这里指的TDOA算法,实际是解两个双曲线方程,由于两个二次方程设计东西较多,如果强解,计算量很大,从网上参考了如下链接:
算法推到:https://blog.csdn.net/lpsl1882/article/details/51519303
Matlab实现:https://blog.csdn.net/chenxy_bwave/article/details/86650983
我主要讲matlab 相关算法用python再次实现,后期TDOA上位机会基于Python去写
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def distance(x1,y1,x2,y2):
dist =math.sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2) + (y1-y2)*(y1-y2))
return dist
x1 = 10
y1 = 10
x2 = 240
y2 = 20
x3 = 124
y3 = 250
x = 123
y = 134
#
print(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x,y)
plt.scatter(x1,y1,label="1")
plt.scatter(x2,y2,label="2")
plt.scatter(x3,y3,label="3")
plt.scatter(x,y,label="x")
plt.legend()
#
plt.plot([x1,x],[y1,y])
plt.plot([x2,x],[y2,y])
plt.plot([x,x3],[y,y3])
r1 = distance(x1, y1, x, y)
r2 = distance(x2, y2, x, y)
r3 = distance(x3, y3, x, y)
print("distance")
print(r1,r2,r3)
r21 = r2 - r1
r31 = r3 - r1
print(r21,r31)
x21 = x2 - x1
x31 = x3 - x1
y21 = y2 - y1
y31 = y3 - y1
print([x21, x31, y21, y31])
P1_tmp = np.array([[x21,y21],[x31,y31]])
print("P1_tmp:")
print(P1_tmp)
P1 = (-1)*linalg.inv(P1_tmp)
print(P1)
P2= np.array([[r21], [r31]])
print("P2")
print(P2)
K1 = x1*x1 + y1*y1;
K2 = x2*x2 + y2*y2;
K3 = x3*x3 + y3*y3;
print(K1,K2,K3)
P3 = np.array([ [ (-K2 + K1 + r21*r21)/2], [(-K3 + K1 + r31*r31)/2 ]])
print("P3:")
print(P3)
xy_esti = (np.dot(P1 , P2)) * r1 +np.dot( P1 , P3)
print("xy_esti")
#print(type(xy_esti[0]))
print(int(xy_esti[0]),int(xy_esti[1]))
运行结果截图:
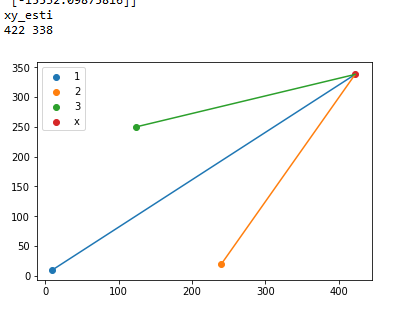
标签节点无论是在三个基站组成的范围内还是范围外面,都能正确计算出结果。
以上全部执行print以及绘图,所有时间开销为:Time used: 0.0519 秒
将print 和 绘图去掉,单独计算坐标解算时间:Time used: 0.0013 秒
测试机器:Win7,CPU:E5-2670