学习了几天Linux下ftp和ssh的搭建和使用,故记录一下。学习ftp和ssh的主要目的是为了连接远程主机,并且进行文件传输。废话不多说,直接开讲!
ftp服务器
1. 环境搭建
本人的系统是Archlinux,我是基于vsftpd来搭建的,首先需要安装它: pacman -S vsftpd
接着对其配置文件进行编辑,打开/etc/vsftpd.conf(也可能在/etc/vsftdp/.vsftpd.conf)
以下是我的配置文件内容:
# Example config file /etc/vsftpd.conf # # The default compiled in settings are fairly paranoid. This sample file # loosens things up a bit, to make the ftp daemon more usable. # Please see vsftpd.conf.5 for all compiled in defaults. # # READ THIS: This example file is NOT an exhaustive list of vsftpd options. # Please read the vsftpd.conf.5 manual page to get a full idea of vsftpd's # capabilities. # # Allow anonymous FTP? (Beware - allowed by default if you comment this out). anonymous_enable=YES # # Uncomment this to allow local users to log in. #local_enable=YES # # Uncomment this to enable any form of FTP write command. write_enable=YES # # Default umask for local users is 077. You may wish to change this to 022, # if your users expect that (022 is used by most other ftpd's) #local_umask=022 # # Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. This only # has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. Also, you will # obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user. anon_upload_enable=YES anon_other_write_enable=YES # # Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create # new directories. #anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES # # Activate directory messages - messages given to remote users when they # go into a certain directory. #dirmessage_enable=YES # # Activate logging of uploads/downloads. #xferlog_enable=YES # # Make sure PORT transfer connections originate from port 20 (ftp-data). connect_from_port_20=YES # # If you want, you can arrange for uploaded anonymous files to be owned by # a different user. Note! Using "root" for uploaded files is not # recommended! #chown_uploads=YES #chown_username=whoever # # You may override where the log file goes if you like. The default is shown # below. #xferlog_file=/var/log/vsftpd.log # # If you want, you can have your log file in standard ftpd xferlog format. # Note that the default log file location is /var/log/xferlog in this case. #xferlog_std_format=YES # # You may change the default value for timing out an idle session. #idle_session_timeout=600 # # You may change the default value for timing out a data connection. #data_connection_timeout=120 # # It is recommended that you define on your system a unique user which the # ftp server can use as a totally isolated and unprivileged user. #nopriv_user=ftpsecure # # Enable this and the server will recognise asynchronous ABOR requests. Not # recommended for security (the code is non-trivial). Not enabling it, # however, may confuse older FTP clients. #async_abor_enable=YES # # By default the server will pretend to allow ASCII mode but in fact ignore # the request. Turn on the below options to have the server actually do ASCII # mangling on files when in ASCII mode. # Beware that on some FTP servers, ASCII support allows a denial of service # attack (DoS) via the command "SIZE /big/file" in ASCII mode. vsftpd # predicted this attack and has always been safe, reporting the size of the # raw file. # ASCII mangling is a horrible feature of the protocol. #ascii_upload_enable=YES #ascii_download_enable=YES # # You may fully customise the login banner string: #ftpd_banner=Welcome to blah FTP service. # # You may specify a file of disallowed anonymous e-mail addresses. Apparently # useful for combatting certain DoS attacks. #deny_email_enable=YES # (default follows) #banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd.banned_emails # # You may specify an explicit list of local users to chroot() to their home # directory. If chroot_local_user is YES, then this list becomes a list of # users to NOT chroot(). # (Warning! chroot'ing can be very dangerous. If using chroot, make sure that # the user does not have write access to the top level directory within the # chroot) #chroot_local_user=YES #chroot_list_enable=YES # (default follows) #chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list # # You may activate the "-R" option to the builtin ls. This is disabled by # default to avoid remote users being able to cause excessive I/O on large # sites. However, some broken FTP clients such as "ncftp" and "mirror" assume # the presence of the "-R" option, so there is a strong case for enabling it. #ls_recurse_enable=YES # # When "listen" directive is enabled, vsftpd runs in standalone mode and # listens on IPv4 sockets. This directive cannot be used in conjunction # with the listen_ipv6 directive. listen=YES # # This directive enables listening on IPv6 sockets. To listen on IPv4 and IPv6 # sockets, you must run two copies of vsftpd with two configuration files. # Make sure, that one of the listen options is commented !! #listen_ipv6=YES anon_root=/var/ftp
在以上的配置文件中,我们允许匿名用户登录,并且其有删除和上传的权限,不过这些操作仅限于在权限为777的目录下进行。我们配置匿名用户默认进入的目录为/var/ftp,此外,我们要创建一个目录upload权限为777,匿名用户可以在其中任意的操作文件。这些操作如下(本机中):
mkdir -p /var/upload
chmod 777 /var/ftp/upload
至此,我们的环境搭建完成。
2. 使用示例
首先,配置好ftp服务器之后,需要重启,Archlinux下是
system restart vsftpd
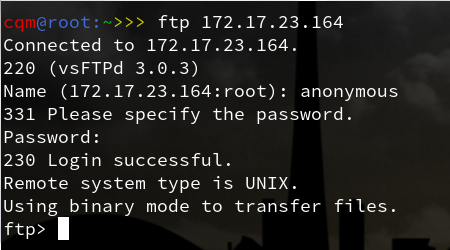
其中,172.17.23.164是要连接的ftp服务器的IP地址
接着我们匿名登录,即用户名为anonymous,密码为空即可
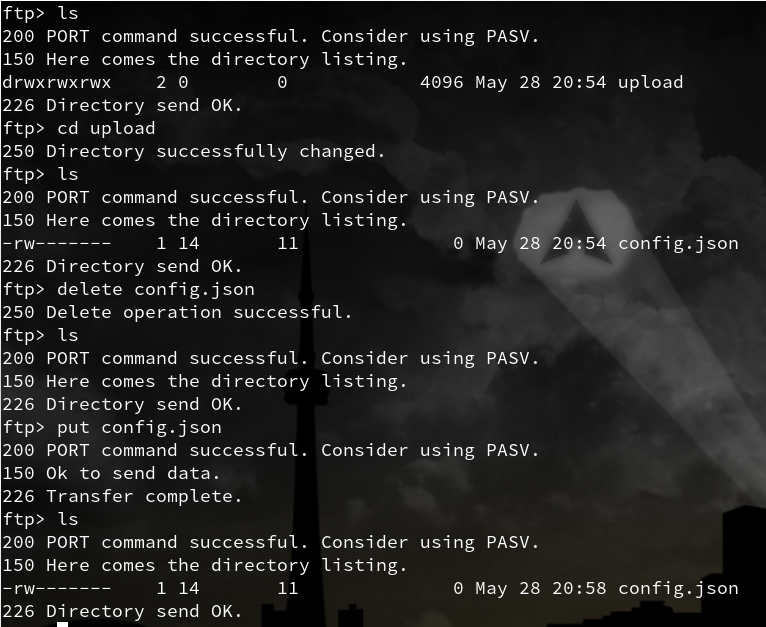
这里我们用到了一些基本的命令,ls,cd等,put、get为上传/下载命令,这些百度都能轻易得知。
上图可知,我们能够在upload目录中随意操作!
ssh服务器
1. 环境搭配
安装openssh,Archlinux下直接:
pacman -S openssh
它的配置文件为/etc/ssh/sshd_config,配置后如下:
# $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.101 2017/03/14 07:19:07 djm Exp $ # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See # sshd_config(5) for more information. # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where # possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options override the # default value. Port 22 #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress :: #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key # Ciphers and keying #RekeyLimit default none # Logging #SyslogFacility AUTH #LogLevel INFO # Authentication: #LoginGraceTime 2m PermitRootLogin prohibit-password #StrictModes yes #MaxAuthTries 6 #MaxSessions 10 #PubkeyAuthentication yes # The default is to check both .ssh/authorized_keys and .ssh/authorized_keys2 # but this is overridden so installations will only check .ssh/authorized_keys AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #AuthorizedPrincipalsFile none #AuthorizedKeysCommand none #AuthorizedKeysCommandUser nobody # For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts #HostbasedAuthentication no # Change to yes if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for # HostbasedAuthentication #IgnoreUserKnownHosts no # Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files #IgnoreRhosts yes # To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here! #PasswordAuthentication yes #PermitEmptyPasswords no # Change to no to disable s/key passwords ChallengeResponseAuthentication no # Kerberos options #KerberosAuthentication no #KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes #KerberosTicketCleanup yes #KerberosGetAFSToken no # GSSAPI options #GSSAPIAuthentication no #GSSAPICleanupCredentials yes # Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing, # and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will # be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and # PasswordAuthentication. Depending on your PAM configuration, # PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass # the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password". # If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without # PAM authentication, then enable this but set PasswordAuthentication # and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'. UsePAM yes #AllowAgentForwarding yes #AllowTcpForwarding yes #GatewayPorts no #X11Forwarding no #X11DisplayOffset 10 #X11UseLocalhost yes #PermitTTY yes PrintMotd no # pam does that #PrintLastLog yes #TCPKeepAlive yes #UseLogin no #PermitUserEnvironment no #Compression delayed #ClientAliveInterval 0 #ClientAliveCountMax 3 #UseDNS no #PidFile /run/sshd.pid #MaxStartups 10:30:100 #PermitTunnel no #ChrootDirectory none #VersionAddendum none # no default banner path #Banner none # override default of no subsystems Subsystem sftp /usr/lib/ssh/sftp-server # Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis #Match User anoncvs # X11Forwarding no # AllowTcpForwarding no # PermitTTY no # ForceCommand cvs server
这里需要注意的是:
1. 打开port端口,将Port 22注释去除
2. 设置允许以root登录,将PermitRootLogin prohibit-password的注释去除
至此,最简单的配置完成了!
2. 密钥
一般而言,如果知道远程服务器的ip地址(假设是1.1.1.1)以及其某个用户(假设是root)的密码为000000,则可以直接:
ssh root@1.1.1.1
接着根据提示输入密码即可
但是每次都要输入密码未免太烦,于是可以采用ssh密钥机制
将ssh密钥理解为指纹,客户端的指纹在服务器端留下备份,访问的时候服务器查看客户端指纹,发现存在列表中,就可以免去登录了。
要做到这些,首先需要生成客户端自己的指纹:
ssh-keygen -t rsa
一路回车,会看到在.ssh目录下生成了密钥id_rsa和公钥id_rsa.pub,接着需要将公钥上传至服务器主机.ssh下authorized_keys中即可
一种做法是:
scp .ssh/id_rsa.pub root@1.1.1.1:/root/
这个命令将公钥上传到了服务器的/root目录下,接着进入服务器(输密码):
echo id_rsa.pub >> .ssh/authorized_keys