Linux系统命令“rm -rf”的实现
一、基本概念
1、“rm -rf”的意义
-r或-R:递归处理,将指定目录下的所有文件与子目录一并处理;
-f:强制删除文件或目录;
由于rm命令只能删除空的目录,因此当我们需要删除一个非空目录时可以使用“rm -rf”命令,通过递归的方式先将该目录中的文件删除使其成为一个空的目录后再将其删除,从而达到删除一个非空目录的效果。
二、重要函数与结构体
1、目录操作函数
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <dirent.h> 3 4 DIR *opendir(const char *name); 5 DIR *fdopendir(int fd); 6 7 8 #include <dirent.h> 9 10 struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dirp); 11 12 struct dirent { 13 ino_t d_ino; /* inode number */ 14 off_t d_off; /* offset to the next dirent */ 15 unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this record */ 16 unsigned char d_type; /* type of file; not supported by all file system types */ 17 char d_name[256]; /* filename */ 18 };
2、 获取文件信息
这里必须使用 int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); 函数,否则在处理链接文件时会将其链接的原文件作为处理对象,而不是其本身。
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <sys/stat.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 5 int stat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); 6 int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf); 7 int lstat(const char *path, struct stat *buf); 8 9 struct stat { 10 dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */ 11 ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */ 12 mode_t st_mode; /* protection */ 13 nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */ 14 uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ 15 gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ 16 dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */ 17 off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */ 18 blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for file system I/O */ 19 blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */ 20 time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ 21 time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ 22 time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */ 23 };
3、文件类型及权限的判断
1 The following POSIX macros are defined to check the file type using the st_mode field:
2
3 S_ISREG(m) is it a regular file?
4 S_ISDIR(m) directory?
5 S_ISCHR(m) character device?
6 S_ISBLK(m) block device?
7 S_ISFIFO(m) FIFO (named pipe)?
8 S_ISLNK(m) symbolic link? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)
9 S_ISSOCK(m) socket? (Not in POSIX.1-1996.)
4、当前用户ID
1 #include <sys/types.h> 2 #include <pwd.h> 3 4 struct passwd *getpwnam(const char *name); 5 struct passwd *getpwuid(uid_t uid); 6 7 8 The passwd structure is defined in <pwd.h> as follows: 9 10 struct passwd { 11 char *pw_name; /* username */ 12 char *pw_passwd; /* user password */ 13 uid_t pw_uid; /* user ID */ 14 gid_t pw_gid; /* group ID */ 15 char *pw_gecos; /* user information */ 16 char *pw_dir; /* home directory */ 17 char *pw_shell; /* shell program */ 18 };
5、 删除文件函数
该函数比较危险,测试代码时建议先注释,通过printf函数查看删除文件路径,确认后再使用。
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int remove(const char *pathname); 4 5 On success, zero is returned. On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
三、执行结果及对比
1、 执行前
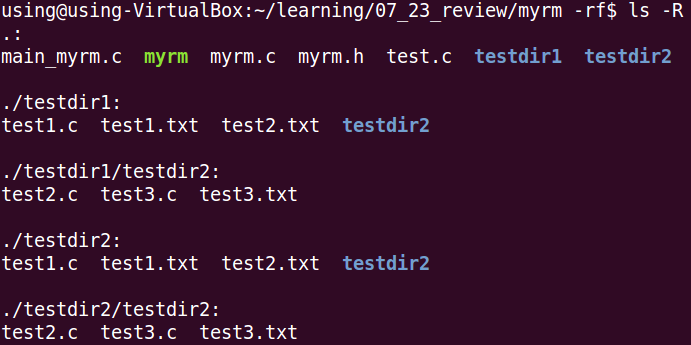
2、执行效果

3、 执行后
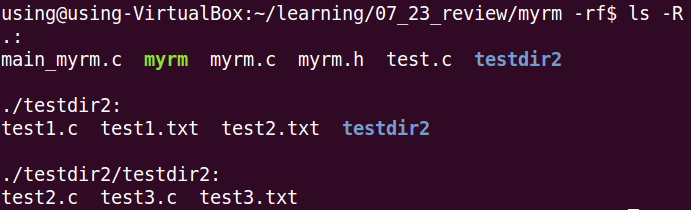
四、总结
总的来说,实现“rm -rf”功能所涉及的知识面不广,代码有较多的重复片段,可以在实现“ls -R”功能的基础上进行,但程序细节部分较多,而且程序测试的风险极高,总体难度一般,最重要的是要做好安全备份工作。细节部分具体可以参考程序中的注释,这里主要说明下前期的安全准备工作:
1. 进行Linux系统的备份,Ubuntu虚拟机系统可以通过Virtual box进行系统备份;
2. 在进入删除函数之前加一道“确认”流程,以免误操作;
3. 将所有remove函数注释,先输出所删除文件路径,所有路径确认无误后再取消注释。
五、实现代码
1、 myrm.h
1 #ifndef _MYRM_H_ 2 #define _MYRM_H_ 3 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 #include <stdlib.h> 6 #include <string.h> 7 #include <limits.h> 8 #include <unistd.h> 9 #include <dirent.h> 10 #include <sys/stat.h> 11 #include <sys/types.h> 12 #include <fcntl.h> 13 #include <time.h> 14 #include <pwd.h> 15 #include <grp.h> 16 #include <stdbool.h> 17 18 // 该头文件包含了自定义函数getch(),其功能是:接收单个键盘按键值,无需结束标志enter 19 #include "getch.h" 20 21 // 处理错误 22 void error_printf(const char* ); 23 24 // 删除路径下的文件 25 void rm_dir(const char* ); 26 27 // 判断目录下文件的拥有者是否是程序调用者 28 bool ismine_dir(const char* ); 29 bool ismine(const char* ); 30 31 #endif//_MYRM_H_
2、myrm.c
1 #include "myrm.h" 2 3 4 int main(const char argc, const char** argv) 5 { 6 char path[PATH_MAX+1] = {}; 7 8 if(argc == 2 && !(strcmp(argv[1],"-rf"))) // 判断命令格式 9 strcpy(path,"."); 10 else if(argc != 3) 11 { 12 printf("格式有误! "); 13 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 14 } 15 else 16 strcpy(path,argv[2]); 17 18 if(!(strcmp(argv[1],"-rf"))) 19 { 20 struct stat file_message = {}; 21 int ret_stat = lstat(path, &file_message); 22 23 if(ret_stat == -1) 24 error_printf("stat"); 25 26 if(S_ISDIR(file_message.st_mode)) // 判断是否为目录 27 { 28 printf("路径[%s]下的目录将会被删除,按‘enter’确认,其他任意键取消 ",path); // 防止误操作 29 if(10 == getch()) // 自定义函数getch(),其功能是:接收单个键盘按键值,无需结束标志enter 30 rm_dir(path); 31 else 32 return 0; 33 } 34 else 35 printf("It is not dir!"); 36 } 37 else 38 { 39 printf("error in main! "); 40 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 41 } 42 return 0; 43 }
3、main_myrm.c
1 #include "myrm.h" 2 3 // 处理错误 4 void error_printf(const char* funname) 5 { 6 perror(funname); 7 exit(EXIT_FAILURE); 8 } 9 10 // 删除路径下的文件 11 void rm_dir(const char* pathname) 12 { 13 if(!ismine_dir(pathname)) // 判断该路径目录中包含的文件是否全部属于程序调用者 14 { 15 printf("权限不足,无法删除!"); 16 return; 17 } 18 19 char nextpath[PATH_MAX+1]; 20 21 DIR* ret_opendir = opendir(pathname); // 打开目录"pathname" 22 if(ret_opendir == NULL) 23 error_printf("opendir"); 24 25 struct dirent* ret_readdir = NULL; // 定义readdir函数返回的结构体变量 26 while(ret_readdir = readdir(ret_opendir)) // 判断是否读取到目录尾 27 { 28 char* filename = ret_readdir->d_name; // 获取文件名 29 30 int end = 0; // 优化路径 (其实无论几个“/”叠加都不会影响路径) 31 while(pathname[end]) 32 end++; 33 strcpy(nextpath,pathname); 34 if(pathname[end-1] != '/') 35 strcat(nextpath,"/"); 36 strcat(nextpath,filename); 37 38 struct stat file_message = {}; // 定义stat函数返回的结构体变量 39 int ret_stat = lstat(nextpath, &file_message); // 获取文件信息 40 if(ret_stat == -1) // stat读取文件错误则输出提示信息 41 { 42 printf("%s error!", filename); 43 } 44 // 注意屏蔽当前目录和上一级目录,但不能用filename[0]='.'来判断,这样会导致无法删除隐藏文件,从而导致目录文件删除失败 45 else if(S_ISDIR(file_message.st_mode) && strcmp(filename,".") && strcmp(filename,"..")) 46 { 47 rm_dir(nextpath); 48 printf("delete dir :%s ",nextpath); 49 remove(nextpath); 50 } 51 else if(strcmp(filename,".") && strcmp(filename,"..")) // 同上 52 { 53 struct passwd* pwd = getpwuid(file_message.st_uid); 54 55 if(pwd->pw_uid == getuid()) // 再次检查,双重保险 56 { 57 printf("delete file:%s ",nextpath); 58 remove(nextpath); 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 closedir(ret_opendir); 63 printf("delete dir :%s ",pathname); 64 remove(pathname); // 删除完目录中的文件后将自身删除 65 } 66 67 bool ismine_dir(const char* pathname) 68 { 69 char nextpath[PATH_MAX+1]; 70 71 if(!ismine(pathname)) 72 return false; 73 74 DIR* ret_opendir = opendir(pathname); // 打开目录"pathname" 75 if(ret_opendir == NULL) 76 error_printf("opendir"); 77 78 struct dirent* ret_readdir = NULL; // 定义readdir函数返回的结构体变量 79 while(ret_readdir = readdir(ret_opendir)) // 判断是否读取到目录尾 80 { 81 char* filename = ret_readdir->d_name; // 获取文件名 82 83 int end = 0; // 优化路径 84 while(pathname[end]) 85 end++; 86 strcpy(nextpath,pathname); 87 if(pathname[end-1] != '/') 88 strcat(nextpath,"/"); 89 strcat(nextpath,filename); 90 91 struct stat file_message = {}; // 定义stat函数返回的结构体变量 92 int ret_stat = lstat(nextpath, &file_message); // 获取文件信息 93 if(ret_stat == -1) // stat读取文件错误则输出提示信息 94 { 95 printf("%s error!", filename); 96 } 97 else if(S_ISDIR(file_message.st_mode) && strcmp(filename,".") && strcmp(filename,"..")) 98 { 99 if(!ismine_dir(nextpath)) 100 return false; 101 } 102 else if(strcmp(filename,".") && strcmp(filename,"..")) 103 { 104 if(!ismine(nextpath)) 105 return false; 106 } 107 } 108 closedir(ret_opendir); 109 return true; 110 } 111 112 bool ismine(const char* pathname) 113 { 114 struct stat file_message = {}; // 定义stat函数返回的结构体变量 115 int ret_stat = lstat(pathname, &file_message); // 获取文件信息 116 if(ret_stat == -1) // stat读取文件错误则输出提示信息 117 { 118 printf("stat error!"); 119 } 120 struct passwd* pwd = getpwuid(file_message.st_uid); 121 if(pwd->pw_uid == getuid()) // 判断该文件是否属于程序调用者 122 return true; 123 else 124 return false; 125 }