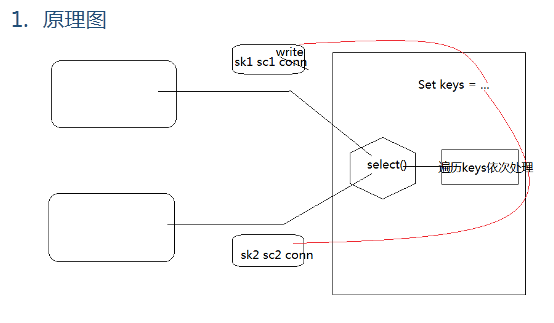
1. 目标 利用Selector+channel+Buffer实现 少量线程处理多个客户端请求 2. 客户端 package cn.tedu.nio.selector; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; public class SocketChannelDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //0.创建选择器 Selector selc = Selector.open(); //1.创建SocketChannel SocketChannel sc = SocketChannel.open(); //2.设定非阻塞模式 sc.configureBlocking(false); //3.连接服务端 sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 44444)); sc.register(selc, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); //4.通过选择器实行选择操作 while(true){ selc.select();//选择器尝试选择就绪的键 选不到就阻塞 选择到就返回就绪的键的数量 //5.得到并遍历就绪的键们 Set<SelectionKey> keys = selc.selectedKeys(); Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ //6.得到每一个就绪的键 SelectionKey key = it.next(); //7.获取就绪的键 对应的 操作 和 通道 if(key.isAcceptable()){ }else if(key.isConnectable()){ //--是通道的Connect操作 //--获取通道 SocketChannel scx = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); //--完成连接 if(!scx.isConnected()){ while(!scx.finishConnect()){}; } //--将通道再次注册到selc中 关注WRITE操作 scx.register(selc, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE); }else if(key.isReadable()){ }else if(key.isWritable()){ //--发现是Write操作就绪 //--获取通道 SocketChannel scx = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); //--写出数据 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello nio~ hello java~".getBytes()); while(buf.hasRemaining()){ scx.write(buf); } //--取消掉当前通道 在选择器中的注册 放置重复写出 key.cancel(); }else{ throw new RuntimeException("未知的键,见了鬼了~"); } //8.移除就绪键 it.remove(); } } } } 3. 服务端 package cn.tedu.nio.selector; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey; import java.nio.channels.Selector; import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel; import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; public class ServerSocketDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //0.创建选择器 Selector selc = Selector.open(); //1.创建代表服务器的ServerSocketChannel对象 ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2.设置为非阻塞模式 ssc.configureBlocking(false); //3.设置监听的端口 ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(44444)); //4.将ssc注册到选择器中关注ACCEPT操作 ssc.register(selc, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //5.通过选择器选择就绪的键 while(true){ selc.select();//尝试到注册的键集中来寻找就绪的键 如果一个就绪的键都找不到 就进入阻塞 直到找到就绪的键 返回就绪的键的个数 //6.获取就绪的键的集合 Set<SelectionKey> keys = selc.selectedKeys(); //7.遍历处理就绪的键 代表的操作 Iterator<SelectionKey> it = keys.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()){ //--获取到就绪的键 根据键代表的操作的不同 来进行不同处理 SelectionKey key = it.next(); if(key.isAcceptable()){ //--发现了Accept操作 //--获取通道 ServerSocketChannel sscx = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); //--完成Accept操作 SocketChannel sc = sscx.accept(); //--在sc上注册读数据的操作 sc.configureBlocking(false); sc.register(selc, SelectionKey.OP_READ); }else if(key.isConnectable()){ }else if(key.isWritable()){ }else if(key.isReadable()){ //--发现了Read操作 //--获取就绪的通道 SocketChannel scx = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); //--完成读取数据的操作 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); while(buf.hasRemaining()){ scx.read(buf); } String msg = new String(buf.array()); System.out.println("[收到来自客户端的消息]:"+msg); }else{ throw new RuntimeException("未知的键,见了鬼了~"); } //8.移除处理完的键 it.remove(); } } } }