synchronized是什么
- java内置锁,可以保证方法或者代码块在运行时候,同一时刻只有一个线程进入临界区,同时它还保证了共享变量的可见性(限定同一个临界区,等同于volatile)
synchronized几种用法
- 修饰普通方法,锁的是当前实例
- 修饰代码块,锁的括号里面的对象
- 修改静态方法,锁的是当前类的class对象
举个例子
1. 修饰普通方法
点击查看代码
public class SynchNoStaticClass {
public synchronized void test2() {
int i = 5;
while (i-- > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchNoStaticClass synchNoStaticClass = new SynchNoStaticClass();
new Thread(()->{
synchNoStaticClass.test2();
},"thread--1").start();
new Thread(()->{
synchNoStaticClass.test2();
},"thread--2").start();
}
}
结果:
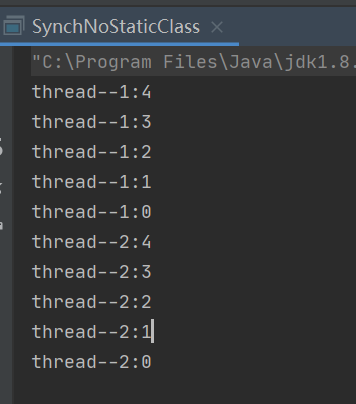
分析:不同线程访问同一个对象的临界方法,需要等前一个线程执行完毕后把锁释放才能执行(执行结果是顺序的),如果是多个线程作用的是不同的对象,那么执行结果就可能不是顺序的,因为不同的对象锁,互不影响。
2. 修饰静态方法
点击查看代码
public class TestSynchronized {
public static synchronized void test2() {
int i = 5;
while (i-- > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
}
public void test1(){
test2();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()-> {
TestSynchronized testSynchronizedOne = new TestSynchronized();
testSynchronizedOne.test1();
}, "thread--1").start();
new Thread(()->{
TestSynchronized testSynchronizedTwo = new TestSynchronized();
testSynchronizedTwo.test1();
},"thread--2").start();
}
}
结果:
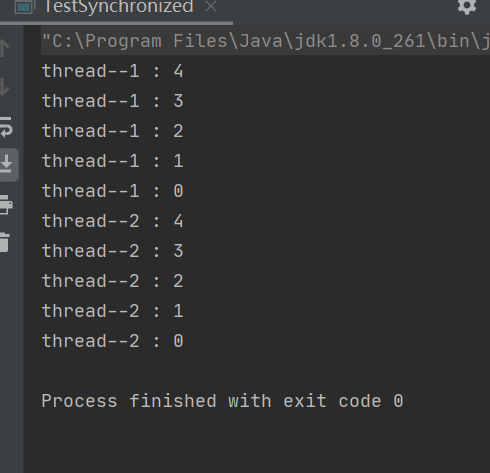
分析:不同线程访问不同的对象,但是访问方法是静态的,当前class的对象锁生效,结果就是顺序执行(可以把synchronized去掉,结果是交替输出的)
3.修饰代码块
为啥需要修饰代码块呢,因为修饰方法的范围粒度太大了,我们往往需要方法中的某段代码互斥进行同步操作
点击查看代码
public class SynchNoStaticClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynchNoStaticClass synchNoStaticClass = new SynchNoStaticClass();
new Thread(() -> {
synchNoStaticClass.test3();
}, "test3").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchNoStaticClass.test3();
}, "test4").start();
}
public void test3() {
synchronized (SynchNoStaticClass.class) {
int i = 5;
while (i-- > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
}
}
}
结果:
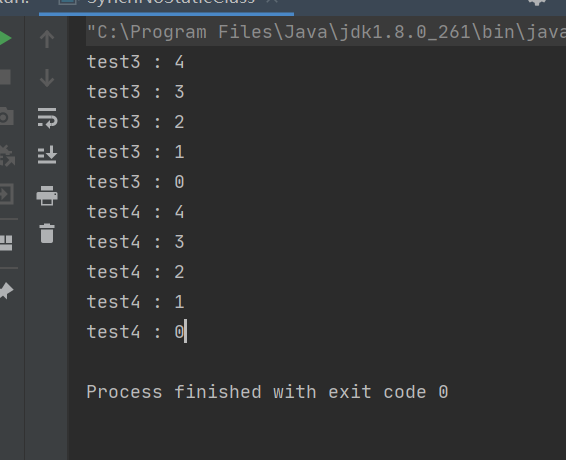
分析:每次当线程进入synchronized包裹的代码块时就会,就会获取SynchNoStaticClass.class对象锁,那么其他线程在进来需要等待
synchronized的可重入性
什么是可重入锁呢?当一个线程再次请求由自己持有的对象锁时候是可以获取成功的,看下面代码
点击查看代码
public class SynchDoubleClass {
public synchronized void test2() {
int i = 5;
while (i-- > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "test2:" + i);
}
test3();
}
public synchronized void test1() {
int i = 5;
while (i-- > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "test1:" + i);
}
test2();
}
public synchronized void test3() {
int i = 5;
while (i-- > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "test3:" + i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
SynchDoubleClass synchDoubleClass = new SynchDoubleClass();
synchDoubleClass.test1();
}).start();
}
}

分析:因为synchronized 锁是可重入的,所以在test1方法没执行完,在去调用test2方法,因为是同一个对象锁,它依然会获得锁。
synchronized与awit/notify/notifyAll使用(等待通知机制)
- awit阻塞当前线程,就是释放当前线程的锁
- notify通知某个阻塞线程,notifyall 通知所有的阻塞线程
synchronized的底层实现
- 字节码反编译结果

分析: - 先说结论,修饰方法JVM通过ACC_SYNCHRONIZED标识实现,修饰代码块,JVM通过 monitorenter和monitorexit两个指令实现同步,而monitor(对象监视器)的本质依赖于底层操作系统的 互斥锁(Mutex Lock) 实现,
- 关于class文件结构以及更底层的c++文件源码解读,当前笔者还是小白,无法更深入了解,留待后续补充