激活函数的作用如下-引用《TensorFlow实践》:
这些函数与其他层的输出联合使用可以生成特征图。他们用于对某些运算的结果进行平滑或者微分。其目标是为神经网络引入非线性。曲线能够刻画出输入的复杂的变化。TensorFlow提供了多种激活函数,在CNN中一般使用tf.nn.relu的原因是因为,尽管relu会导致一些信息的损失,但是性能突出。在刚开始设计模型时,都可以采用relu的激活函数。高级用户也可以自己创建自己的激活函数,评价激活函数是否有用的主要因素参看如下几点:
1)该函数是单调的,随着输入的增加增加减小减小,从而利用梯度下降法找到局部极值点成为可能。
2)该函数是可微分的,以保证函数定义域内的任意一点上导数都存在,从而使得梯度下降法能够正常使用来自这类激活函数的输出。
常见的TensorFlow提供的激活函数如下:(详细请参考http://www.tensorfly.cn/tfdoc/api_docs/python/nn.html)
1.tf.nn.relu(features, name=None)
Computes rectified linear: max(features, 0).
features: ATensor. Must be one of the following types:float32,float64,int32,int64,uint8,int16,int8.name: A name for the operation (optional).
注:
优点在于不受‘梯度消失’的影响,取值范围为[0,+∞]。
缺点在于当使用了较大的学习速率时,易受到饱和的神经元的影响。
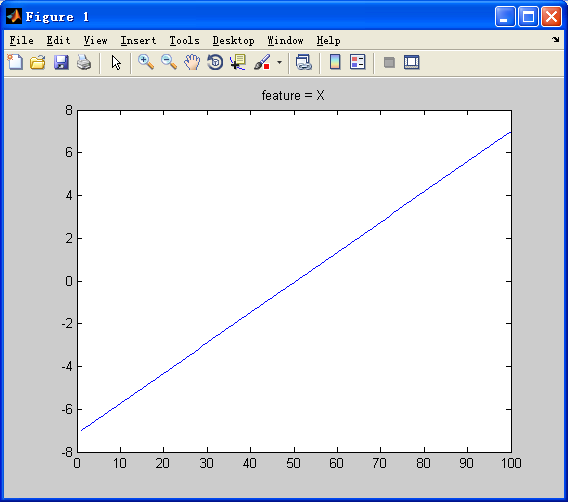
2.tf.nn.relu6(features, name=None)
Computes Rectified Linear 6: min(max(features, 0), 6).
features: ATensorwith typefloat,double,int32,int64,uint8,int16, orint8.name: A name for the operation (optional).
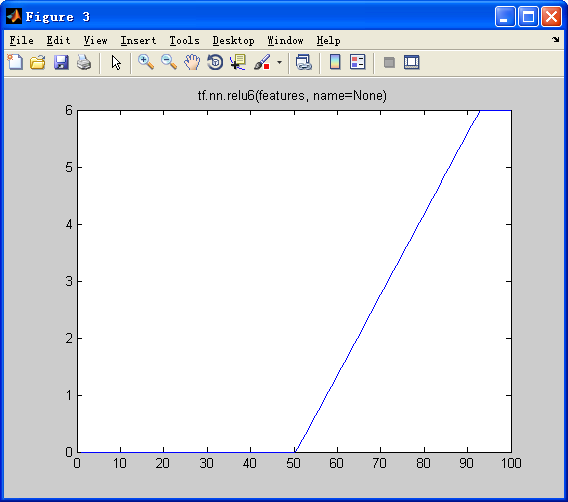
3.tf.sigmoid(x, name=None)
Computes sigmoid of x element-wise.
Specifically, y = 1 / (1 + exp(-x)).
x: A Tensor with typefloat,double,int32,complex64,int64, orqint32.name: A name for the operation (optional).
注:
优点在于sigmoid函数在样本训练的神经网络中可以将输出保持在[0.0,1.0]内部的能力非常有用。
缺点在于当输出接近饱和或剧烈变化时,对输出范围的这种缩减往往会带来一些不利影响。
4.tf.nn.softplus(features, name=None)
Computes softplus: log(exp(features) + 1).
features: ATensor. Must be one of the following types:float32,float64,int32,int64,uint8,int16,int8.name: A name for the operation (optional).
5.tf.tanh(x, name=None)
Computes hyperbolic tangent of x element-wise.
x: A Tensor with typefloat,double,int32,complex64,int64, orqint32.name: A name for the operation (optional).
注:
优点在于双曲正切函数和sigmoid函数比较相似,tanh拥有sigmoid的优点,用时tanh具有输出负值的能力,tanh的值域为[-1.0,1.0].
MATLAB代码来体现函数的类型
clear all close all clc % ACTVE FUNCTION % X = linspace(-5,5,100); plot(X) title('feature = X') % tf.nn.relu(features, name=None):max(features, 0) % Y_relu = max(X,0); figure,plot(Y_relu) title('tf.nn.relu(features, name=None)') % tf.nn.relu6(features, name=None):min(max(features, 0), 6) % Y_relu6 = min(max(X,0),6); figure,plot(Y_relu6) title('tf.nn.relu6(features, name=None)') % tf.sigmoid(x, name=None):y = 1 / (1 + exp(-x))% Y_sigmoid = 1./(1+exp(-1.*X)); figure,plot(Y_sigmoid) title('tf.sigmoid(x, name=None)') % tf.nn.softplus(features, name=None):log(exp(features) + 1) % Y_softplus = log(exp(X) + 1); figure,plot(Y_softplus) title('tf.nn.softplus(features, name=None)') % tf.tanh(x, name=None):tanh(features) % Y_tanh = tanh(X); figure,plot(Y_tanh) title('tf.tanh(x, name=None)')
X=feature tf.nn.relu(features, name=None)

tf.nn.relu6(features, name=None) tf.sigmoid(x, name=None)
tf.nn.softplus(features, name=None) tf.tanh(x, name=None)


归一化函数的重要作用-引用《TensorFlow实践》:
归一化层并非CNN所独有。在使用tf.nn.relu时,考虑输出的归一化是有价值的(详细参看http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf)。由于relu是无界函数,利用某些形式的归一化来识别哪些高频特征通常是十分有用的。local response normalization最早是由Krizhevsky和Hinton在关于ImageNet的论文里面使用的一种数据标准化方法,即使现在,也依然会有不少CNN网络会使用到这种正则手段。
tf.nn.local_response_normalization(input, depth_radius=None, bias=None, alpha=None, beta=None, name=None)
Local Response Normalization.
The 4-D input tensor is treated as a 3-D array of 1-D vectors (along the last dimension), and each vector is normalized independently. Within a given vector, each component is divided by the weighted, squared sum of inputs within depth_radius. In detail,
sqr_sum[a, b, c, d] =
sum(input[a, b, c, d - depth_radius : d + depth_radius + 1] ** 2)
output = input / (bias + alpha * sqr_sum ** beta)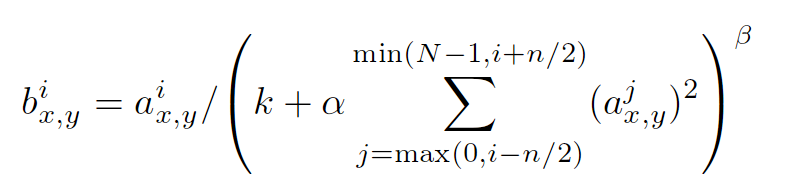
- 第一个参数input:这个输入就是feature map了
,既然是feature map,那么它就具有[batch, height, width, channels]这样的shape - 第二个参数depth_radius:这个值需要自己指定,就是上述公式中的n/2
- 第三个参数bias:上述公式中的k
- 第四个参数alpha:上述公式中的α
- 第五个参数beta:上述公式中的β
- 第六个参数name:上述操作的名称
- 返回值是新的feature map,它应该具有和原feature map相同的shape
以上是这种归一手段的公式,其中a的上标指该层的第几个feature map,a的下标x,y表示feature map的像素位置,N指feature map的总数量,公式里的其它参数都是超参,需要自己指定的。
这种方法是受到神经科学的启发,激活的神经元会抑制其邻近神经元的活动(侧抑制现象),至于为什么使用这种正则手段,以及它为什么有效,查阅了很多文献似乎也没有详细的解释,可
能是由于后来提出的batch normalization手段太过火热,渐渐的就把local response normalization掩盖了吧。
import tensorflow as tf a = tf.constant([ [[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0], [8.0, 7.0, 6.0, 5.0], [4.0, 3.0, 2.0, 1.0]], [[4.0, 3.0, 2.0, 1.0], [8.0, 7.0, 6.0, 5.0], [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0], [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0]] ]) #reshape a,get the feature map [batch:1 height:2 2 channels:8] a = tf.reshape(a, [1, 2, 2, 8]) normal_a=tf.nn.local_response_normalization(a,2,0,1,1) with tf.Session() as sess: print("feature map:") image = sess.run(a) print (image) print("normalized feature map:") normal = sess.run(normal_a) print (normal)
运行结果:

解释:
这里我取了n/2=2,k=0,α=1,β=1。公式中的N就是输入张量的通道总数:由a = tf.reshape(a, [1, 2, 2, 8]) 得到 N=8,变量i代表的是不同的通道,从0开始到7.
举个例子,比如对于一通道的第一个像素“1”来说,我们把参数代人公式就是1/(1^2+2^2+3^2)=0.07142857,对于四通道的第一个像素“4”来说,公式就是4/(2^2+3^2+4^2+5^2+6^2)=0.04444445,以此类推。转载:http://blog.csdn.net/mao_xiao_feng/article/details/53488271