单例模式
单例模式,即单个实例,只有一个实例
1、饿汉式
饿汉模式,可以想象一个很饿的人,需要立马吃东西,饿汉模式便是这样,在类加载时就创建对象,由于在类加载时就创建单例,因此不存在线程安全问题。反射可破坏。
public class HungryDemon { private static final HungryDemon hungry = new HungryDemon(); private HungryDemon() { } public static HungryDemon getInstance(){ return hungry; } } // 测试 class HungryTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { HungryDemon instance1 = HungryDemon.getInstance(); HungryDemon instance2 = HungryDemon.getInstance(); System.out.println(instance1.equals(instance1)); // true,说明实例一样 } }
但饿汉式也存在一定的问题,即如果在该类里面存在大量开辟空间的语句,如很多数组或集合,但又不马上使用他们,这时这样的单例模式会消耗大量的内存,影响性能。
2、懒汉式
顾名思义,懒汉式,就是懒,即在类加载时并不会立马创建单例对象,而是只生成一个单例的引用,即可以延时加载。
单线程懒汉式:
public class LazyDemon { private static LazyDemon lazy; private LazyDemon() {} public static LazyDemon getInstance(){ if(lazy == null){ lazy = new LazyDemon(); } return lazy; } } // 测试 class LazyTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { LazyDemon instance1 = LazyDemon.getInstance(); LazyDemon instance2 = LazyDemon.getInstance(); System.out.println(instance1.equals(instance2)); // true } }
该懒汉式,在单线程下是安全的,但是在多线程之下是不安全的。
比如:
public class LazyDemon { private static LazyDemon lazy; private LazyDemon() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" OK"); } public static LazyDemon getInstance(){ if(lazy == null){ lazy = new LazyDemon(); } return lazy; } } // 测试 class LazyTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(()->{ LazyDemon.getInstance(); }).start(); } } } /* 输出结果: Thread-0 OK Thread-2 OK Thread-1 OK // 可见,这次执行至少创建了3个实例,就不是单实例了
解决:可通过加Lock锁解决,也可以通过synchronized去解决,但是效率低。
// 在 LazyDemon 方法上加上了 synchronized 关键字 public static synchronized LazyDemon getInstance(){ if(lazy == null){ lazy = new LazyDemon(); } return lazy; } /* 输出结果: Thread-0 OK 永远只有一个单实例*/ // 在 LazyDemon 方法上加上了 Lock 锁 private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); public static LazyDemon getInstance(){ lock.lock(); try{ if(lazy == null){ lazy = new LazyDemon(); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally { lock.unlock(); return lazy; } } /* 输出结果: Thread-0 OK 永远只有一个单实例*/
多线程安全懒汉式
public class LazyDemon { private static LazyDemon lazy; private LazyDemon() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" OK"); } public static synchronized LazyDemon getInstance(){ if(lazy == null){ lazy = new LazyDemon(); } return lazy; } } class LazyTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(()->{ LazyDemon.getInstance(); }).start(); } } }
3、DCL懒汉式
DCL懒汉(双重监测懒汉式),同样是在类加载时只提供一个引用,不会直接创建单例对象,不需要对整个方法进行同步,缩小了锁的范围,只有第一次会进入创建对象的方法,提高了效率。
public class DCLLazyDemon { private static volatile DCLLazyDemon dclLazy; // 1 private DCLLazyDemon(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " OK"); }; public static DCLLazyDemon getInstance(){ if (dclLazy == null){ synchronized (DCLLazyDemon.class){ if(dclLazy==null){ dclLazy = new DCLLazyDemon(); } } } return dclLazy; } } // 测试 class DCLLazyTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(()->{ DCLLazyDemon.getInstance(); }).start(); } } }
1号代码为什么要加volatile关键字?
在极端情况时,会出现问题。可能会出现重排问题。在new一个实例时,不是原子性操作,创建实例分为
1.分配内存空间
2.执行构造方法
3.将空间地址复制给变量
以上3步执行完成之后,才创建完整的一个实例。
可能当底层重排的时候,执行顺序为132。以这个顺序执行到3,但还没来得及执行2还没来得及将对象初始化,这时又来了一个线程在执行这个方法,此刻dclLazy就已经不是null了,但是dclLazy引用的是空间是空的,该空间是没有任何东西的,这时这个线程返回的对象就是不存在的。因此就会出现问题。为了解决该问题,需要在1号代码上加volatile关键字。private static volatile DCLLazyDemon dclLazy;
通过反射破坏单实例
第1种
public class DCLLazyDemon { private static volatile DCLLazyDemon dclLazy; private DCLLazyDemon(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " OK"); }; public static DCLLazyDemon getInstance(){ if (dclLazy == null){ synchronized (DCLLazyDemon.class){ if(dclLazy==null){ dclLazy = new DCLLazyDemon(); } } } return dclLazy; } } class DCLLazyTest{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Constructor<DCLLazyDemon> constructor = DCLLazyDemon.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); constructor.setAccessible(true); DCLLazyDemon instance1 = constructor.newInstance(); DCLLazyDemon instance2 = constructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(instance1); System.out.println(instance2); } } /*输出: main OK main OK singletonmode.DCLLazyDemon@74a14482 singletonmode.DCLLazyDemon@1540e19d 可见被创建了2个实例,这里是反射通过构造器去创建对象的,因此可以给构造器一个信号量*/
解决:
public class DCLLazyDemon { private static volatile DCLLazyDemon dclLazy; private static boolean flag = false; // 1 private DCLLazyDemon(){ synchronized (DCLLazyDemon.class){ if(flag == false){ // 2 flag = true; // 如果为false,设置为true并初始化对象 }else { throw new RuntimeException("不要使用反射来破坏"); } } }; public static DCLLazyDemon getInstance(){ if (dclLazy == null){ synchronized (DCLLazyDemon.class){ if(dclLazy==null){ dclLazy = new DCLLazyDemon(); } } } return dclLazy; } } class DCLLazyTest{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Constructor<DCLLazyDemon> constructor = DCLLazyDemon.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); constructor.setAccessible(true); DCLLazyDemon instance1 = constructor.newInstance(); DCLLazyDemon instance2 = constructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(instance1); System.out.println(instance2); } } /*输出: Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: 不要使用反射来破坏 通过添加代码1,修改代码2。当通过反射来创建多个实例,会得到异常抛出。*/
第2种
通过上一种的升级,但还是可能会出现安全问题。尽管信号变量通过加密成了一个很难破解的变量,但是依旧会有被破解的可能。如果被破解知道了信号量,那么安全问题如下:
public class DCLLazyDemon { private static volatile DCLLazyDemon dclLazy; private static boolean flag = false; private DCLLazyDemon(){ synchronized (DCLLazyDemon.class){ if(flag == false){ flag = true; }else { throw new RuntimeException("不要使用反射来破坏"); } } }; public static DCLLazyDemon getInstance(){ if (dclLazy == null){ synchronized (DCLLazyDemon.class){ if(dclLazy==null){ dclLazy = new DCLLazyDemon(); } } } return dclLazy; } } class DCLLazyTest{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Constructor<DCLLazyDemon> constructor = DCLLazyDemon.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); // 如果获取到了信号量的变量,就可通过反射获取该变量 Field flag = DCLLazyDemon.class.getDeclaredField("flag"); // 并设置该变量不进行安全监测 flag.setAccessible(true); constructor.setAccessible(true); DCLLazyDemon instance1 = constructor.newInstance(); // 在第一个实例创建完成之后,将信号量的值更改为true,又可以创建一个实例 flag.set(instance1,false); DCLLazyDemon instance2 = constructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(instance1); System.out.println(instance2); } } /*输出: singletonmode.DCLLazyDemon@677327b6 singletonmode.DCLLazyDemon@14ae5a5 创建了2个实例*/
如何解决该问题呢?
通过反射的分析newInstance()源码
if ((clazz.getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects");
得出,枚举不能被反射创建。因此使用单例枚举式
4、静态内部类
使用静态内部类在类加载器加载的时候static就已经被创建,解决了线程安全问题,并实现了延时加载。可被反射破坏。
public class StaticClass { private static StaticClass staticClass; private StaticClass(){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " OK"); }; private static class StaticClassIn{ private static final StaticClass instance = new StaticClass(); } public static StaticClass getInstance(){ return StaticClassIn.instance; } } // 测试 class StaticClassTest{ public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { new Thread(()->{ StaticClass.getInstance(); }).start(); } } }
5、枚举
public enum EnumDemon { INSTANCE; public static EnumDemon getInstance(){ return INSTANCE; } } class EnumTest{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ EnumDemon instance1 = EnumDemon.getInstance(); EnumDemon instance2 = EnumDemon.getInstance(); System.out.println(instance1.equals(instance2)); // true } }
尝试反射获取枚举实例
通过反射的分析newInstance()源码
if ((clazz.getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects");
得出,枚举不能被反射创建。
第一种尝试
【查看枚举的构造器】
通过查看IDEA生成的class文件:

通过javap -p命令对class文件进行反编译:
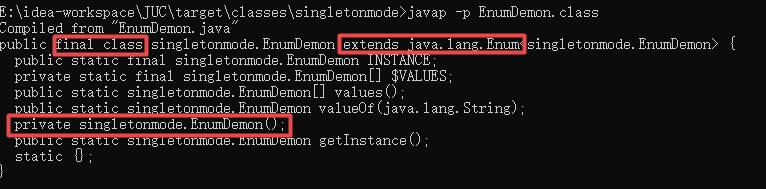
得知,枚举其实是一个final类继承了枚举类。
这里得知枚举的构造器为空构造器。
public enum EnumDemon { INSTANCE; public static EnumDemon getInstance(){ return INSTANCE; } } class EnumTest{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Constructor<EnumDemon> constructor = EnumDemon.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); constructor.setAccessible(true); EnumDemon enumDemon = constructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(enumDemon); } }
输出:
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: // singletonmode.EnumDemon.<init>()
说明这构造器是假的。尝试失败!
第二种尝试
通过jad工具反编译class字节码文件,会生成一个java文件:

通过jad反编译生成的java文件,可以看到构造器是有参数的。这才是枚举的真正构造器。
public enum EnumDemon { INSTANCE; public static EnumDemon getInstance(){ return INSTANCE; } } class EnumTest{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 通过查看到的真正构造器的参数,进行反射获取实例 Constructor<EnumDemon> constructor = EnumDemon.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class); constructor.setAccessible(true); EnumDemon enumDemon = constructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(enumDemon); } }
输出:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: // Cannot reflectively create enum objects at java.lang.reflect.Constructor.newInstance(Constructor.java:417) at singletonmode.EnumTest.main(EnumDemon.java:30)
看到了源码的那句话,Cannot reflectively create enum objects 证实了枚举单例不可通过反射手段获取实例。尝试失败!
总结
- 饿汉式:线程安全(反射可破坏),调用效率高,不能延时加载
- 懒汉式:线程安全(反射可破坏),调用效率不高,可以延时加载
- DCL懒汉式:线程安全(反射可破坏)。由于JVM底层模型原因,偶尔出现问题,不建议使用。
- 静态内部类式:线程安全(反射可破坏),调用效率高,可以延时加载
- 枚举单例:线程安全,调用效率高,不能延时加载