中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
首先何为中缀表达式。中缀表达式就是我们最为常见的算术表达式形式,即操作符在操作数中间。比如 3 + 4。
后缀表达式是将操作符置于操作数后面,即如下形式:3 4 +。
给定一个中缀表达式,我们如何将其转换为后缀表达式?
我们这里涉及的操作符只局限于加、减、乘、除四种运算,即四则运算,外加括号功能。
比如给定一个中缀表达式:
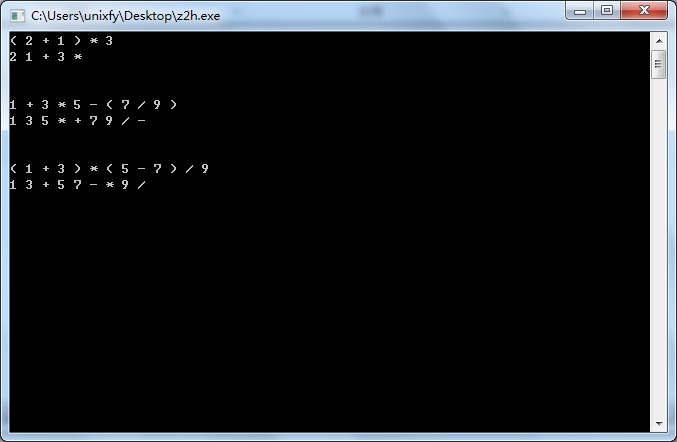
1 + 3 * 5 – ( 7 / 9 )
其后缀表达式应为:
1 3 5 * + 7 9 / -
中缀表达式:
( 1 + 3 ) * ( 5 – 7 ) / 9
其后缀表达式为:
1 3 + 5 7 - * 9 /
我们先给出其程序实现如下:
// 中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式 #include <iostream> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <stack> #include <map> using namespace std; void get_infix(vector<string>& inf) { inf.clear(); string line; getline(cin, line); istringstream sin(line); string tmp; while (sin >> tmp) { inf.push_back(tmp); } } void show(const vector<string>& hs) { for (vector<string>::size_type i = 0; i != hs.size(); ++i) { cout << hs[i] << ' '; } cout << endl; } void init_op(map<string, int>& ops) { ops.clear(); ops["+"] = 100; ops["-"] = 100; ops["*"] = 200; ops["/"] = 200; ops["("] = 1000; ops[")"] = 0; } bool is_operator(const string& hs, const map<string, int>& ops) { map<string, int>::const_iterator cit = ops.find(hs); if (cit != ops.end()) { return true; } else { return false; } } void in2post(const vector<string>& inf, vector<string>& postf, map<string, int>& ops) { postf.clear(); stack<string> op_st; for (vector<string>::size_type i = 0; i != inf.size(); ++i) { if (!is_operator(inf[i], ops)) { postf.push_back(inf[i]); } else { if (inf[i] == "(") { op_st.push(inf[i]); } else if (inf[i] == ")") { while (!op_st.empty()) { if (op_st.top() == "(") { op_st.pop(); } else { postf.push_back(op_st.top()); op_st.pop(); } } } else // 若为其他运算符 { if (op_st.empty()) // 若为空栈,则直接入栈 { op_st.push(inf[i]); } else { if (ops[inf[i]] > ops[op_st.top()]) { // 如果当前操作符优先级高于站定操作符优先级 // 则直接入栈 op_st.push(inf[i]); } else { // 否则弹出栈中优先级大于等于当前操作符优先级 // 的操作符,并最后将当前操作符压栈 while (!op_st.empty() && ops[op_st.top()] >= ops[inf[i]] && op_st.top() != "(") { /* 等价于 && op_st.top != "(" if (op_st.top() == "(") { // 如果当前栈顶操作符为 "(" // 则终止操作,继续保留 "(" 的栈顶位置 break; } */ postf.push_back(op_st.top()); op_st.pop(); } op_st.push(inf[i]); } } } } } while (!op_st.empty()) { postf.push_back(op_st.top()); op_st.pop(); } } int main() { map<string, int> ops; init_op(ops); vector<string> inf, postf; while (1) { get_infix(inf); // show(inf); in2post(inf, postf, ops); show(postf); } system("PAUSE"); return 0; }
下面我们主要讲解一下中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式的数据结构与算法逻辑。
首先我们在进行后缀表达式转换为后缀表达式的过程中,利用了一种常见的数据结构:栈。我们利用栈先进后出的特性进行转换操作。该栈用于存储表达式中的操作符:
+、-、*、/、(、)
所以,我们将该栈称作为操作符栈。
借助于栈这种数据结构,我们的算法逻辑为:
1.顺序扫描整个中缀表达式;
2.中缀表达式的元素类型分为两类:操作数和操作符,如果当前元素为操作数,则将该
元素直接存入到后缀表达式中;
3.如果当前元素为操作符,分为以下几种情况进行讨论:
3.1 如果为“(”,则将其直接入栈;
3.2 如果为“)”,则将栈中的操作符弹栈,并将弹栈的操作符存入到后缀表达式中,
直至遇到“(”,将“(”从栈中弹出,并不将其存入到后缀表达式中(后缀表
达式是不需要“(”和“)”的);
3.3 如果是其他操作符(+、-、*、/),如果其优先级高于栈顶操作符的优先级,则
将其入栈,如果是小于或低于站定操作符优先级,则依次弹出栈顶操作符并存
入后缀表达式中,直至遇到一个站定优先级小于当前元素优先级时或者栈顶元
素为“(”为止,保持当前栈顶元素不变,并将当前元素入栈;
4.扫描完毕整个中缀表达式后,检测操作符栈,依次弹出其元素,并将其元素顺序存入
到后缀表达式中。
相关讨论
在进行中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式过程中,除了中缀表达式、后缀表达式外,还涉及了中间结果即:操作符栈。利用操作符栈存储在转换过程中涉及优先级先后顺序的操作符。操作符的优先级是根据 +、- 小于 *、/,运算顺序是先左后右,括号操作最优先的规则进行的。
中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式关键点主要有以下几点:
1.使用操作符栈
2.对于操作数直接进入后缀表达式
3.对于“(”,入栈
4.对于“)”,弹栈,直至“(”
5.对于其他操作符,弹栈并进入后缀表达式,直至小于当前操作符优先级或者“(”
6.扫描中缀表达式后,弹出栈中所有操作符并进入后缀表达式。