State状态模式(行为型)
作用
状态模式可以看作是策略模式的动态版本。当对象状态发生变化时,它的行为也装换成另一组操作了。通过在一个体系中切换对象的子类实现状态变化和行为变换。
Role
the State pattern, can be seen as a dynamic version of the Strategy pattern. When the state inside an object changes, it can change its behavior by switching to a set of different operations. This is achieved by an object variable changing its subclass, within a hierarchy.
设计
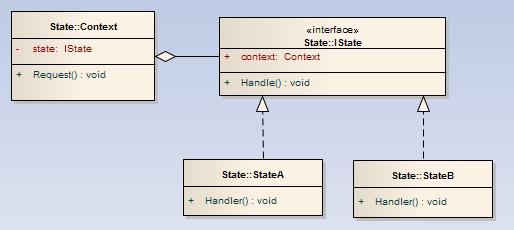
Context,一个含有状态实例的的类,具有当前的上下文信息和客户端需要的接口
IState,状态接口,
StateA and StateB,实现了状态接口的各个状态类,每个状态类都有自己独特的行为
举例
Context, 航空公司会员的积分管理
Request,会员的服务请求,如积分换里程,到VIP休息室,机票兑换积分等
IState,各级会员所能享受的服务
StateA,StateB,各级会员如金卡可以进入VIP,银卡可以积分换里程等等
Handler,各状态下的活动
实现
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace State
{
interface IState
{
int MoveUp(Context context);
int MoveDown(Context context);
}
// State 1
class NormalState : IState
{
public int MoveUp(Context context)
{
context.Counter+=2;
return context.Counter;
}
public int MoveDown(Context context)
{
if (context.Counter < Context.limit)
{
context.State = new FastState();
Console.Write("|| ");
}
context.Counter-=2;
return context.Counter;
}
}
// State 2
class FastState : IState
{
public int MoveUp(Context context)
{
context.Counter+=5;
return context.Counter;
}
public int MoveDown(Context context)
{
if (context.Counter < Context.limit)
{
context.State = new NormalState();
Console.Write("||");
}
context.Counter-=5;
return context.Counter;
}
}
// Context
class Context
{
public const int limit = 10;
public IState State {get; set; }
public int Counter = limit;
public int Request(int n)
{
if (n==2)
return State.MoveUp(this);
else
return State.MoveDown(this);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Context context = new Context();
context.State = new NormalState();
Random r = new Random(37);
for (int i = 5; i<=25; i++)
{
int command = r.Next(3);
Console.Write(context.Request(command)+" ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
/*
Random r = new Random(37);
Random r1 = new Random(37);
Random r2 = new Random(32);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
Console.Write(r.Next(5) + " " + r1.Next(5) + " " + r2.Next(5) + " /n");
}
Console.ReadLine();
*/
}
}
}
/* Output
8 10 8 || 6 11 16 11 6 ||1 3 || 1 ||-4 || -6 -1 4 ||-1 || -3 2 7 ||2 4
*/
应用场景
如果你的对象:
在运行时会根据上下文的信息改变自己的行为
在顺着对象的运行,它会变得逐渐复杂,而且带有很多条件分支
你计划:
动态的变换处理对象的请求
灵活的分配请求的处理
Use the State pattern when…
You have objects that:
• Will change their behavior at runtime, based on some context
• Are becoming complex, with many conditional branches
You want to:
• Vary the set of handlers for an object request dynamically
• Retain flexibility in assigning requests to handlers
总结
State模式的目的是能够无需客户代码的干预而让对象自己动态的选择某些算法。它非常像策略模式的动态版。使用State模式最好先定义一个缺省状态。GOF《设计模式》中给状态模式下的定义为:允许一个对象在其内部状态改变时改变它的行为。这个对象在运行时可以修改了它所在的类的状态。
策略与状态的对比:Brandon Goldfedder在《模式的乐趣》里是怎么说的:“strategy模式在结构上与state模式非常相似,但是在概念上,他们的目的差异非常大。区分这两个模式的关键是看行为是由状态驱动还是由一组算法驱动,这条规则似乎有点随意,但是在判断时还是需要考虑它。通常,State模式的“状态”是在对象内部的,Strategy模式的“策略”可以在对象外部,不过这也不是一条严格、可靠的规则。”两个模式的划分,就在于使用的目的是不同的——策略模式用来处理算法变化,而状态模式则是处理状态变化。策略模式中,算法是否变化完全是由客户程序来决定的,而且往往一次只能选择一种算法,不存在算法中途发生变化的情况。从《深入浅出策略模式》中的例子可以很好的看出。而状态模式在它的生命周期中存在着状态的转变和行为得更改,而且状态变化是一个线性的整体;对于客户程序来言,这种状态变化往往是透明的。