Java NIO是什么
Java NIO( New IO) 是从Java 1.4版本开始引入的一个新的IO API,可以替代标准的Java IO API。NIO与原来的IO有同样的作用和目的,但是使用的方式完全不同, NIO支持面向缓冲区的、基于通道的IO操作。 NIO将以更加高效的方式进行文件的读写操作。
Java NIO 与 IO 的主要区别
| IO | NIO |
|---|---|
| 面向流(Stream Oriented) | 面向缓冲区(Buffer Oriented) |
| 阻塞IO(Blocking IO) | 非阻塞IO(Non Blocking IO) |
| (无) | 选择器(Selectors) |
缓冲区( Buffer)
一个用于特定基本数据类型的容器。由 java.nio 包定义的,所有缓冲区都是 Buffer 抽象类的子类。Buffer 主要用于与 NIO 通道进行交互,数据是从通道读入缓冲区,从缓冲区写入通道中的。Buffer 就像一个数组,可以保存多个相同类型的数据。根据数据类型不同(boolean 除外) ,有以下 Buffer 常用子类:
- ByteBuffer
- CharBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
上述 Buffer 类 他们都采用相似的方法进行管理数据,只是各自管理的数据类型不同而已。
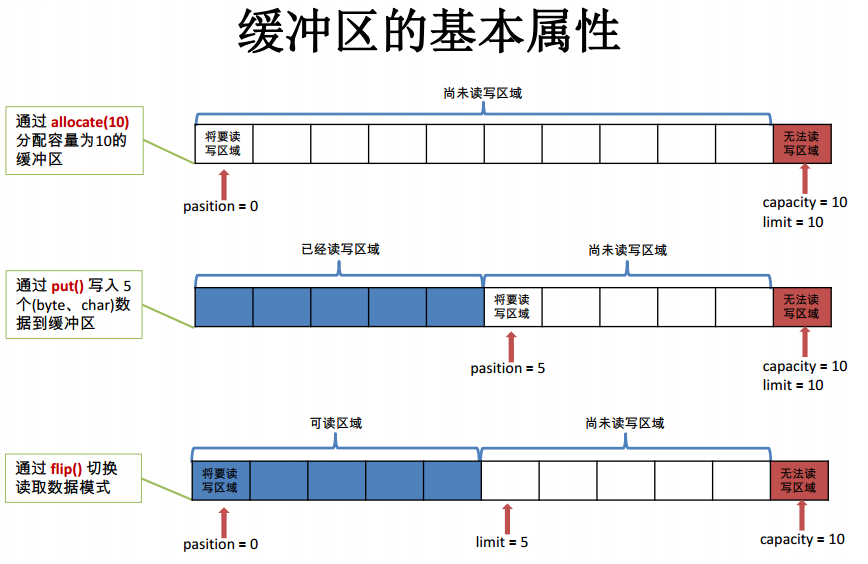
缓冲区的基本属性
- 容量 (capacity) :表示 Buffer 最大数据容量,缓冲区容量不能为负,并且创建后不能更改.
- 限制 (limit):第一个不应该读取或写入的数据的索引,即位于 limit 后的数据不可读写。缓冲区的限制不能为负,并且不能大于其容量。
- 位置 (position):下一个要读取或写入的数据的索引。缓冲区的位置不能为负,并且不能大于其限制.
- 标记 (mark)与重置 (reset):标记是一个索引,通过 Buffer 中的 mark() 方法指定 Buffer 中一个特定的 position,之后可以通过调用 reset()方法恢复到这个 position.
标记、 位置、 限制、 容量遵守以下不变式: 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
缓冲区的数据操作
Buffer 所有子类提供了两个用于数据操作的方法: get()与 put() 方法
获取 Buffer 中的数据
- get() :读取单个字节
- get(byte[] dst):批量读取多个字节到 dst 中
- get(int index):读取指定索引位置的字节(不会移动 position)
放入数据到 Buffer 中
- put(byte b):将给定单个字节写入缓冲区的当前位置
- put(byte[] src):将 src 中的字节写入缓冲区的当前位置
- put(int index, byte b):将指定字节写入缓冲区的索引位置(不会移动 position)
public class TestBuffer {
@Test
public void test1() {
//分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println(buffer.position());//0 返回缓冲区的当前位置 position
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//1024 返回 Buffer 的界限(limit) 的位置
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024 返回Buffer的capacity 大小
//将数据存入缓冲区
buffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
System.out.println(buffer.position());//5
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//1024
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024
//切换到读取数据的模式
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(buffer.position());//0
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//5
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024
//读取缓冲区的数据
byte[] bs = new byte[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(bs);
System.out.println(new String(bs, 0, bs.length));//abcde
System.out.println(buffer.position());//5
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//5
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024
//回到读模式,可重复读数据
buffer.rewind();//将位置设为为 0, 取消设置的 mark
System.out.println(buffer.position());//0
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//5
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024
//清空缓冲区,回到最初状态。但是缓冲区的数据还在,处于被遗忘状态。
buffer.clear();//清空缓冲区并返回对缓冲区的引用
System.out.println(buffer.position());//0
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//1024
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024
}
@Test
public void test2() {
String str = "abcde";
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buffer.put(str.getBytes());
System.out.println(buffer.position());//5
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//1024
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024
buffer.flip();
byte[] bs = new byte[buffer.limit()];
buffer.get(bs, 0, 2);
System.out.println(new String(bs, 0, 2));//ab
System.out.println(buffer.position());//2
System.out.println(buffer.limit());//5
System.out.println(buffer.capacity());//1024
//标记position的位置
buffer.mark();
buffer.get(bs, 2, 2);
System.out.println(new String(bs, 2, 2));//cd
System.out.println(buffer.position());//4
//重置position的位置到标记的地方
buffer.reset();
System.out.println(buffer.position());//2
//缓冲区中是否还有课操作的字节
if (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
//剩余可操作的字节数
System.out.println(buffer.remaining());//3 返回 position 和 limit 之间的元素个数
}
}
@Test
public void test3() {
//创建直接缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(1024);
//判断是否为直接缓冲区
System.out.println(buffer.isDirect());//true
}
}
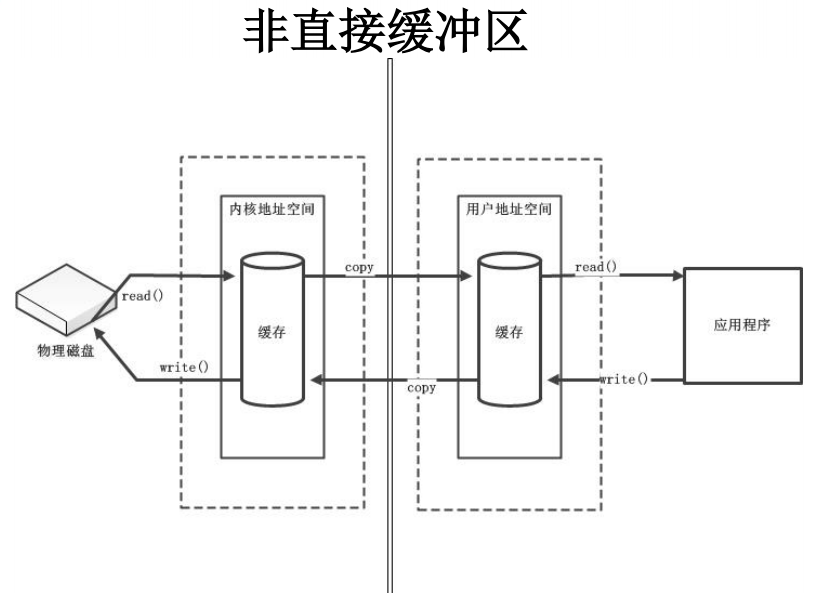
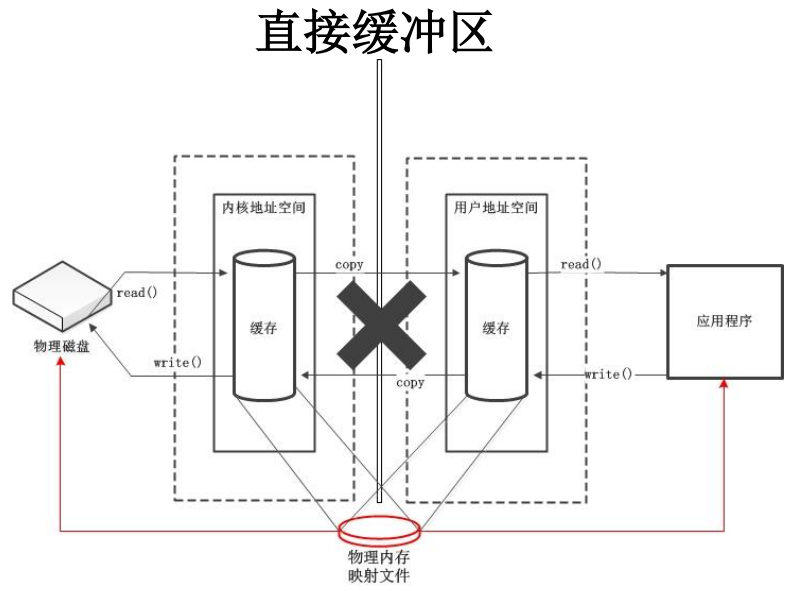
直接与非直接缓冲区
- 字节缓冲区要么是直接的,要么是非直接的。如果为直接字节缓冲区,则 Java 虚拟机会尽最大努力直接在此缓冲区上执行本机 I/O操作。也就是说,在每次调用基础操作系统的一个本机 I/O 操作之前(或之后),虚拟机都会尽量避免将缓冲区的内容复制到中间缓冲区中(或从中间缓冲区中复制内容)。
- 直接字节缓冲区可以通过调用此类的 allocateDirect() 工厂方法来创建。此方法返回的缓冲区进行分配和取消分配所需成本通常高于非直接缓冲区。直接缓冲区的内容可以驻留在常规的垃圾回收堆之外,因此,它们对应用程序的内存需求量造成的影响可能并不明显。所以,建议将直接缓冲区主要分配给那些易受基础系统的本机 I/O 操作影响的大型、持久的缓冲区。一般情况下,最好仅在直接缓冲区能在程序性能方面带来明显好处时分配它们。
- 直接字节缓冲区还可以通过 FileChannel 的 map() 方法将文件区域直接映射到内存中来创建。该方法返回MappedByteBuffer。Java 平台的实现有助于通过 JNI从本机代码创建直接字节缓冲区。如果以上这些缓冲区中的某个缓冲区实例指的是不可访问的内存区域,则试图访问该区域不会更改该缓冲区的内容,并且将会在访问期间或稍后的某个时间导致抛出不确定的异常。
- 字节缓冲区是直接缓冲区还是非直接缓冲区可通过调用其 isDirect() 方法来确定。提供此方法是为了能够在性能关键型代码中执行显式缓冲区管理。
通道Channel
通道表示打开到 IO 设备(例如:文件、套接字)的连接。若需要使用 NIO 系统,需要获取用于连接 IO 设备的通道以及用于容纳数据的缓冲区。然后操作缓冲区,对数据进行处理。Channel 负责传输, Buffer 负责存储。通道是由 java.nio.channels 包定义的。 Channel 表示 IO 源与目标打开的连接。Channel 类似于传统的“流”。只不过 Channel本身不能直接访问数据, Channel 只能与Buffer 进行交互。
Java 为 Channel 接口提供的最主要实现类
- FileChannel:用于读取、写入、映射和操作文件的通道。
- DatagramChannel:通过 UDP 读写网络中的数据通道。
- SocketChannel:通过 TCP 读写网络中的数据。
- ServerSocketChannel:可以监听新进来的 TCP 连接,对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个 SocketChannel。
获取通道
获取通道的一种方式是对支持通道的对象调用getChannel() 方法。支持通道的类如下:
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
- RandomAccessFile
- DatagramSocket
- Socket
- ServerSocket
获取通道的其他方式是使用 Files 类的静态方法 newByteChannel() 获取字节通道。或者通过通道的静态方法 open() 打开并返回指定通道。
通道的数据传输
//通道用于源节点与目标节点之间的连接,在NIO中负责缓冲区中数据的传输。
//Channel本身不存储数据,需要配合缓冲区进行数据传输
/**
* 通道的主要实现类
* java.nio.channels.Channel接口
* |--FileChannel
* |--SocketChannel
* |--ServerSocketChannel
* |--DatagramChannel
*
* 获取通道
* 1.Java针对支持通道的类提供了getChannel()方法
* 本地IO:
* FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
* RandomAccessFile
*
* 网络IO:
* Socket
* ServerSocket
* DatagramSocket
*
* 2.在JDK1.7中NIO.2针对各个通道提供了静态方法open()
* 3.在JDK1.7中NIO.2的Files工具类的newByteChannel()
*/
public class TestChannel {
//利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区)
@Test
public void test1() {
//26088
//6479
//6587
//6464
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
FileChannel inChannel = null;
FileChannel outChannel = null;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:\BaiduYunDownload\juc.zip");
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("F:\juc_copy2.zip");
//获取通道
inChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
outChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//将通道中的数据存入缓冲区
while (inChannel.read(buffer) != -1) {
//切换成读取数据模式
buffer.flip();
//将缓冲区中的数据写入通道中
outChannel.write(buffer);
//清空缓冲区
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭通道 省略if判断
outChannel.close();
inChannel.close();
//关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
fileInputStream.close();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
//1190
//5144
//5932
//1316
//1126
//998
//1242
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件)
//只有ByteBuffer支持直接缓冲区
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\BaiduYunDownload\", "juc.zip"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
//StandardOpenOption.CREATE_NEW若存在则报错
//StandardOpenOption.CREATE若存在则覆盖
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("F:/", "juc-3.zip"), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//内存映射文件。缓冲区在物理内存中。
MappedByteBuffer inMappedByteBuffer = inChannel.map(MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMappedByteBuffer = outChannel.map(MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());
//直接对缓冲区进行数据读写操作
byte[] dst = new byte[inMappedByteBuffer.limit()];
inMappedByteBuffer.get(dst);
outMappedByteBuffer.put(dst);
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
@Test
public void test3() throws IOException {
//将数据从源通道传输到其他 Channel 中
//729
//684
//601
//706
//625
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("E:\BaiduYunDownload\", "juc.zip"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("F:/", "juc-4.zip"), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//通道之间的数据传输
//inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel);
outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel, 0, inChannel.size());
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
@Test
public void test4() throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile1 = new RandomAccessFile("E:/a.txt", "rw");
//获取通道
FileChannel fileChannel1 = randomAccessFile1.getChannel();
//分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//分散读取,从 Channel 中读取的数据“分散” 到多个 Buffer 中
ByteBuffer[] buffers = {buffer1, buffer2};
fileChannel1.read(buffers);
for (int i = 0; i < buffers.length; i++) {
buffers[i].flip();
}
System.out.println(new String(buffers[0].array(), 0, buffers[0].limit()));
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println(new String(buffers[1].array(), 0, buffers[1].limit()));
//聚集写入,将多个 Buffer 中的数据“聚集”到 Channel
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile2 = new RandomAccessFile("E:/b.txt", "rw");
FileChannel fileChannel2 = randomAccessFile2.getChannel();
fileChannel2.write(buffers);
}
@Test
public void test5() {
/**
* 编码:字符串->字节数组
* 解码:字节数组->字符串
*/
//获取所有支持的字符集
SortedMap<String, Charset> availableCharsets = Charset.availableCharsets();
Set<Entry<String, Charset>> set = availableCharsets.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, Charset> entry: set) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "--" + entry.getValue());
}
}
@Test
public void test6() throws CharacterCodingException {
Charset charset = Charset.forName("GBK");
//编码器
CharsetEncoder charsetEncoder = charset.newEncoder();
//解码器
CharsetDecoder charsetDecoder = charset.newDecoder();
CharBuffer charBuffer = CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
charBuffer.put("你好");
charBuffer.flip();
//编码
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = charsetEncoder.encode(charBuffer);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//字节数组
System.out.println(byteBuffer.get());
}
//切换到读模式
byteBuffer.flip();
//解码
CharBuffer charBuffer2 = charsetDecoder.decode(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(charBuffer2.toString());
}
}