
static void Main1() { //通过委托开启一个线程 Action a = Test1; a.BeginInvoke(null, null);//开启一个新的线程去执行a所引用的方法 Console.WriteLine("main");//启动方法之后,先输出了main,再输出test Console.ReadKey(); } static void Test1() { Console.WriteLine("test"); }

static void Main2() { //通过委托开启一个线程 Action<string, int> a = Test2; a.BeginInvoke("vichin", 27, null, null);//开启一个新的线程去执行a所引用的方法,"vichin"和27是调用Test2时,所需要传入的参数。 Console.WriteLine("main");//启动方法之后,先输出了main,再输出test Console.ReadKey(); } static void Test2(string name, int age) { Console.WriteLine("My name is {0}。My age is {1}", name, age); }

static void Main3()
{
//通过委托开启一个线程
Func<string, int, string> a = Test3;
//声明一个变量iar来取得当前线程的状态。
//BeginInvoke参数中:
//"vichin"和27是调用Test3时所需要传递的参数。
//第三个参数是一个委托,表示当a线程结束的时候会调用该方法。
//第四个参数是用来传递数据给回调函数的。该数据可以是任何类型的。(只要是继承了Object了就行。该demo中是将一个委托对象传递了过去。接收时需要作类型转换。)
IAsyncResult iar = a.BeginInvoke("vichin", 27, null, null);//开启一个新的线程去执行a所引用的方法
#region 使用一个死循环来检测副线程是否执行完毕
//while (!iar.IsCompleted)
//{
// Console.WriteLine("副线程还没有执行完毕");
//}
//string result = a.EndInvoke(iar);
//Console.WriteLine(result);
#endregion
#region 使用等待句柄来检测副线程是否执行完毕。因为在a.BeginInvoke方法中传递了回调函数,所以下面这段代码就没有用了。
//若WaitOne返回的是true,则表示副线程已经运行结束,否则表示没有结束。
bool isDone = iar.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(5000);//设置一个等待时间,检测是否超时。
if (isDone)
{
string result = a.EndInvoke(iar);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
#endregion
Console.WriteLine("main");//启动方法之后,先输出了main,再输出test
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Test3(string name, int age)
{
return "My name is " + name + ", My age is " + age.ToString();
}
//使用回调函数
static void Main3()
{
//通过委托开启一个线程
Func<string, int, string> a = Test3;
//声明一个变量iar来取得当前线程的状态。
//BeginInvoke参数中:
//"vichin"和27是调用Test3时所需要传递的参数。
//第三个参数是一个委托,表示当a线程结束的时候会调用该方法。
//第四个参数是用来传递数据给回调函数的。该数据可以是任何类型的。(只要是继承了Object了就行。该demo中是将一个委托对象传递了过去。接收时需要作类型转换。)
IAsyncResult iar = a.BeginInvoke("vichin", 27, CallBackFunction, a);//开启一个新的线程去执行a所引用的方法
Console.WriteLine("main");//启动方法之后,先输出了main,再输出test
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Test3(string name, int age)
{
return "My name is " + name + ", My age is " + age.ToString();
}
/// <summary>
/// 副线程的回调函数
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ar">副线调用该方法时,会自动传递IAsyncResult类型的参数</param>
static void CallBackFunction(IAsyncResult iar)
{
Func<string, int, string> a = iar.AsyncState as Func<string, int, string>;
string result = a.EndInvoke(iar);
Console.WriteLine("在回调函数中取得结果,结果是:" + result);
Console.WriteLine("副线程运行结束,调用了该回调函数。");
}
//使用委托(lambda表达式)
static void Main3()
{
//通过委托开启一个线程
Func<string, int, string> a = Test3;
//声明一个变量iar来取得当前线程的状态。
//BeginInvoke参数中:
//"vichin"和27是调用Test3时所需要传递的参数。
//第三个参数是一个委托,表示当a线程结束的时候会调用该方法。
//第四个参数是用来传递数据给回调函数的。该数据可以是任何类型的。(只要是继承了Object了就行。该demo中是将一个委托对象传递了过去。接收时需要作类型转换。)
a.BeginInvoke("vichin", 27, iar =>
{
string result = a.EndInvoke(iar);
Console.WriteLine("副线程执行完毕,结果是:" + result+"。 本段代码是在lambda表达式中执行的!");
}, null);//开启一个新的线程去执行a所引用的方法
Console.WriteLine("main");//启动方法之后,先输出了main,再输出test
Console.ReadKey();
}
static string Test3(string name, int age)
{
return "My name is " + name + ", My age is " + age.ToString();
}
委托:

delegate int MyDel();//声明委托 委托返回值是int类型,委托的类型的MyDel类型的 class MyClass { int valInt = 5; public int Add2() { valInt += 2; return valInt; } public int Add3() { valInt += 3; return valInt; } }

MyClass mc = new MyClass(); MyDel md = mc.Add2;//创建并初始化委托 md += mc.Add3;//增加方法 md();//一次性会调用两个方法 md -= mc.Add2;//减掉一个方法

delegate int MyDel(int para); public partial class A : WebPageBase { protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { MyDel del = delegate(int x) { return x + 1; };//使用匿名方法声明委托 MyDel le1 = (int x) => { return x + 1; };//lambda表达式 MyDel le2 = (x) => { return x + 1; };//lambda表达式 MyDel le3 = x => { return x + 1; };//lambda表达式 MyDel le4 = x => x + 1; //lambda表达式 } }
委托的实际应用(在窗体之间,传递方法:有点调用一个公共方法的意思。)

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace FormDelegate { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { deliver dl = new deliver(UpdateValue); //dl += UpdateValue; Form2 form2 = new Form2(textBox1.Text.Trim(), UpdateValue);//调用窗体2的时候,会将窗体1内的文本值和UpdateValue方法传递给了Form2 form2.Show(); } void UpdateValue(string val) { this.textBox1.Text = val; } public delegate void deliver(string val); } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data; using System.Drawing; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace FormDelegate { public partial class Form2 : Form { public Form2() { InitializeComponent(); } public Form2(string n, FormDelegate.Form1.deliver updateVale) : this()//这里创建一个新的构造函数,让它继承默认的构造函数。若是不继承,那么InitializeComponent方法就没有执行,会导致控件没被初始化 { this.textBox1.Text= n; this.dlv = updateVale; } private FormDelegate.Form1.deliver dlv;//声明一个deliver类型的变量,用于接收form1传递过来的方法。 private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.dlv(textBox1.Text.Trim());//将Form2内的文本框中的值,更新到form1的文本框中。 this.Close(); } } }

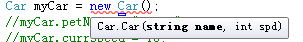
构造函数:

class Car { //car 的状态 public string petName; public int currSpeed; //构造函数是类的特殊方法。构造函数永远都不会有返回值,并且它的名字总是和需要构造的类的名字相同。 public Car(string name, int spd) { petName = name; currSpeed = spd; } //Car的功能 public void PrintState() { Console.WriteLine("{0} is going {1} MPH.", petName, currSpeed); } public void SpeedUp(int delta) { currSpeed += delta; } }
使用了构造函数之后,就可以在创建对象的时候,直接为对象的属性赋值了(对象初始化语法声明变量)
ctor+tab+tab:快速生成构造函数

public Student(string name,int age,int height,string sid) : base(name,age,height){ this.Sid=sid; }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Web; namespace WebApplication1 { public class Person { public int Age { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Height { get; set; } public string Email { get; set; } public Person(string name, int age, int height, string email) { this.Name = name; this.Age = age; this.Height = height; this.Email = email; } /// <summary> /// 传入name和age /// </summary> /// <param name="name"></param> /// <param name="age"></param> public Person(string name, int age) : this(name, age, 0, string.Empty) { } /// <summary> /// 创建对象时传入name和email这两个参数 /// </summary> /// <param name="name"></param> /// <param name="email"></param> public Person(string name, string email) : this(name, 0, 0, email) { } } }
每一个类都有一个默认的构造函数(无参数的),每个类的构造函数是不能被继承的
封装

class Employee { string empName; int empID; float currPay; public string Name { get { return empName; } set { if (value.Length > 15) Console.WriteLine("Error! Name must be less than 16 characters!"); else empName = value; } } public int ID { get; set; } } 封装的目的在于不让外界访问到对象的内部属性(在这里就是 empName、empID和currPay)。外界可以访问到的是Name和ID。在调用的地方给Name赋值的时候,可以让Employee自己内部 对这个值进行检查(这里让我感觉,empName变量的存在就是为Name服务的)。set语句块负责提供检查逻辑。 如果不需要检查值的话(打包类的业务规则),可以直接使用自动属性{get;set;},而且,不需要创建额外字段。
prop + tab+tab :快速构造自动属性
propfull +tab+tab:快速构造 字段+属性
多态:把不同的子类对象,都当作父类来看待。可以屏蔽不同子类对象之间的差异,写出通用的代码,做出通用的编程以适应需求的不断变化。
virtual override sealed

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { public class Person { public int Age { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public Person(string name, int age) { this.Age = age; this.Name = name; } public virtual void SayHi() { Console.WriteLine("NI HAO"); } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { public class Chinese : Person { public string Sex { get; set; } public Chinese(string name, string sex, int age) : base(name, age) { this.Sex = sex; } public override void SayHi() { Console.WriteLine("你好!"); } } }

1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 6 namespace ConsoleApplication1 7 { 8 public class American : Person 9 { 10 public string Sex { get; set; } 11 public American(string name, string sex, int age) 12 : base(name, age) 13 { 14 this.Sex = sex; 15 } 16 public override void SayHi() 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine("Hello!"); 19 } 20 } 21 }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Person[] psn = new Person[2]; psn[0] = new Chinese("陈伟", "男", 25); psn[1] = new American("vichin", "M", 25); for (int i = 0; i < psn.Length; i++) { Console.WriteLine(psn[i].Name); Console.WriteLine(psn[i].Age); psn[i].SayHi(); //第一次是: //陈伟 //25 //你好! //第二次是: //vichin //25 //Hello! } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
如果不想让孙子类改变儿子类中的那些重写的方法,可以在儿子类中的那些重写的方法上增加sealed(密封),将方法密封起来。
这是一个儿子类中的方法
public override sealed void GiveBonus(float amount) { int salesBonus = 0; }
sealed关键字也可以用来密封类,如果在类前面加了这个关键字,那么该类就不能继承。

sealed class Person{
string name{get;set;}
int age{get;set;}
}
//写成下面这样,VS就会报错
class Teacher:Person{
…………
}
抽象类 abstract
在类的前面使用abstract后,该类就不能被实例化了。他只提供其他类的继承的接口。
比如。我们的老爹类中有一些原始的方法,这些方法都需要在子孙类中,进行二次加工之后,才能拿出来用的。这个时候,abstract关键字就起作用了。
抽象方法 abstract
抽象方法只能定义在抽象类中。抽象方法中只定义名字,返回值(可以没有返回值)和参数(可以没有参数)
抽象类可以包含abstract方法,也可包含实例化方法,但继承的类(非抽象类)必须实现abstract方法
接口:抽象成员的命名集合。(一个接口最好只包含一个方法,当某个类被实例化的时候,就可以直接用那个类去继承这个接口。)
只有类和结构才能实现接口。接口中的所有成员必须被继承者一一实现。
可以同时继承多个接口,这是类所不具备的。

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { interface IIfac1 { void PrintOut(string s);//分号代替方法体 } } //接口中的方法,默认是public,而非private。void前面不能写public/private或者protect等修饰符

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class MyClass : IIfac1 { public void PrintOut(string s)//实现接口中的声明的方法 { Console.WriteLine("Calling through: {0}", s); } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MyClass mc = new MyClass(); mc.PrintOut("Hello Word");//调用方法 } } }
泛型:让多个类共享一组代码。泛型允许我们声明类型参数化的代码,可以用不同的类型进行实例化。

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class MyStack<T> { T[] StackArray; int StackPointer = 0; public void Push(T x) { if (!IsStackFull) StackArray[StackPointer++] = x; } public T Pop() { return (!IsStackEmpty) ? StackArray[--StackPointer] : StackArray[0]; } const int MaxStack = 10; bool IsStackFull { get { return StackPointer >= MaxStack; } } bool IsStackEmpty { get { return StackPointer <= 0; } } public MyStack() { StackArray = new T[MaxStack]; } public void Print() { for (int i = StackPointer - 1; i >= 0; i--) { Console.WriteLine(" Value:{0}", StackArray[i]); } } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MyStack<int> StackInt = new MyStack<int>(); MyStack<string> StackString = new MyStack<string>(); StackInt.Push(3); StackInt.Push(5); StackInt.Push(7); StackInt.Push(9); StackInt.Print(); StackString.Push("This is fun"); StackString.Push(" HI here"); StackString.Print(); } } }
使用 Where 字句来对泛型类进行约束

class MyClass <T> where T:Customer{ …… } class MyClass<T, T1, T2> where T1 : Customer where T2:IEnumerable { //T1的约束 //T2的约束 } class Customer { }
约束的5种类型:
类名: 只有这个类型的类或者从它继承的类才能用作类型实参。
class:任何引用类型,包括类,数组,委托和接口都可以用作类型实参。
struct:任何值类型都可以用作类型实参。
接口名:只有这个接口或者实现这个接口的类型才能用作类型实参。
new():任何带有无参数公共构造函数的类型都可以用作类型实参。这叫做构造函数约束。
where 字句中,约束的顺序
1,、最多只能有一个主约束,如果有则必须放在第一位。
2、可以有多个接口名约束。
3、如果存在构造函数,则必须放在最后。
泛型方法

public void PrintData<S, V>(S p, V v) where S : Person { //<S,V>:类型参数列表 //(S p,V v)方法参数列表 }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace myFunc { class Simple { static public void ReverseAndPrint<T>(T[] ary)//泛型方法 { Array.Reverse(ary); foreach (T item in ary)//使用类型参数T { Console.Write("{0},", item.ToString()); } Console.WriteLine(" "); } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace myFunc { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var intAry = new int[] { 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 }; var stringAry = new string[] { "first", "second", "third" }; var doubleAry = new double[] { 3.567, 7.891, 2.345 }; Simple.ReverseAndPrint<int>(intAry);//调用方法 Simple.ReverseAndPrint(intAry);//推断参数intAry的类型,并调用 Simple.ReverseAndPrint<string>(stringAry);//调用方法 Simple.ReverseAndPrint(stringAry);//推断参数intAry的类型,并调用 Simple.ReverseAndPrint<double>(doubleAry);//调用方法 Simple.ReverseAndPrint(doubleAry);//推断参数intAry的类型,并调用 Console.ReadKey(); } } }
在操作集合的时候,会频繁的做拆箱、装箱,所有性能不如泛型来的高。

//值类型自动装箱 ArrayList myInts=new ArrayList(); myInts.Add(10); myInts.Add(20); myInts.Add(30); int i=myInts[0]; //拆箱
初始化器:

person p2 = new person { age = 25, name = "curry" };

List<Product> proList = new List<Product> { new Product { ProductID = 1234, Name = "西瓜", Price = 2.3M }, new Product { ProductID = 2345, Name = "苹果", Price = 5.9M }, new Product { ProductID = 3456, Name = "樱桃", Price = 4.6M } };

string[] fruitArray = {"apple","orange","plum" };

var books = new { Title = "ASP.NET MVC 入门", Author = "小王", Price = 20 };

Dictionary<string, int> fruitDic = new Dictionary<string, int>() { { "apple", 10 }, { "orange", 20 }, { "plum", 30 } };
拓展方法:

class person { public string name { get; set; } public int age { get; set; } public void eat() { Console.WriteLine("having dinner"); } } //person类中并没有driving这个方法。

person p2 = new person { age = 25, name = "curry" }; p2.eat(); p2.Driving();

public static class MyExtentsionMethods { public static void Driving(this person people) { Console.WriteLine("I like BMW"); } }
拓展方法必须为静态方法(静态方法只能出现在静态类中)。
第一个参数person类的前面有一个this,将driving标注为静态方法。
泛型委托

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace myFunc { public delegate TR Func<T1, T2, TR>(T1 para1, T2 para2);//泛型委托 //T1、T2是传入参数类型,TR是返回类型 //参数类型列表(尖括号中的参数)至少需要两个,一个是传入类型,一个是返回类型 class Simple { static public string PrintStr(int para1, int para2)//方法匹配委托 { int total = para1 + para2; return total.ToString(); } } }

var myDel = new Func<int, int, string>(Simple.PrintStr);//创建委托实例 Console.WriteLine("Total:{0}", myDel(15, 13));//调用委托
泛型接口

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace myFunc { interface IMyIfc<T>//泛型接口 { T ReturnIt(T inValue); } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace myFunc { public delegate TR Func<T1, T2, TR>(T1 para1, T2 para2);//泛型委托 //T1、T2是传入参数类型,TR是返回类型 //参数类型列表(尖括号中的参数)至少需要两个,一个是传入类型,一个是返回类型 class Simple : IMyIfc<string>, IMyIfc<int>//源于同一个泛型接口的两个不同接口。。。。simple——非泛型类 { public int ReturnIt(int inValue)//实现int类型接口 { return inValue; } public string ReturnIt(string inValue)//实现string类型接口 { return inValue; } } }

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace myFunc { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Simple trival = new Simple(); Console.WriteLine("{0}", trival.ReturnIt(5)); Console.WriteLine("{0}", trival.ReturnIt("Hi there")); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
线程

给线程传递参数可以采用两种方式: 1、使用带ParameterizedThreadStart委托参数的Thread的构造函数。 2、创建自定义类,把线程的方法定义为实例方法,这样就可以初始化实例的数据,再去启动某个线程 //1、使用带ParameterizedThreadStart委托参数的Thread的构造函数。 //定义一个类型用来传递数据 public struct Data { public string Message; } //定义一个方法,用来开启一个线程并执行这个方法 private static void ThreadMainWithParameters(object obj) { Data d = (Data)obj; Console.WriteLine("Running in a thread,received:{0}", d.Message); } //主程序 static void Main(string[] args) { var d = new Data { Message = "My name is vichin!" }; var t2 = new Thread(ThreadMainWithParameters); t2.Start(d); Thread.Sleep(1); Console.ReadKey(); } //2、创建自定义类,把线程的方法定义为实例方法,这样就可以初始化实例的数据,再去启动某个线程 //定义一个类 public class MyThread { private string data; public MyThread(string _data) { data = _data; } public void ThreadMain(object obj) { Console.WriteLine("Running in a thread,data:{0}", data); } } //主程序 static void Main(string[] args) { var obj = new MyThread("info"); var t3 = new Thread(obj.ThreadMain); t3.Start(); } 在默认情况下,Thread类创建的线程都是前台线程。当主线程的方法运行完了之后,前台线程若是没有运行完,那么整个进程也不会被关闭。 如果想要主线程运行完就关闭整个进程(副线程也要关闭,而不是等待运行完了之后再关),可以考虑创建后台线程。 //创建后台线程 //t3.IsBackground = true; 线程在start()方法之后并不是处于running状态了(状态为unstarted),而是在操作系统调度器用它的时候才会running Thread.Join()会停止当前线程,并在加入进来的线程完成之后继续执行当前线程 死锁:两个线程挂起,并且同时等待对方解除锁定.
默认使用thread类产生的线程都是前台线程,使用线程池ThreadPool产生的线程都是后台线程。
当所有的前台线程运行完毕,如果还有后台线程运行的话,所有的后台线程会被终止。
当存在多个线程的时候,可以为每一个线程设置优先级(thread的Priority属性),让计算机去执行它们。(ThreadPriority枚举中存在Highest,AboveNormal,BelowNormal和Lowest)。
线程在创建之初为Unstarted状态,调用Start方法的时候仍然处于Unstarted状态。当操作系统任务调度器运行线程的时候,这个线程的状态才会变成Running状态。当我们使用Sleep方法的
时候,线程的状态会变更为WaitSleepJoin状态。

static void Main(string[] args) { #region 创建线程1(方法名当做参数传入) //Thread t = new Thread(DownLoad); //t.Start(); #endregion #region 创建线程2(使用lambda表达式) Thread t = new Thread(() => { Console.WriteLine("开始下载,当前线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("下载完成"); }); t.Start("我正在学习开启线程,并向方法中传递数据"); #endregion Console.ReadKey(); } /// <summary> /// /// </summary> /// <param name="msg">只接收object类型的参数</param> static void DownLoad(object msg) { Console.WriteLine("开始下载,传入的信息是:{0},当前线程ID:{1}", msg, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("下载完成"); }
线程池中所有的线程都是后台线程,如果所有的前台线程都结束了,所有的后台线程就会停止。
不能把入池的线程改为前台线程。不能修改入池线程的优先级与名称。
入池的线程只能用于用时较短的任务。如果线程一直运行就应该使用Thread类来创建一个线程。

static void Main(string[] args) { ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(ThreadMethod);//开启一个工作线程 } static void ThreadMethod(object state) { Console.WriteLine("线程开始"); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("线程结束"); }

static void Main(string[] args) { #region 开启任务的第一种方法 Task t = new Task(ThreadMethod);//传递一个需要线程去执行的方法。 t.Start(); t.Wait(); #endregion #region 开启任务的第二种方法 TaskFactory tf = new TaskFactory(); Task t1 = tf.StartNew(ThreadMethod); #endregion #region 连续任务的使用。(在运行完t1任务之后,便同时运行t2和t3这两个任务。) Task t2 = t1.ContinueWith(DoSth); Task t3 = t1.ContinueWith(DoSth); Task.WaitAll(t2, t3);//等待所有任务执行完成, Task.WaitAny(t2, t3);//等待任意一个执行成功 #endregion } static void ThreadMethod() { Console.WriteLine("任务开始"); Thread.Sleep(2000); Console.WriteLine("任务结束"); } static void DoSth(Task t) { Console.Write("连续任务!"); }
反射

//反射当前项目中的类 Assembly assembly = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly(); // 获取当前程序集 object obj = assembly.CreateInstance("类的完全限定名(即包括命名空间)"); // 创建类的实例,返回为 object 类型,需要强制类型转换 //创建类的实例时,传入参数 Assembly assembly = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly(); object[] ParaAry = { strModelFun, this }; Form obj = (Form)assembly.CreateInstance("nameSpace." + className, true, System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Default, null, ParaAry, null, null);// 创建类的实例 obj.Show(); //跨程序集反射 Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFile().CreateInstance("类的完全限定名(即包括命名空间)"); //LoadFile与后面的两者有所不同,它不会加载此程序集引用的其他程序集,也就是不会加载程序的依赖项。此外它和LoadForm一样,不能加载同标识不同路径的程序集 Assembly assembly1 = Assembly.LoadFrom().CreateInstance("类的完全限定名(即包括命名空间)"); //"D:\workspace\LatestWebTestSite\TestLib.dll" Assembly assembly2 = Assembly.Load().CreateInstance("类的完全限定名(即包括命名空间)"); //"TestLib, Version=1.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=null" 程序集的长格式。 //LoadForm和Load方法的相同点:LoadForm和Load方法会将所要加载的程序集的依赖项一起加载进来。 // 不同点:LoadFrom只能用于加载不同标识的程序集, 也就是唯一的程序集, 不能用于加载标识相同但路径不同的程序集 //反射的一种用法 public T xmltoT<T>() where T : class, new() { T t = new T(); //GetType()会返回一个T类型的实例。GetProperties方法会返回T类型的属性。GetFields返回字段.GetMethods返回方法名称 var items = t.GetType().GetProperties(); foreach (var item in items) { item.SetValue(t, "要赋的值", null); } var itemMethods = t.GetType().GetMethods(); foreach (var item in itemMethods) { } return t; }
补充:跨程序集反射
如果我们反射A.dll,而A.dll中引用了B.dll,那么在assembly.GetTypes(); //运行到这个地方会弹出如下错误描述
“未处理 System.Reflection.ReflectionTypeLoadException Message="无法加载一个或多个请求的类型。有关更多信息,请检索LoaderExceptions属性。”
这种情况可以:
Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom("A.dll") ;
Type type = assembly.GetType("xxx.myclassname") ; //传入对应的需要反射的类型 而不能GetTypes。且,应用程序需要应用A.dll锁依赖的B.dll。
依赖注入(片段)
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhaopei/p/5078539.html
我们有没有发现。我们只是在DAL新增了一个mysql的实现和修改了下UI层的接口构造。其中BLL我们根本就没有动它的。
是的,这样我们就可以说这里的UI对于BLL来说就是”依赖注入“,BLL对于UI来说就是”控制反转“。所以,我觉得依赖注入和控制反转是同一个概念,只是立场不同。

//没有使用依赖注入 ISqlHelper sqlhelper = new DALMsSqlHelper(); BLLAddStudent s = new BLLAddStudent(sqlhelper); s.addStudent(); //当sqlHelper对象不要指向DALMsSqlHelper类的时候,就需要重新改动代码,当改动多的时候,就要出问题。 //使用依赖注入 string dllNameStr = "";//从配置文件中获取到名字,以后要改的话,只需要改名字就行了。 Assembly asm2 = Assembly.LoadFrom("DAB.DLL"); ISqlHelper SQLHELPERR = (ISqlHelper)asm2.CreateInstance("net.DalMySqlHelper", true);//net.DalMySqlHelper 这个字符串将从webConfig中获取 SQLHELPERR.add("string para"); //当SQLHELPERR实例不要指向DalMySqlHelper对象的时候,只需要更改webConfig内的配置即可。

给线程传递参数可以采用两种方式: 1、使用带ParameterizedThreadStart委托参数的Thread的构造函数。 2、创建自定义类,把线程的方法定义为实例方法,这样就可以初始化实例的数据,再去启动某个线程 //1、使用带ParameterizedThreadStart委托参数的Thread的构造函数。 //定义一个类型用来传递数据 public struct Data { public string Message; } //定义一个方法,用来开启一个线程并执行这个方法 private static void ThreadMainWithParameters(object obj) { Data d = (Data)obj; Console.WriteLine("Running in a thread,received:{0}", d.Message); } //主程序 static void Main(string[] args) { var d = new Data { Message = "My name is vichin!" }; var t2 = new Thread(ThreadMainWithParameters); t2.Start(d); Thread.Sleep(1); Console.ReadKey(); } //2、创建自定义类,把线程的方法定义为实例方法,这样就可以初始化实例的数据,再去启动某个线程 //定义一个类 public class MyThread { private string data; public MyThread(string _data) { data = _data; } public void ThreadMain(object obj) { Console.WriteLine("Running in a thread,data:{0}", data); } } //主程序 static void Main(string[] args) { var obj = new MyThread("info"); var t3 = new Thread(obj.ThreadMain); t3.Start(); } 在默认情况下,Thread类创建的线程都是前台线程。当主线程的方法运行完了之后,前台线程若是没有运行完,那么整个进程也不会被关闭。 如果想要主线程运行完就关闭整个进程(副线程也要关闭,而不是等待运行完了之后再关),可以考虑创建后台线程。 //创建后台线程 //t3.IsBackground = true; 线程在start()方法之后并不是处于running状态了(状态为unstarted),而是在操作系统调度器用它的时候才会running Thread.Join()会停止当前线程,并在加入进来的线程完成之后继续执行当前线程 死锁:两个线程挂起,并且同时等待对方解除锁定. _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 进程:构成运行程序的资源的集合(虚地址空间、文件句柄……) 默认情况下一个进程值包含一个线程 线程可以派生其他线程。 若一个进程中包含多个线程,那么他们就共享进程的资源。 系统为处理器执行所规划的单元是线程。而非进程。 异步方法: 1、方法头中包含async方法修饰符 2、在方法中包含一个或多个await表达式。 3、方法的返回列表必须是Task、Task<T>或void 4、方法的参数列表中不能有out或者ref传参 5、异步方法的方法名一般以Async结尾 6、除方法外,Lambda表达式和匿名方法也可以作为异步对象 namespace ConsoleApplication1 { public class MyDownLoadString { Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); public void DoRun() { const int LargeNumer = 6000000; sw.Start(); //异步编程,首先t1 t2和CountToALarageNumber(1, LargeNumer);这3个对象在各自运行的时候,都不会影响到对方,因此,可以使用异步编程。 //创建t1对象后,不会立即运行Countcharacters中代码,而是继续走到下一行,创建t2。t2和t1一样,也不会走Countcharacters而是继续走下一行代码CountToALarageNumber方法 Task<int> t1 = Countcharacters(1, "http://www.microsoft.com"); Task<int> t2 = Countcharacters(2, "http://www.illustratedcsharp.com"); CountToALarageNumber(1, LargeNumer); CountToALarageNumber(2, LargeNumer); CountToALarageNumber(3, LargeNumer); CountToALarageNumber(4, LargeNumer); Console.WriteLine(" Chars in http://www.microsoft.com :{0}", t1.Result);//t1.result暂且认为是执行Countcharacters方法后返回的值。 Console.WriteLine(" Chars in http://www.illustratedcsharp.com :{0}", t2.Result); } private void CountToALarageNumber(int id, int value) { for (long i = 0; i < value; i++) ; Console.WriteLine(" End counting {0} : {1}ms", id, sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); } //方法中包含了async //方法的返回值为Task<T> private async Task<int> Countcharacters(int id, string uriString) { WebClient wc1 = new WebClient(); Console.WriteLine(" Starting call{0} : {1}ms", id, sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); //在方法中包含了至少一个await表达式 string result = await wc1.DownloadStringTaskAsync(new Uri(uriString)); Console.WriteLine(" Call {0} completed:{1}ms", id, sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds); return result.Length; } } } 主程序代码 static void Main(string[] args) { MyDownLoadString ds = new MyDownLoadString(); ds.DoRun(); Console.ReadKey(); } //返回值为Task<T>的异步方法 namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Task<int> value = DoAsyncStuff.CalculateSumAsync(5, 6); //这里可以去做其他的操作 Console.WriteLine("value :{0}", value.Result); } } static class DoAsyncStuff { public static async Task<int> CalculateSumAsync(int p1, int p2) { int sum = await Task.Run(() => GetSum(p1, p2));//匿名方法 gos to 后面是返回值,返回值是GetSum方法 return sum; } private static int GetSum(int p1, int p2) { return p1 + p2; } } } //返回值为Task的异步方法 namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Task someTask = DoAsyncStuff.CalculateSumAsync(5, 6); //这里可以去做其他的操作 someTask.Wait(); Console.WriteLine("Async stuff is done"); Console.ReadKey(); } } static class DoAsyncStuff { public static async Task<int> CalculateSumAsync(int p1, int p2) { int sum = await Task.Run(() => GetSum(p1, p2)); return sum; } private static int GetSum(int p1, int p2) { return p1 + p2; } } } //返回值为void的异步方法 namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { DoAsyncStuff.CalculateSumAsync(5, 6); //这里可以去做其他的操作 Thread.Sleep(200);//挂起线程,以防下面的语句执行完毕之后,CalculateSumAsync方法还没执行完 Console.WriteLine("Async stuff is done"); } } static class DoAsyncStuff { public static async void CalculateSumAsync(int p1, int p2) { int value = await Task.Run(() => GetSum(p1, p2)); Console.WriteLine("value :{0}", value); } private static int GetSum(int p1, int p2) { return p1 + p2; } } } namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Task t = (new MyClass()).DoWorkAsync(); } } class MyClass { public int Get10() { return 10; } public async Task DoWorkAsync() { Func<int> ten = new Func<int>(Get10); int a = await Task.Run(ten); int b = await Task.Run(new Func<int>(Get10)); int c = await Task.Run(() => { return 10; }); Console.WriteLine("{0} {1} {2}", a, b, c); } } } //同步等待任务 Task t = (new MyClass()).DoWorkAsync(); Task t1=(new MyClass()).DoWorkAsync(); Task<int>[] tasks=new Task<int>[]{t,t1}; t.Wait();//等待t完成之后吗,再继续执行后面的代码 t.WaitAll();//等待一组任务全都完成之后,再继续执行。 t.WaitAny();//任意一个任务执行完成后,就往下执行。 //WaitAll和WaitAny有重载,可以指定超时时间。 //在异步方法中异步等待任务 //Task.WhenAll和Task.WhenAny //CountCharsAsync是一个异步方法,在这个异步方法内,还存在等待异步方法的行为 async Task<int> CountCharsAsync(string site1,string site2){ WebClient wc1=new WebClient(); WebClient wc2=new WebClient(); Task<string>t1=wc1.DownloadStringTaskAsync(new Uri(site1)); Task<string>t2=wc2.DownloadStringTaskAsync(new Uri(site2)); List<Task<string>> tasks=new List<Task<string>>(); tasks.Add(t1); tasks.Add(t2); await Task.WhenAll(tasks);//异步等待任务完成 } //使用Task.Delay可以延迟执行异步方法中的代码。并且它并不会像Thread.Sleep()那样将线程挂起! async void ShowDelayAsync(){ Console.WriteLine("before Delay"); await Task.Delay(1000);//会创建一个task类型的对象在内存中,并在一定时间之后完成。 Console.WriteLine("after Delay"); }
一片有关C#异步编程的博客: https://blog.csdn.net/kebi007/article/details/76899078?locationNum=4&fps=1
Thread.Sleep(2000);//2秒后再继续执行(线程挂起2秒) Response.Buffer = true;//(默认值就是true)启用缓冲区 Response.Flush();//将缓冲区的内容立刻发送到客户端 Response.Clear();//清空缓冲区 Response.End();//终止响应,将缓冲区的东西发送到客户端 Stream getContentStr = Response.OutputStream;//获得将要发送的流(流≈字节数组)
当每个页面都需要做检查是否登录(session中是否有值),可以建一个basePage类并且让这个类继承system.web.UI.Page。在basePage类中写一个Page_Init方法(就跟Page_Load方法一样),在该方法中去验证session中是否有值。

//virtual 虚方法,便于子类重写 public virtual void Page_Init(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (Session["User"] == null) { //do sth.... } }
页面整体缓存
在 <%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="WebForm1.aspx.cs" Inherits="AddStudent.WebForm1" %> 下增加
<%@ OutputCache Duration="15" VaryByParam="*" %> Duration表示页面缓存时间是15秒,VaryByParam后面的*表示当请求报文中的发生任何改动。VaryByParam="Id"___当url中的Id发生变化

Session :存放键值对;每个浏览器只要访问服务器就会被分配一个session,每个session都会有一个ID。sessionID会被放在Cookie中,当浏览器端的cookie被禁用,session也就没法用了。
Cookie : 存放在浏览器所在的机器上。
Cache : 局部缓存,拥有更好的性能。
ViewState : 实质上就是一个隐藏域,在同一个页面中存取值可以使用。
Application: 只要应用程序启动就会被创建,任何地方都能被获取到。

Cache["key"] = "vichin"; Cache.Remove("key"); Cache.Insert("key", DateTime.Now.ToString(), null, DateTime.Now.AddDays(3), TimeSpan.Zero);//设置绝对过期时间。3天后过期。 Cache.Insert("key", DateTime.Now.ToString(), null, DateTime.MaxValue, new TimeSpan(0, 0, 10));//设置滑动过期时间10秒。(10秒内,若缓存没有被访问,则过期。否则缓存过期时间重新变成10秒) //依赖文件缓存。 string file = Request.MapPath("08a.txt");//依赖一个txt文本,当文本内的内容发生变化的时候,缓存过期。(页面菜单可以使用这个功能) Cache.Insert("key",DateTime.Now.ToString(),new CacheDependency(file)); //依赖数据库缓存 // ……
linq中的find()与where(),where每次都会去数据库执行,而find会去实体(缓存中)去找。
MVC能够快速的CURD是得益于实体在前后台的绑定。 前台可以直接取到实体中的值,从而生成页面。后台也可以将前台HTML标签中的name来映射到实体中,从而取到值。

//LinQ联合查询 masterList为武林高手集合,kongfuList为武功集合 var result = from m in masterList from k in kongfuList where m.Kongfu == k.name && k.power > 90 select new { master=m,kongfu=k}; //使用方法语法进行查询 var result1 = masterList.SelectMany(m => kongfuList, (m, k) => new { master = m,kongfu = k}).Where(x => x.Power > 90 && x.master.kongfu == x.kongfu.name); //m => kongfuList表示将masterList和kongfuList进行联合查询, //SelectMany方法的第二个参数表示,将两个对象进行联合查询之后,组合成的一个新的结果。 //使用join on 进行联合查询 var result = from m in masterList join k in kongfuList on m.kongfu equals k.name select new { master = m, kongfu = k };
排序
orderby(p => p.age).thenby(p => p.times);
String 的特性
1、不可继承性(微软内部使用了sealed关键字)
2、不可变性
string a = "vichin";在内存区域开辟一个空间,存放vichin这个固定字符串。将a变量指向这个空间
string b = "james";在内存区域开辟一个空间,存"放james这个固定字符串。将b变量指向这个空间
a = a + b; 开辟一块空间,存放a变量(vichin)与 b变量(james)相加后的值 这里并不是将原先a变量指向的内存空间内的值(vichin)替换成(vichinjames),
而是重新开辟一块内存空间,用于存放"vichinjames"。之前用于存放vichin那个字符串的空间并不会被GC回收————字符串暂存池(驻留池)。
3、字符串暂存池(驻留池)
接上————1、上面a变量重新指向了新的对象"vichinjames",老的对象"vichin"并没被GC回收,依然存留在内存空间当中(只有当程序完全结束的时候,这些对象才会消除)。
当一个程序内多次使用字符串相加操作之后,就会在内存中多次开辟内存空间,对内存产生大量不必要的消耗。 2、string a="vichin",想这样将一个固定的字符串赋值给a变量,a变量将会被存放在暂存池中。如果通过调用一个方法比如说string a=GetName();来获取的话, 那么a变量将不会被存放在暂存池中。

Dictionary<string, int> Player = new Dictionary<string, int>(); Player.Add("vichin", 8); Player.Add("james", 23); Player.Add("stephen", 30); for (int i = 0; i < Player.Count; i++) { var item = Player.ElementAt(i); string name = item.Key; int num = item.Value; } foreach (var item in Player) { string name = item.Key; int num = item.Value; } foreach (var item in Player.Keys) { int num = Player[item]; } foreach (var item in Player.Values) { int i = 0; i = i + item; } foreach (KeyValuePair<string, int> item in Player) { }

ToString()可空参数单独使用,同时可以加一个格式化参数,具体方式如下: 1. 取中文日期显示_年月 currentTime.ToString("y"); 格式:2007年1月 2. 取中文日期显示_月日 currentTime.ToString("m"); 格式:1月30日 3. 取日期显示_年月日 currentTime.ToString("d"); 格式:2007-1-30 4. 取日期显示_时分 currentTime.ToString("t"); 格式:15:35 5. Int32.Parse(变量) Int32.Parse("常量") 字符型转换 转为32位数字型 6. 变量.ToString() 字符型转换 转为字符串 12345.ToString("n"); //生成 12,345.00 12345.ToString("C"); //生成 ¥12,345.00 12345.ToString("e"); //生成 1.234500e+004 12345.ToString("f4"); //生成 12345.0000 12345.ToString("x"); //生成 3039 7. 变量.ToString("yyyyMMdd") ; 格式:20070101 8.变量.ToString(".00") ; 格式:*.??
