Linux系统命令“ls -R”的实现
一、基本概念
1、“ls -R”的意义
递归处理,将指定目录下的所有文件及子目录一并显示。
例: ls -R ./testdir1/
./testdir1/:
test1.c test1.txt test2.txt testdir2
./testdir1/testdir2:
test2.c test3.c test3.txt 到 test1.c 的链接
其中蓝色为目录文件,红色为软连接文件(具体颜色和vimrc配置有关)。
二、重要函数与结构体
1、目录操作函数
这里的 void rewinddir(DIR *dirp); 函数非常重要,在读取一遍目录后,如果遗漏rewinddir函数会导致指向文件的指针停留在该目录文件流的末尾,从而影响之后二次读取。
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <dirent.h> 3 4 DIR *opendir(const char *name); 5 DIR *fdopendir(int fd); 6 7 8 #include <dirent.h> 9 10 struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp); 11 12 struct dirent { 13 ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */ 14 off_t d_off; /* offset to the next dirent */ 15 unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */ 16 unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported by all file system types */ 17 char d_name[256]; /* filename */ 18 };
1 #include <sys/types.h>
2 #include <dirent.h>
3
4 void rewinddir(DIR *dirp);
2、获取文件信息
这里必须使用 int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); 函数,否则在处理链接文件时会将其链接的原文件作为处理对象,而不是其本身。
1 #include <sys/types.h>
2 #include <sys/stat.h>
3 #include <unistd.h>
4
5 int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
6 int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
7 int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf);
8
9 struct stat {
10 dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
11 ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
12 mode_t st_mode; /* protection */
13 nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
14 uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
15 gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
16 dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
17 off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
18 blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */
19 blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
20 time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
21 time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
22 time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
23 };
3、 文件类型及权限的判断
1 The following POSIX macros are defined to check the file type using the st_mode field:
2
3 S_ISREG(m) is it a regular file?
4 S_ISDIR(m) directory?
5 S_ISCHR(m) character device?
6 S_ISBLK(m) block device?
7 S_ISFIFO(m) FIFO (named pipe)?
8 S_ISLNK(m) symbolic link? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)
9 S_ISSOCK(m) socket? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)
三、执行结果及对比
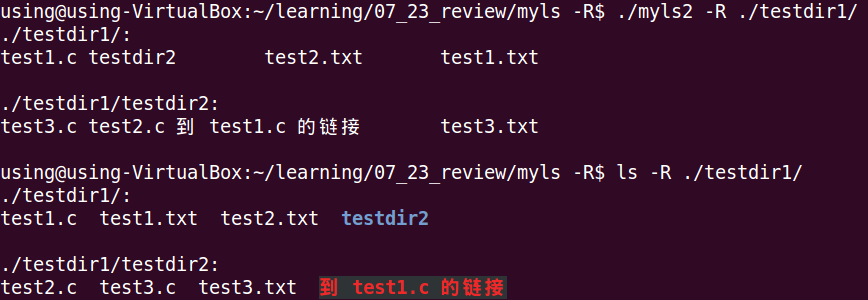
四、总结
总的来说,实现“ls -R”功能所涉及的特殊结构体很少,涉及知识面较窄,代码量少,但细节部分较多,需要一定的经验,经验不足的话调试起来会比较麻烦,总体难度一般。在实现功能的过程中有几点需要注意下:
1. 利用 lstat 函数读取文件信息,否则无法有效处理软连接文件;
2. 利用 rewinddir 函数重置指向文件流的指针,以便之后二次遍历目录;
3. 在读取文件流时,注意屏蔽当前目录(.)、上一级目录(..)和隐藏文件(.*)。
目前暂未实现制表功能,有兴趣的朋友可以尝试着通过读取终端显示宽度与最长文件名长度来加以设计。
五、实现代码
1、 myls2.h
1 #ifndef _MYLS2_H_ 2 #define _MYLS2_H_ 3 4 #include<stdio.h> 5 #include<stdlib.h> 6 #include<string.h> 7 #include<limits.h> 8 #include<unistd.h> 9 #include<dirent.h> 10 #include<sys/stat.h> 11 #include<sys/types.h> 12 #include<fcntl.h> 13 #include<time.h> 14 #include<pwd.h> 15 #include<grp.h> 16 17 // 处理错误 18 void error_printf(const char* ); 19 20 // 处理路径下的文件 21 void list_dir(const char* ); 22 23 // 所显示的文件信息 24 void display_dir(DIR* ); 25 26 #endif//_MYLS2_H_
2、myls2.c
1 #include "myls2.h" 2 3 // 处理错误 4 void error_printf(const char* funname) 5 { 6 perror(funname); 7 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 8 } 9 10 // 读取路径下的文件 11 void list_dir(const char* pathname) 12 { 13 char nextpath[PATH_MAX+1]; 14 15 DIR* ret_opendir = opendir(pathname); // 打开目录"pathname" 16 if(ret_opendir == NULL) 17 error_printf("opendir"); 18 19 printf("%s: ",pathname); // 显示pathname目录路径 20 display_dir(ret_opendir); // 显示pathname目录下所有非隐藏文件名称 21 22 struct dirent* ret_readdir = NULL; // 定义readdir函数返回的结构体变量 23 while(ret_readdir = readdir(ret_opendir)) // 判断是否读取到目录尾 24 { 25 char* filename = ret_readdir->d_name; // 获取文件名 26 27 int end = 0; // 优化显示路径(处理"./test/"与"./test") 28 while(pathname[end]) 29 end++; 30 strcpy(nextpath,pathname); 31 if(pathname[end-1] != '/') 32 strcat(nextpath,"/"); 33 strcat(nextpath,filename); 34 35 struct stat file_message = {}; // 定义stat函数返回的结构体变量 36 int ret_stat = lstat(nextpath, &file_message); // 获取文件信息 37 if(ret_stat == -1) // stat读取文件错误则输出提示信息 38 printf("%s error!", filename); 39 else if(S_ISDIR(file_message.st_mode) && filename[0]!='.') // 筛选"."、".."与隐藏文件 40 { 41 list_dir(nextpath); 42 } 43 } 44 closedir(ret_opendir); 45 } 46 47 // 打印所读取文件的信息 48 void display_dir(DIR* ret_opendir) 49 { 50 struct dirent* ret_readdir = NULL; // 定义readdir函数返回的结构体变量 51 while(ret_readdir = readdir(ret_opendir)) // 判断是否读取到目录尾 52 { 53 char* filename = ret_readdir->d_name; // 获取文件名 54 if(filename[0]!='.') // 不输出当前目录、上一级目录与隐藏文件 55 printf("%s ",ret_readdir->d_name); // 打印文件名 56 } 57 rewinddir(ret_opendir); // 非常重要,将文件流的指针拨回起始位置 58 puts(""); 59 puts(""); 60 }
3、main_myls2.c
1 #include "myls2.h" 2 3 4 int main(const char argc, const char** argv) 5 { 6 char path[PATH_MAX+1] = {}; 7 8 if(argc == 2 && !(strcmp(argv[1],"-R"))) // 判断命令格式 9 strcpy(path,"."); 10 else if(argc != 3) 11 { 12 printf("格式有误! "); 13 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 14 } 15 else 16 strcpy(path,argv[2]); 17 18 if(!(strcmp(argv[1],"-R"))) 19 { 20 struct stat file_message = {}; 21 int ret_stat = lstat(path, &file_message); 22 23 if(ret_stat == -1) 24 error_printf("stat"); 25 26 if(S_ISDIR(file_message.st_mode)) // 判断是否为目录 27 list_dir(path); 28 else 29 printf("It is not dir!"); 30 } 31 else 32 { 33 printf("error in main! "); 34 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 35 } 36 return 0; 37 }