调用mutations里面的方法,是如下代码:
<template> <div> </div> </template> <script type="text/javascript"> export default { data() { return { } }, created() { this.test(); }, methods: { test() { // 调用Mutations 需要时使用 this.$store.commit('ADD', 1) 这样的 Promise.all([this.$store.commit('ADD', 1)]).then(() =>{ console.log(this); }); } } } </script>
打印 如上 this代码后,看到如下图所示:
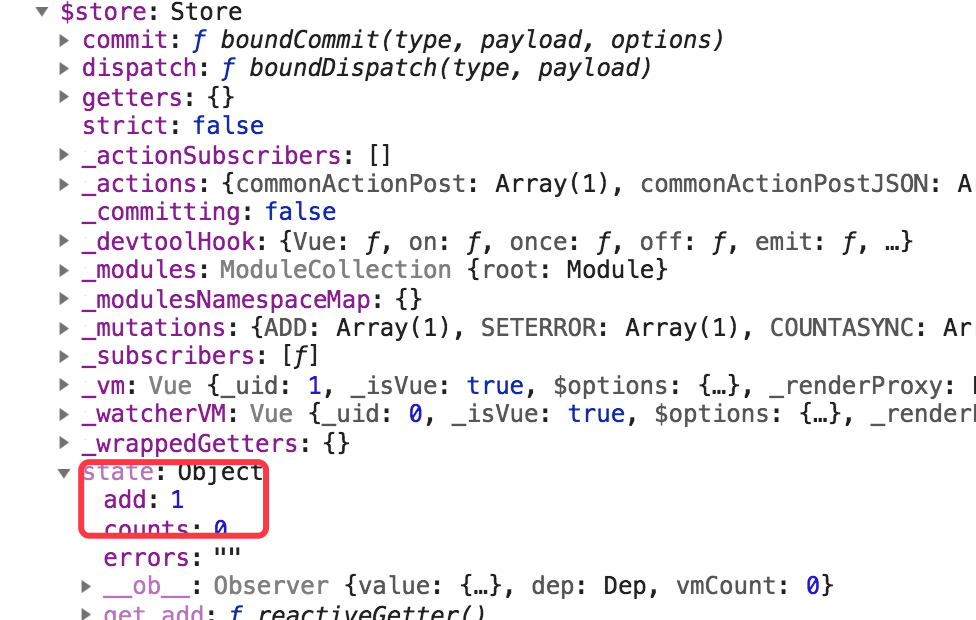
想获取值,使用 this.$store.state.add 就等于1了。
下面我们使用 mapMutations话,代码需要改成如下代码:
<template> <div> </div> </template> <script type="text/javascript"> import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'; export default { data() { return { } }, created() { this.test(); }, methods: { test() { // 使用 mapMutations 调用方式如下: Promise.all([this.ADD(1)]).then(() => { console.log(this); }); }, /* // mapMutations 使用方法1 ...mapMutations(['ADD']), // 会将 this.ADD 映射成 this.$store.commit('ADD') */ // mapMutations 使用方法2 ...mapMutations({ 'ADD': 'ADD' }) } } </script>