第六章 面向对象编程下
6.1 static 关键字




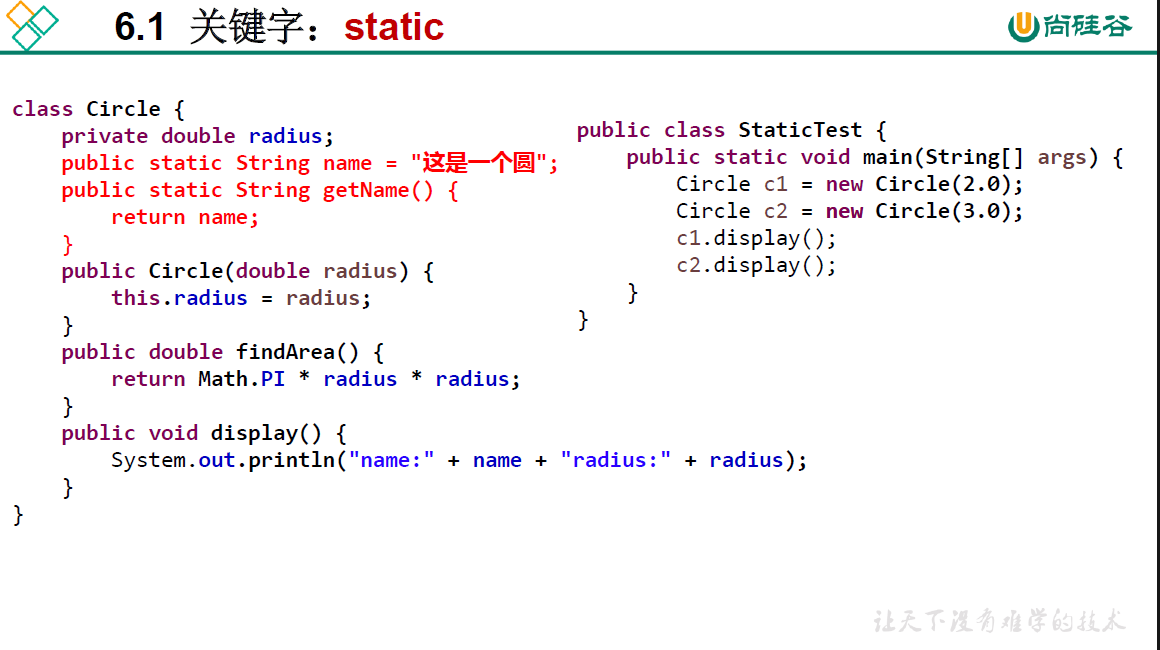
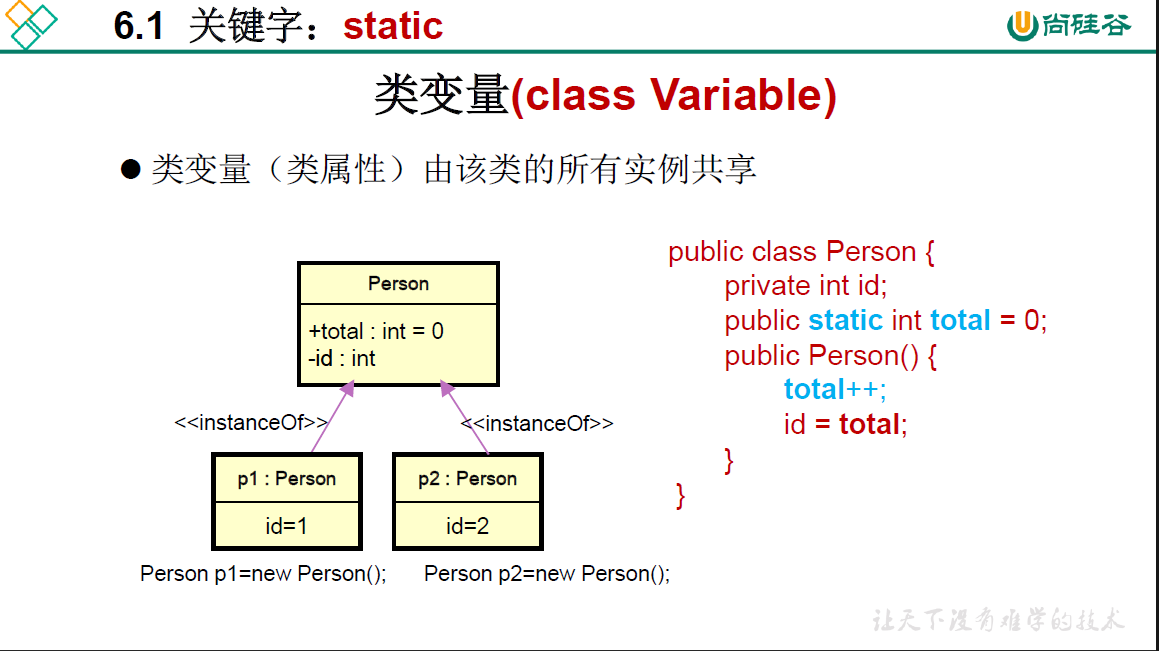
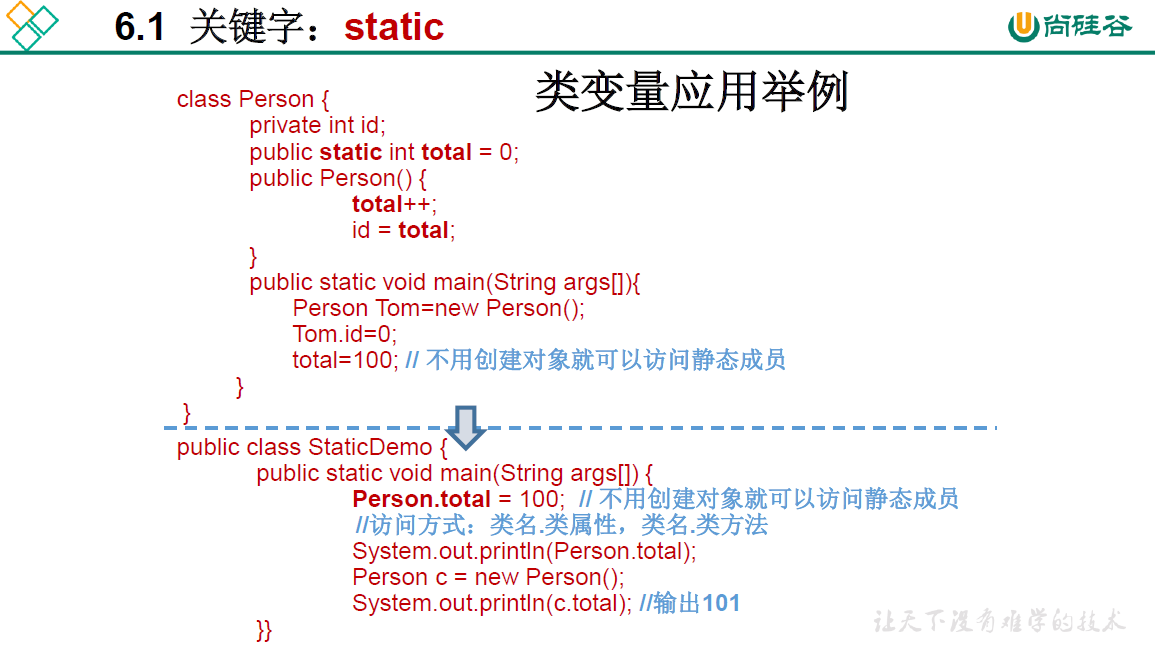


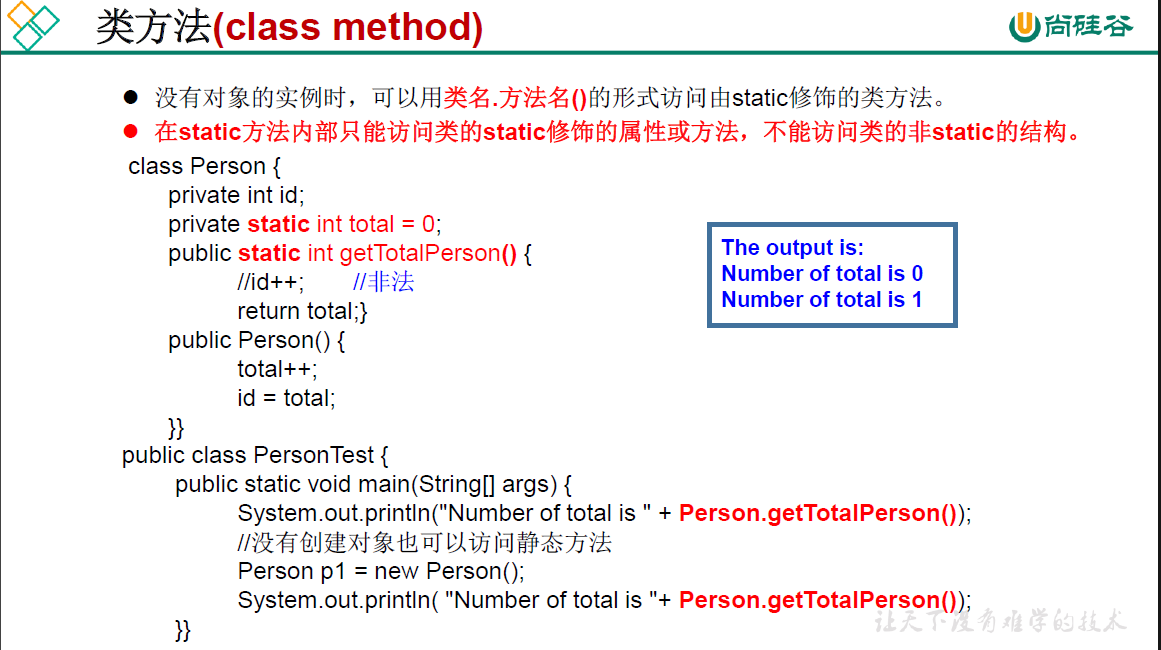
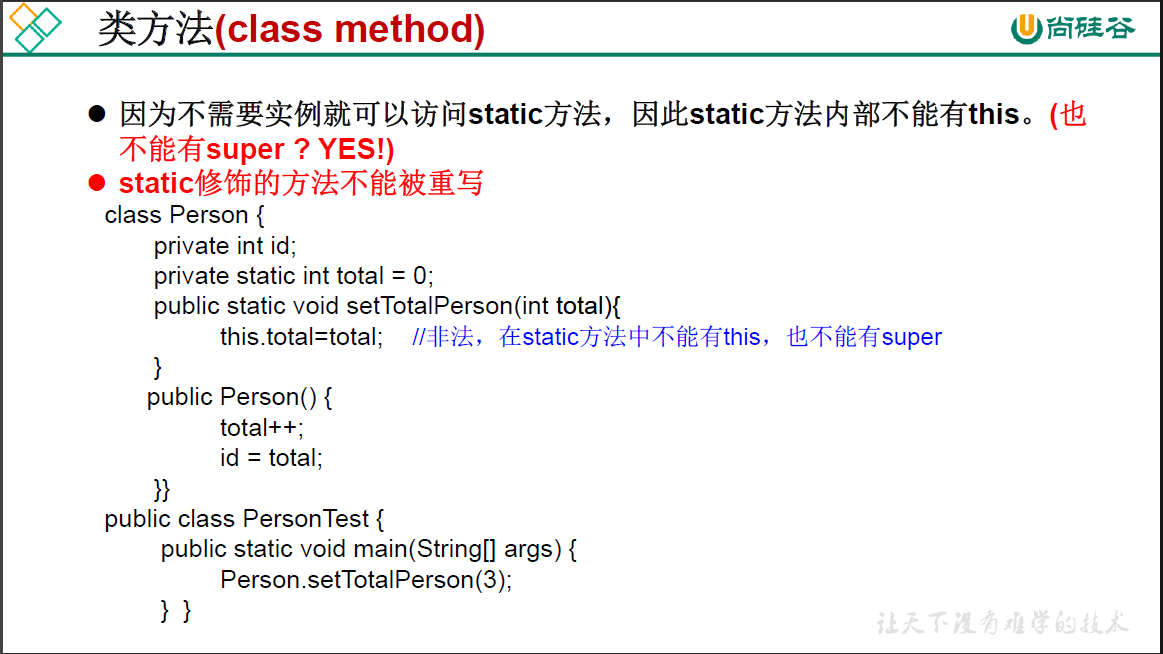
package oop.third;
/*
* static关键字的使用
*
* 1.static:静态的
*
* 2.static可以用来修饰:属性、方法、代码块、内部类
*
* 3.使用static修饰属性:静态变量(或类变量)
* 3.1属性,按是否使用static修饰,又分为:静态属性vs非静态属性(实例变量)
* 实例变量: 我们创建了类的多个对象,每个对象都独立的拥有一套类中的非静态属性。当修改其中一个对象中的
* 非静态属性时,不会导致其他对象中同样的属性值的修改。
* 静态变量:我们创建了类的多个对象,多个对象共享同一个静态变量
* 其他对象调用此静态变量时,是修改过了的。
* 3.2 static修饰属性的其他说明
* ① 静态变量随着类的加载而加载;可以通过“类.静态变量”得方式进行调用
* ② 静态变量的加载早于对象的创建
* ③ 由于类只会加载一次,则静态变量在内存中也只会存在一份,存在方法区的静态域中。
* ④ 类变量 实例变量
* 类 yes no
* 对象 yes yes
*
* 4. 使用static方法:静态方法
* ① 随着类的加载而加载,可以通过"类.静态方法"的方式进行调用
* ② 静态方法 非静态方法
* 类 yes no
* 对象 yes yes
* ③ 静态方法中,只能调用静态的方法或属性
* 非静态方法中,既可以调用非静态的方法或属性,也可以调用静态的方法或属性
* 5. static 注意点
* 5.1 在静态的方法内,不能使用this关键字、super关键字
* 5.2 关于静态属性和静态方法的使用,大家都从生命周期的角度去理解。
*
* 6. 开发中,如何确定一个属性是否要声明为static的?
* -> 属性是可以被多个对象所共享的,不会随着对象的不同而不同的。
* -> 类中的常量也常常申明为static
*
* 7. 开发中,如何确定一个方法是否要声明为static的?
* -> 操作静态属性的方法,通常设置为static的
* -> 工具类中的方法,习惯上声明为static的。比如:Math、Arrays.Collections
*/
public class StaticTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Chinese c1 = new Chinese("jim", 40, "JP");
Chinese c2 = new Chinese("trump", 71, "US");
System.out.println(c1.nation);
System.out.println(c2.nation);
Chinese.speak();
}
}
class Chinese{
String name;
int age;
static String nation;
public Chinese(String name, int age, String nation) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.nation = nation;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Chinese eat Chinese food");
}
//静态方法
public static void speak() {
System.out.println("American speak English");
System.out.println(nation); //调用静态属性
walk(); //调用静态方法
}
public static void walk() {
System.out.println("American walk in the Wall Street");
}
}

package oop.exercise.exer10;
public class AccountTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account acct1 = new Account();
Account acct2 = new Account("666666", 1000);
System.out.println(acct1.getId());
System.out.println(acct1.getPassword());
System.out.println(acct2.getId());
System.out.println(acct2.getPassword());
System.out.println(Account.getInterestRate());
}
}
class Account{
private int id;
private String password = "000000";
private double balance;
private static double interestRate = 0.045;
private static double minimumBalance = 1.0;
private static int init = 1001; //用于自动生成id
public Account() {
id = init++;
}
public Account(String password, double balance) {
id = init++;
this.password = password;
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public static double getInterestRate() {
return interestRate;
}
public static void setInterestRate(double interestRate) {
Account.interestRate = interestRate;
}
public static double getMinimumBalance() {
return minimumBalance;
}
public static void setMinimumBalance(double minimumBalance) {
Account.minimumBalance = minimumBalance;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}

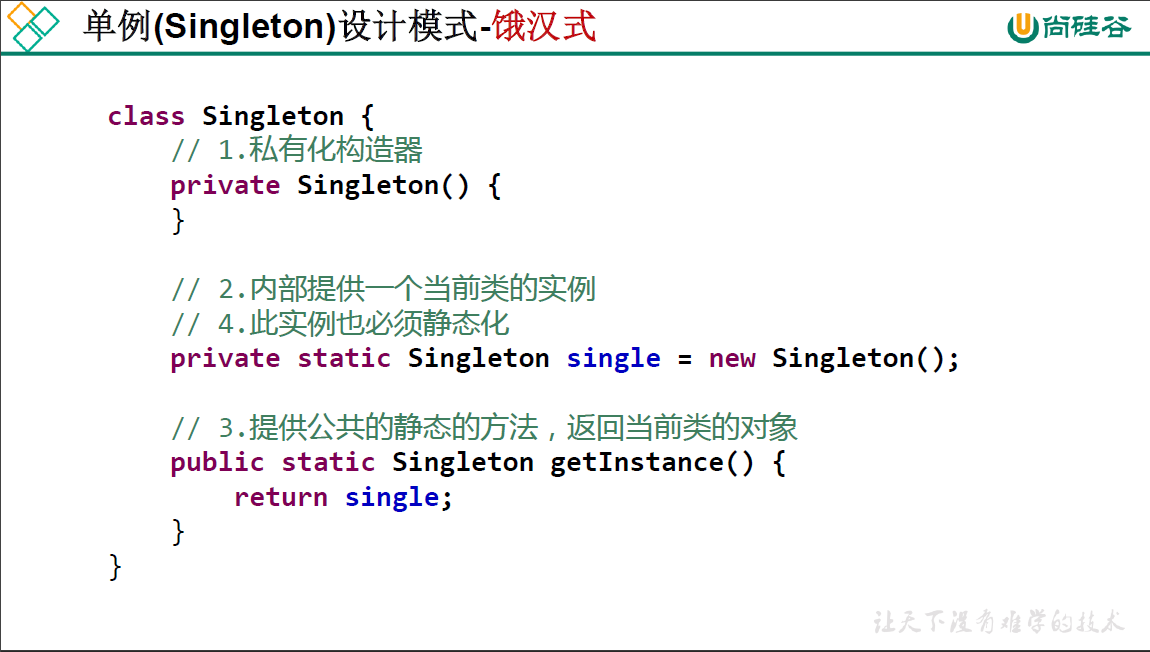


饿汉式(线程安全)
package oop.third;
public class SingletonTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank b1 = Bank.getInstance();
Bank b2 = Bank.getInstance();
System.out.println(b1 == b2);
}
}
//饿汉式
class Bank{
//1. 私有化类的构造器
private Bank() {
}
//2. 内部创建类的对象
//3.要求此对象也必须声明为静态的
private static Bank instance = new Bank();
//4. 提供公共的静态方法,返回类的对象
public static Bank getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
特点:一开始就创建对象
懒汉式(线程不安全)
package oop.third;
public class SingletonTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gun g1 = Gun.getInstance();
Gun g2 = Gun.getInstance();
System.out.println(g1 == g2);
}
}
//懒汉式
class Gun{
//1. 私有化类的构造器
private Gun() {
}
//2. 内部创建类的对象,没有初始化
//3.要求此对象也必须声明为静态的
private static Gun instance = null;
//4. 提供公共的静态方法,返回类的对象
public static Gun getInstance() {
if (instance == null)
instance = new Gun();
return instance;
}
}
特点:需要用的时候才创建对象
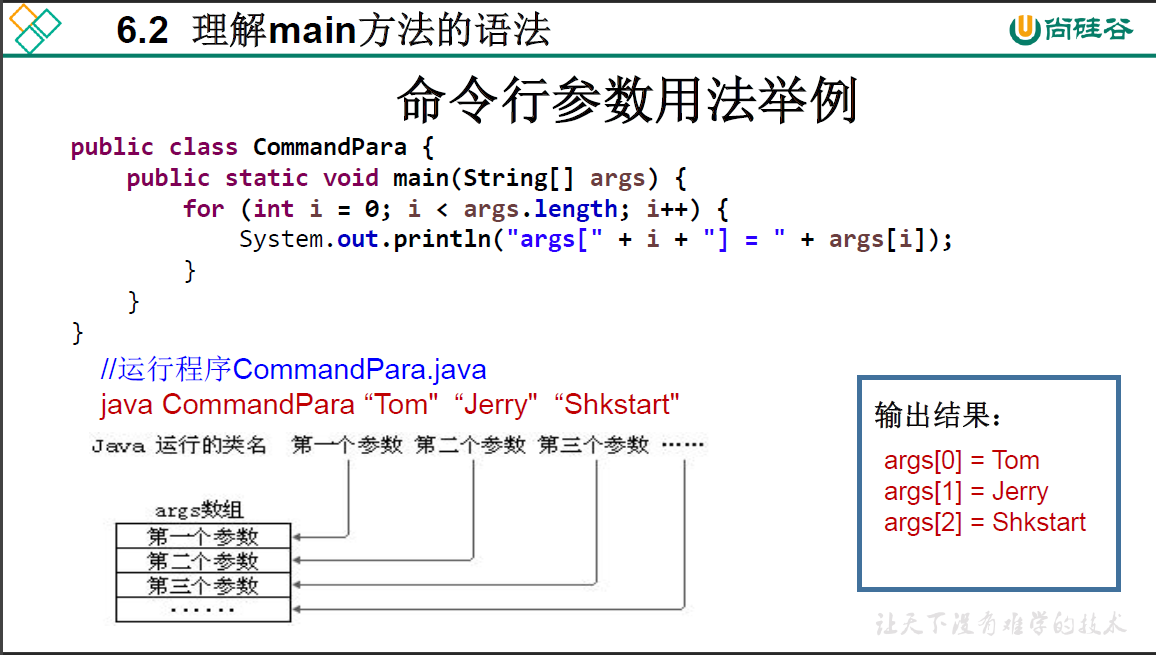
6.2 理解main方法的语法


package oop.third;
/*
* main()方法的使用说明:
* 1. main()方法作为程序的入口
* 2. main()方法也是一个普通的静态方法
* 3. main()方法可以作为我们与控制台交互的方式。之前:使用Scanner
*
*/
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main.main(new String[100]);
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0;i < args.length;i++) {
args[i] = "args_" + i;
System.out.println(args[i]);
}
}
}
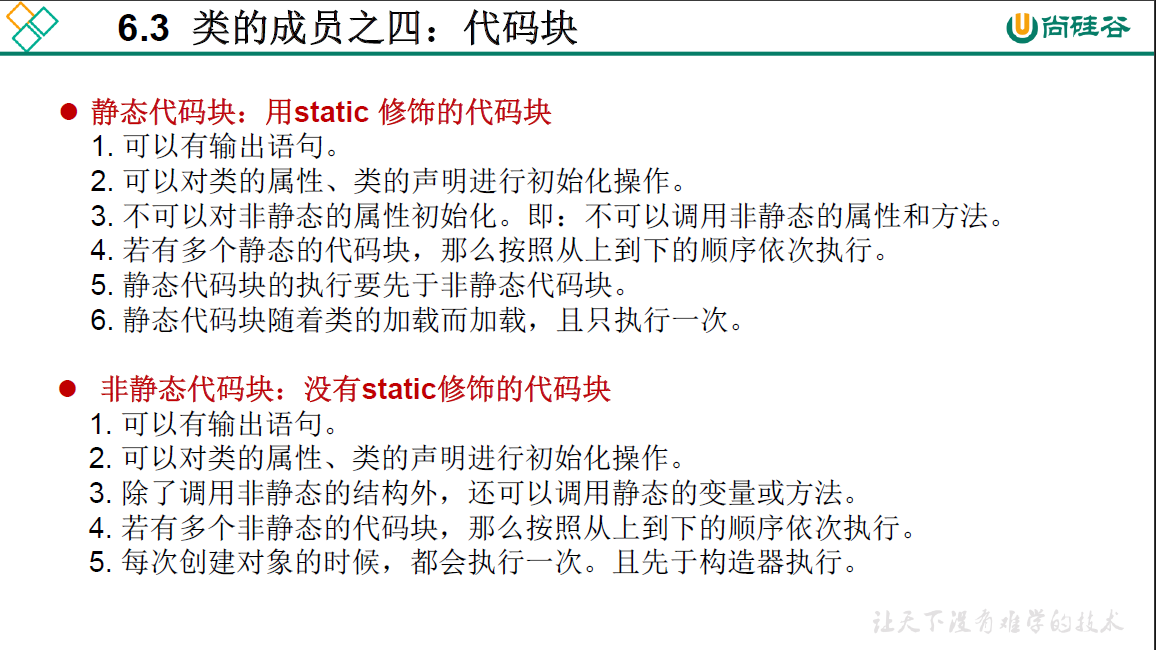
6.3 类的成员之四: 代码块



对属性赋值的先后顺序:
-
① 默认初始化 -
**② 显式初始化 ③ 在代码块中赋值(谁在前,谁先执行)** -
④ 构造器中初始化 -
⑤ 有了对象以后,可以通过"对象.属性"或"对象.方法"的方式,进行赋值
package oop.third;
/*
* 类的成员之四:代码块(或初始化块)
* 1.代码块的作用:用来初始化类、对象
* 2.代码块如果有修饰的话,只能使用static
* 3.分类:静态代码块 VS 非静态代码块
* 4.静态代码块
* >内部可以有输出语句
* >随着类的加载而执行
* >作用:初始化类的信息
* >如果一个类中定义了多个静态代码块,则按照声明的先后顺序执行
* >静态代码块的执行要优先于非静态代码块的执行
* >静态代码块内只能调用静态的属性、静态的方法,不能调用非静态的结构
*
* 5. 非静态代码块
* > 内部可以有输出语句
* > 随着对象的创建而创建
* > 每创建一个对象,就执行一次非静态代码块
* > 作用:可在创建对象时,对对象的属性等进行初始化|
* >如果一个类中定义了多个非静态代码块,则按照声明的先后顺序执行
* >非静态代码块内可以调用静态的属性、静态的方法,或非静态的属性、方法
*/
public class BlockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String description = Person.desc;
System.out.println(description);
Person p1 = new Person();
Person p2 = new Person();
}
}
class Person{
//属性
String name;
int age;
static String desc = "I am a person";
//无参构造器
public Person() {
}
//有参构造器
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//静态代码块1
static {
System.out.println("this is the first static block");
desc = "I am a person who love studying 1";
info(); // 调用静态方法,不能调用非静态方法和属性
}
//静态代码块2
static {
System.out.println("this is the second static block");
desc = "I am a person who love studying 2";
}
//非静态代码块
{
//调用静态结构与非静态结构
System.out.println("this is non-static block");
age = 20;
eat();
info();
System.out.println(desc);
}
//方法
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eat food");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public static void info() {
System.out.println("this is the information of man");
}
}

LeafTest.java
package oop.exercise.exer10;
/*
* 由父及子,静态先行
*/
public class LeafTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Leaf();
}
}
class Root{
static {
System.out.println("Root的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Root的普通初始化块");
}
public Root(){
System.out.println("Root的无参构造器");
}
}
class Mid extends Root{
static {
System.out.println("Mid的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Mid的普通初始化块");
}
public Mid(){
System.out.println("Mid的无参构造器");
}
public Mid(String msg){
//通过this调用同一类中重载的构造器
this();
System.out.println("Mid的带参构造器,其参数值为:" + msg);
}
}
class Leaf extends Mid{
static {
System.out.println("Leaf的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Leaf的普通初始化块");
}
public Leaf(){
super("尚硅谷");
System.out.println("Leaf的无参构造器");
}
}
结果:
Root的静态初始化块
Mid的静态初始化块
Leaf的静态初始化块
Root的普通初始化块
Root的无参构造器
Mid的普通初始化块
Mid的无参构造器
Mid的带参构造器,其参数值为尚硅谷
Leaf的普通初始化块
Leaf的无参构造器
SonTest.java
package oop.exercise.exer11;
class Father{
static {
System.out.println("Father的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Father的普通初始化块");
}
public Father(){
System.out.println("Father的无参构造器");
}
}
public class Son extends Father{
static {
System.out.println("Son的静态初始化块");
}
{
System.out.println("Son的普通初始化块");
}
public Son(){
System.out.println("Son的无参构造器");
}
//静态方法必须用类调用,所以类必须先加载
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Mian方法的输出");
System.out.println("*************");
new Son();
System.out.println("*************");
new Son();
System.out.println("*************");
new Father();
}
}
结果:
Father的静态初始化块
Son的静态初始化块
Mian方法的输出
*************
Father的普通初始化块
Father的无参构造器
Son的普通初始化块
Son的无参构造器
*************
Father的普通初始化块
Father的无参构造器
Son的普通初始化块
Son的无参构造器
*************
Father的普通初始化块
Father的无参构造器
6.4 final关键字



package oop.third;
/*
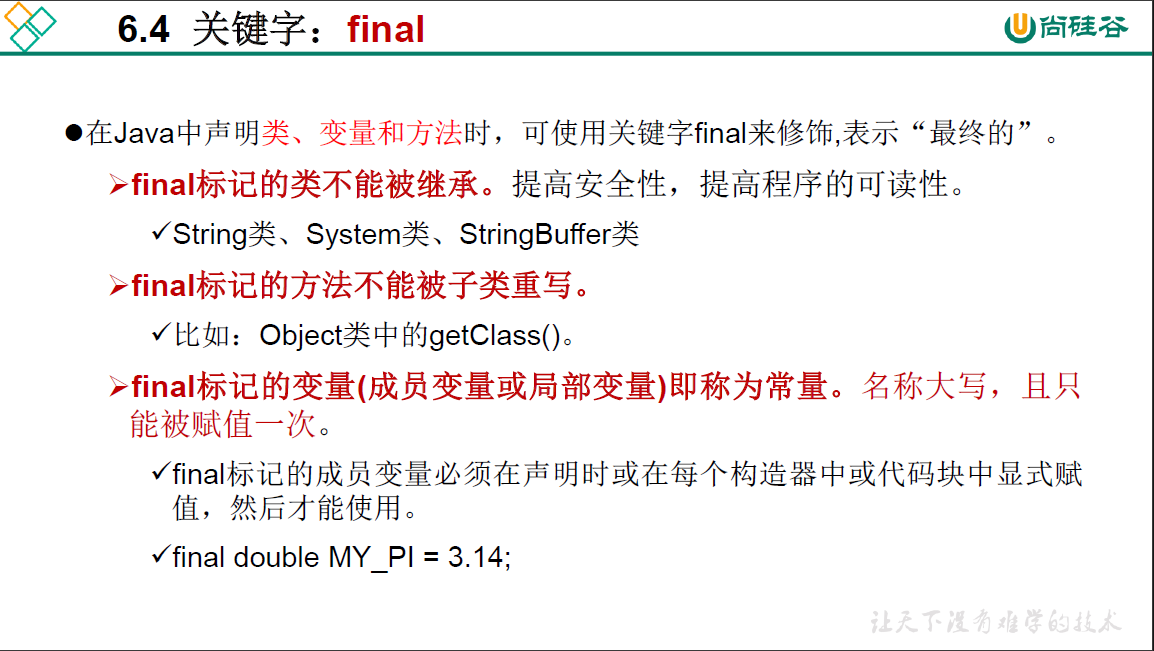
* final :最终的
*
* 1. final可以用来修饰的结构:类、方法、变量
*
* 2. final用来修饰一个类:此洋不能被其他类所继承。
* 比如,String类、System类、StringBuffer类
*
* 3. final用来修饰方法:表明此方法不可以被重写
* 比如:Object类中getClass();
*
* 4. final用来修饰变量:此时的"变量"就称为是一个常量
* 4.1 final修饰属性:可以考虑赋值的位置有:显式初始化、代码块中初始化、构造器中初始化
* 4.2 final修饰局部变量
* 尤其是使用final修饰形参时,表明此形参是一个常量。当我们调用此方法时,给常量形参赋一个实参
* 一旦赋值以后,就只能在方法体内使用此形参,但不能进行重新赋值。
*
* 5. static final用来修饰属性: 全局常量
*/
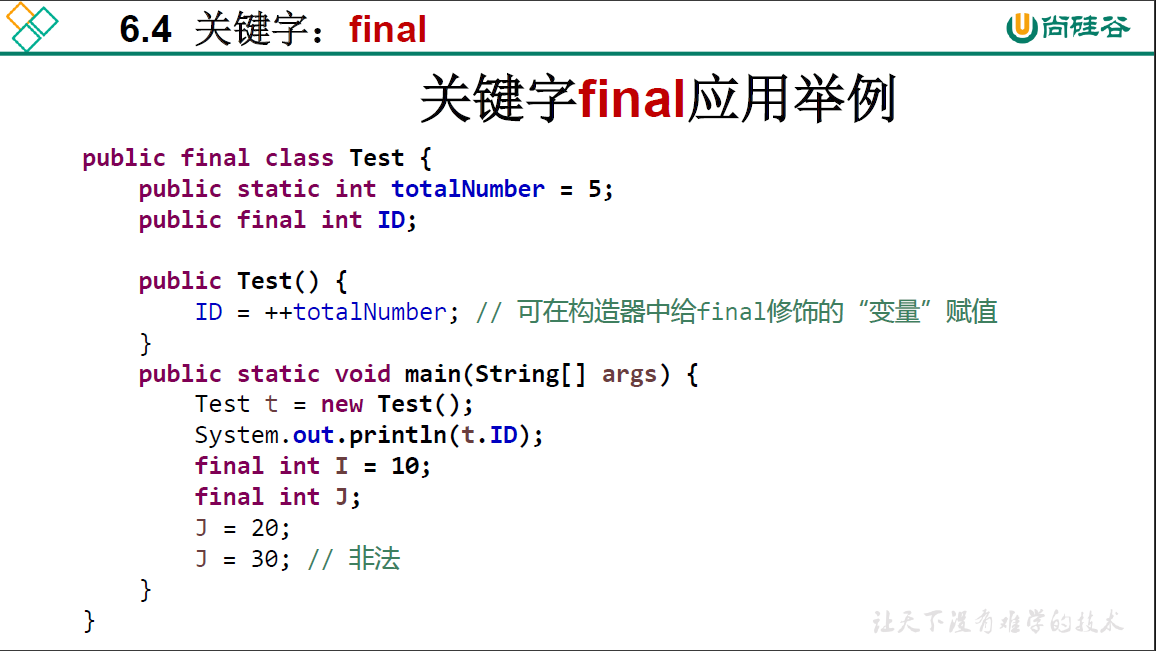
public class FinalTest {
final int UP;
final int DOWN = 1; // 显式初始化之后, 不能再被赋值
final int LEFT;
final int RIGHT;
//代码块中 赋值
{
UP = 2;
}
//构造器中赋值, 都要赋值
public FinalTest() {
this.LEFT = 3;
this.RIGHT = 4;
}
//构造器中赋值,都要赋值
public FinalTest(int left, int right) {
this.LEFT = left;
this.RIGHT = right;
}
//不能使用方法对final修饰的属性进行赋值, 因为使用构造器创建对象后,已经对属性进行了初始化,而此时却需要调用方法对final属性赋值,矛盾
// public void setUP() {
// UP = 3;
// }
//不能对常量进行自增操作
// public void show() {
// final int num = 10;
// num++;
// }
//不能对常量重新赋值
// public void display(final int num) {
// num = 20;
//
// }
public static void main(String[] args) {
FinalTest ft1 = new FinalTest();
FinalTest ft2 = new FinalTest(6, 7);
}
}
final class A{
}
//不能继承A类
//class B extends A{
//
//}
//不能继承String类
//class C extends String{
//
//}
class D{
public final void show() {
System.out.println("final修饰的方法");
}
}
// final用来修饰方法:表明此方法不可以被重写
//class E extends D{
// public void show() {
// System.out.println("final修饰的方法");
// }
//}
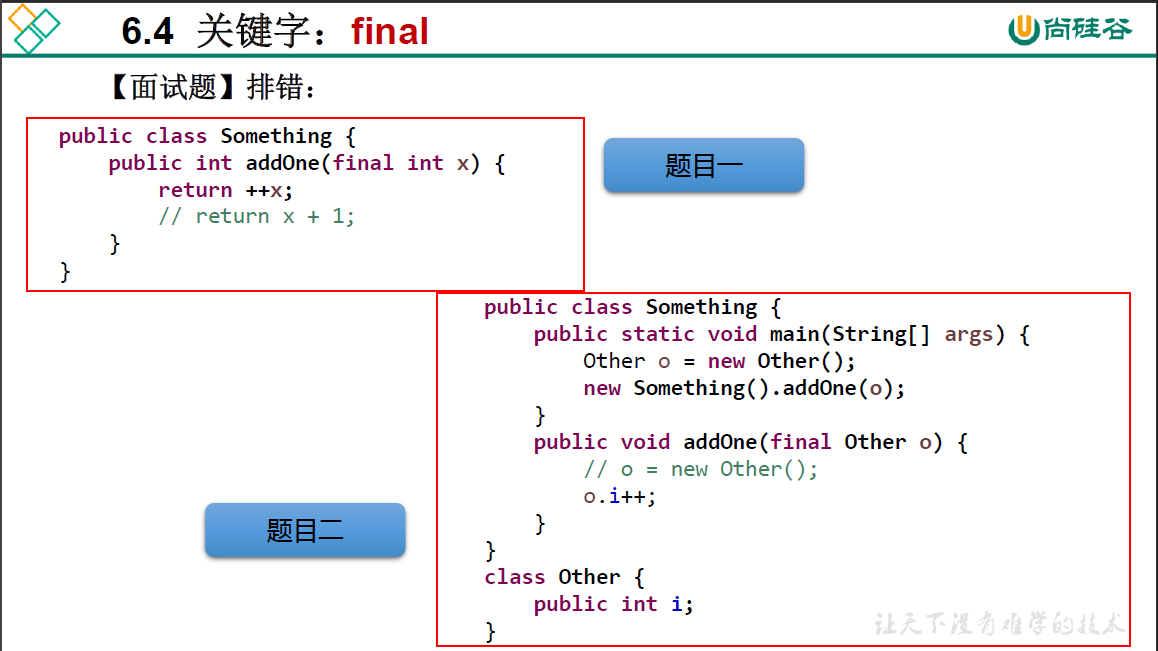
题目一:final修饰的常量不能进行自增操作即重新赋值
题目二: final修饰的局部变量不能重新赋值,对于引用型变量,即这个变量不能指向新的对象,但是对象里面的属性可以重新赋值。所以o.i++编译成功。
复习题
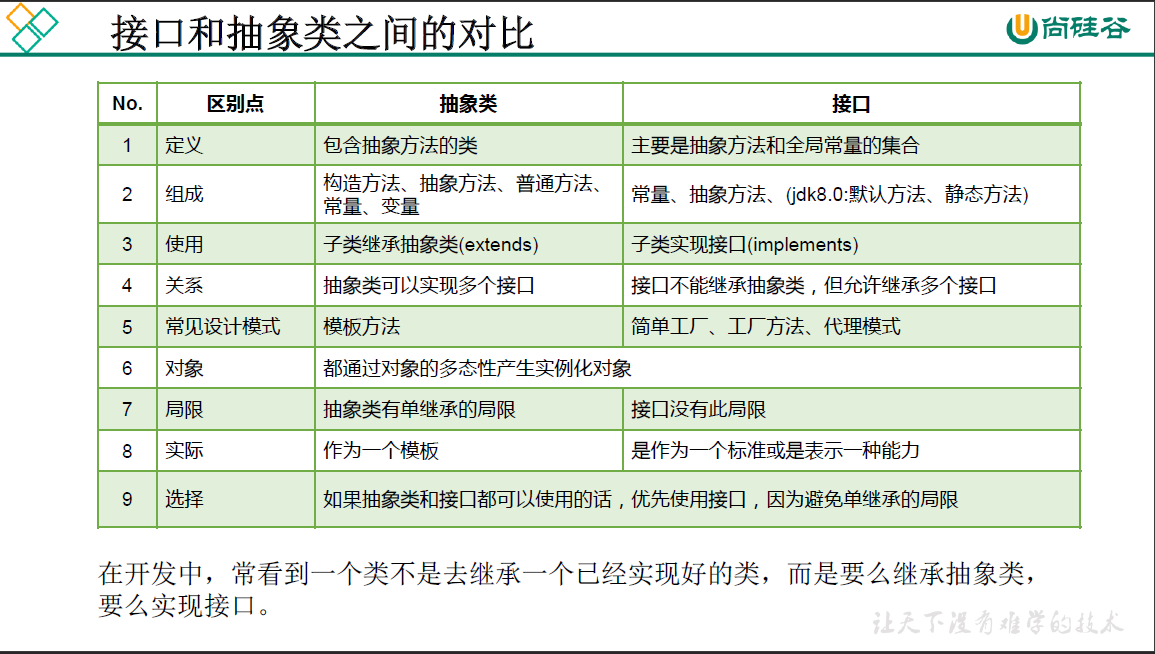
1. static修饰的属性,相较于实例变量,有哪些特别之处(>=3点)
- 随着类的加载而加载;早于对象的创建;
- 只要权限允许,可以通过”对象.static属性”的方式进行调用;
- 存在于方法区的静态域
2. final可以用来修饰哪些结构,分别表示什么意思?
-
final可以用来修饰的结构:类、方法、变量
-
final用来修饰一个类:此洋不能被其他类所继承。
比如,String类、System类、StringBuffer类
-
final用来修饰方法:表明此方法不可以被重写
比如:Object类中getClass();
-
final用来修饰变量:此时的"变量"就称为是一个常量
4.1 final修饰属性:可以考虑赋值的位置有:显式初始化、代码块中初始化、构造器中初始化
4.2 final修饰局部变量
尤其是使用final修饰形参时,表明此形参是一个常量。当我们调用此方法时,给常量形参赋一个实参
一旦赋值以后,就只能在方法体内使用此形参,但不能进行重新赋值。
-
static final用来修饰属性: 全局常量
3. 类的属性赋值的位置有哪些?先后顺序为何?
-
① 默认初始化 -
**② 显式初始化 ③ 在代码块中赋值(谁在前,谁先执行)** -
④ 构造器中初始化 -
⑤ 有了对象以后,可以通过"对象.属性"或"对象.方法"的方式,进行赋值
6.5 抽象类与抽象方法



package oop.third;
/*
* abstract关键字的使用
*
* 1. abstract: 抽象的
* 2. abstract可以用来修饰的结构:类、方法
* 3. abstract修饰类:抽象类
* > 此类不能实例化
* > 抽象类中一定有构造器,便于子类实例化时调用(涉及:子类对象实例化的全过程)
* > 开发中,都会提供抽象类的子类,让子类对象实例化,完成相关的操作
* 4. abstract修饰方法:抽象方法
* > 抽象方法只有方法的声明,没有方法体
* > 包含抽象方法的类,一定是一个抽象类。反之,抽象类中可以没有抽象方法
* >若子类重写了父类中的所有的抽象方法后,此子类方可实例化
* 若子类没有重写父类中的所有的抽象方法,则此子类也是一个抽象类,需要使用abstract修饰
*
*/
public interface AbstractTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//一旦Fish类抽象化,就不可以实例化
// Fish f1 = new Fish();
// f1.eat();
}
}
//抽象类
abstract class Creature{
public abstract void breath();
}
//抽象类
abstract class Fish extends Creature{
String name;
double weight;
public Fish() {
}
public Fish(String name, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.weight = weight;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("fish eat aquatic plants");
}
public void deep() {
System.out.println("fish deep into the water");
}
//抽象方法
public abstract void swim();
}
//实例类
class GrassCarp extends Fish{
public GrassCarp(String name, double weight) {
super(name, weight);
}
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("grass carp swim in the middle of the water");
}
@Override
public void breath() {
System.out.println("grass carp breath with with gills");
}
}
abstract使用上的注意点:
1. abstract不能用来修饰:属性、构造器等结构
2. abstract不能用来修饰私有方法、静态方法、final的方法、final的类
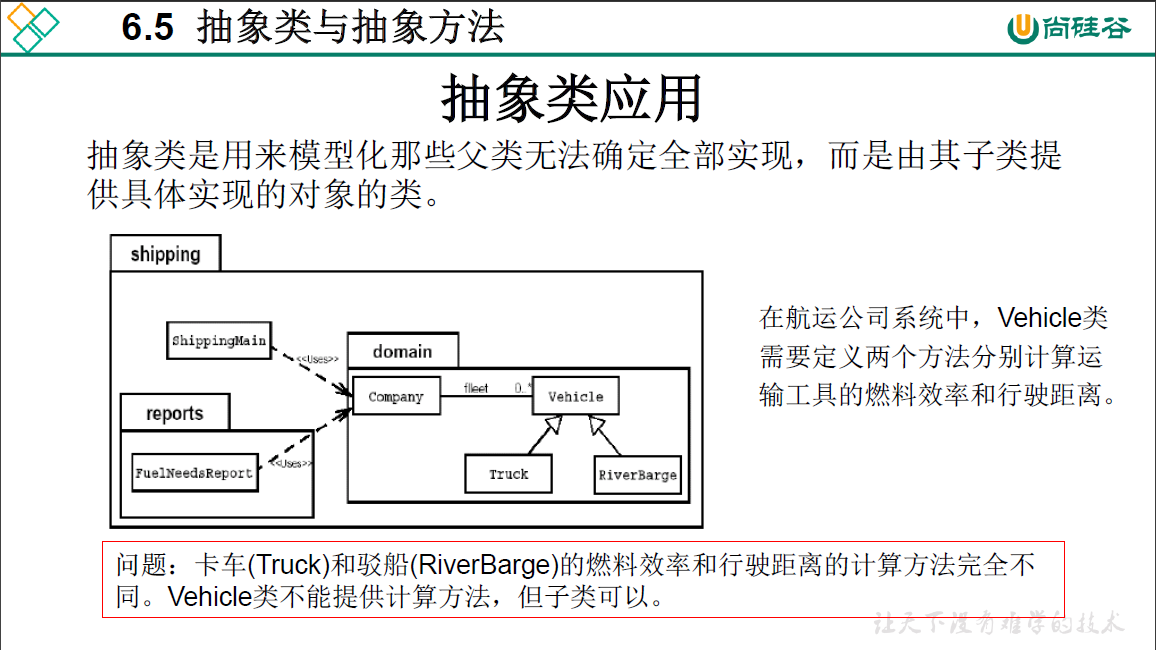


问题一:final修饰的类不能被继承,而抽象方法需要被继承,因此前后矛盾。
问题二: 可以,虽然抽象类不能被实例化,但是子类的构造器需要调用父类的构造器。
问题三:不完全正确,抽象类可以没有抽象方法,但抽象方法所属的类一定为抽象类。

Employee
package oop.exercise.exer12;
public abstract class Employee {
private String name;
private int id;
private double salary;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String name, int id, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public abstract void work();
}
Manager
package oop.exercise.exer12;
public class Manager extends Employee{
private double bonus;
public Manager() {
}
public Manager(String name, int id, double salary, double bonus) {
super(name, id, salary);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("Manager manage common employee");
}
}
CommonEmployee
package oop.exercise.exer12;
public class CommonEmployee extends Employee {
public CommonEmployee() {
}
public CommonEmployee(String name, int id, double salary) {
super(name, id, salary);
}
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("common employee work with hands");
}
}
知识点:抽象类的匿名子类
package oop.third;
public class AnonymousTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Apple a = new Apple();
method(a); //非匿名的类,非匿名的对象
method(new Apple()); //非匿名的类,匿名对象
//匿名子类的对象c
Computer c = new Computer() {
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("this macbook pro");
}
};
c.show();
}
public static void method(Computer c) {
c.show();
}
}
abstract class Computer{
String name;
double price;
public Computer() {
}
public abstract void show();
}
class Apple extends Computer{
@Override
public void show() {
System.out.println("this is Macbook");
}
}

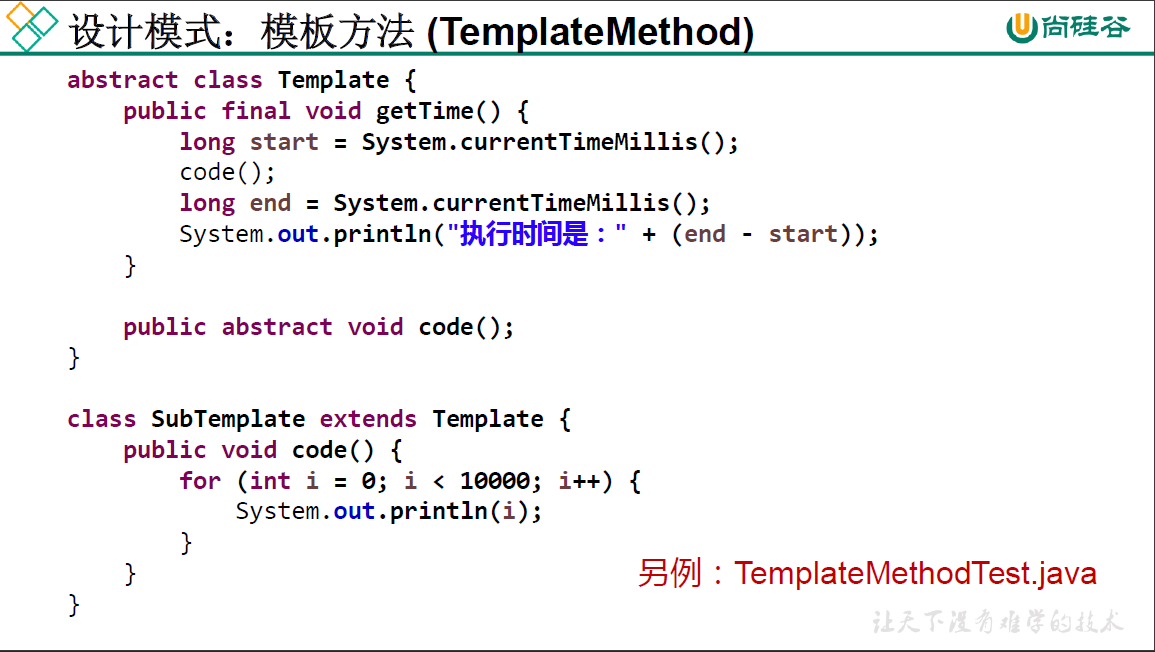
package oop.third;
public class TemplateTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Template t = new SubTemplate();
t.spendTime();
}
}
abstract class Template{
public void spendTime() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
code(); //不确定的, 易变的部分
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("the time is: " + (end - start));
}
public abstract void code();
}
class SubTemplate extends Template{
@Override
public void code() {
for (int i = 0;i < 1000;i++)
System.out.println(i);
}
}



Employee类
package oop.exercise.exer13;
public abstract class Employee {
private String name;
private int number;
private MyDate birthday;
public Employee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.number = number;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public MyDate getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(MyDate birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public abstract double earnings();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "name=" + name + ", number=" + number + ", birthday=" + birthday.toDateString();
}
}
MyDate类
package oop.exercise.exer13;
public class MyDate {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public String toDateString() {
return year + "年" + month + "月" + day + "日";
}
public MyDate(int year, int month, int day) {
super();
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
}
SalariedEmployee类
package oop.exercise.exer13;
public class SalariedEmployee extends Employee {
private double monthlySalary;
public SalariedEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, double monthlySalary) {
super(name, number, birthday);
this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary;
}
public double getMonthlySalary() {
return monthlySalary;
}
public void setMonthlySalary(double monthlySalary) {
this.monthlySalary = monthlySalary;
}
@Override
public double earnings() {
return monthlySalary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SalariedEmployee [ " + super.toString() + " ]";
}
}
HourlyEmployee类
package oop.exercise.exer13;
public class HourlyEmployee extends Employee {
private double wage;
private double hour;
public HourlyEmployee(String name, int number, MyDate birthday, double wage, double hour) {
super(name, number, birthday);
this.wage = wage;
this.hour = hour;
}
public double getWage() {
return wage;
}
public void setWage(double wage) {
this.wage = wage;
}
public double getHour() {
return hour;
}
public void setHour(double hour) {
this.hour = hour;
}
@Override
public double earnings() {
return wage * hour;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HourlyEmployee [ " + super.toString()+ " ]";
}
}
PayrollSystem类:主方法入口
package oop.exercise.exer13;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PayrollSystem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("please input the current month");
int month = sc.nextInt();
Employee[] employee = new Employee[3];
employee[0] = new SalariedEmployee("jack", 1001, new MyDate(1994, 1, 10), 10000);
employee[1] = new SalariedEmployee("jim", 1002, new MyDate(1994, 5, 13), 11000);
employee[2] = new HourlyEmployee("tom", 1003, new MyDate(1995, 6, 7), 50, 50);
for (int i = 0;i < employee.length;i++) {
System.out.println(employee[i]);
double salary = employee[i].earnings();
System.out.println("monthly paymengt is :" + salary);
if (month == employee[i].getBirthday().getMonth())
System.out.println("happy birthday! bonus is : $" + 100);
}
}
}
6.6 接口



package oop.third;
/*
* 接口的使用
* 1. 接口使用interface来定义
* 2. Java中,接口和类是并列的两个结构
* 3. 如何定义接口:定义接口中的成员
*
* 3.1 JDK7及以前:只能定义全局常量和抽象方法
* >全局常量: public static final的.但是书写时,可以省略不写
* >抽象方法: public abstract的
* 3.2 JDK8: 除了定义全局常量和抽象方法之外,还可以定义静态方法、默认方法(略)
*
* 4. 接口中不能定义构造器! 意味着接口不可以实例化
*
* 5. Java开发中,接口通过让类去实现(implements)的方式来使用, 如果实现类覆盖了接口中的所有抽象方法,
* 则此实现类就可以实例化如果实现类凌有覆盖接口中所有的抽象方法,则此实现类仍为一个抽象类
*
* 6. Java类可以实现多个接口 ---> 弥补了Java单继承性的局限性
* 格式: class AA extends BB implements CC, DD, EE
*
* 7. 接口与接口之间可以继承,而且可以多继承
*
* 8. 接口的具体使用,体现多态性
*
* 9. 接口,实际上可以看做一种规范
*
*/
public class InterfaceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Plane p = new Plane();
p.fly();
p.stop();
}
}
interface Flyable{
//全局常量
public static final int MAX_SPEED = 7900;
int MIN_SPEED = 1; //省略了public static final
//抽象方法
public abstract void fly();
//省略了public abstract
void stop();
}
interface Attackable{
void attack();
}
//类实现接口
class Plane implements Flyable{
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("plane fly with engine");
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("plane stop with pilot");
}
}
//抽象类
abstract class Kite implements Flyable{
@Override
public void fly() {
}
}
class Bullet extends Object implements Flyable, Attackable{
@Override
public void attack() {
System.out.println("bullet can kill people");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void stop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
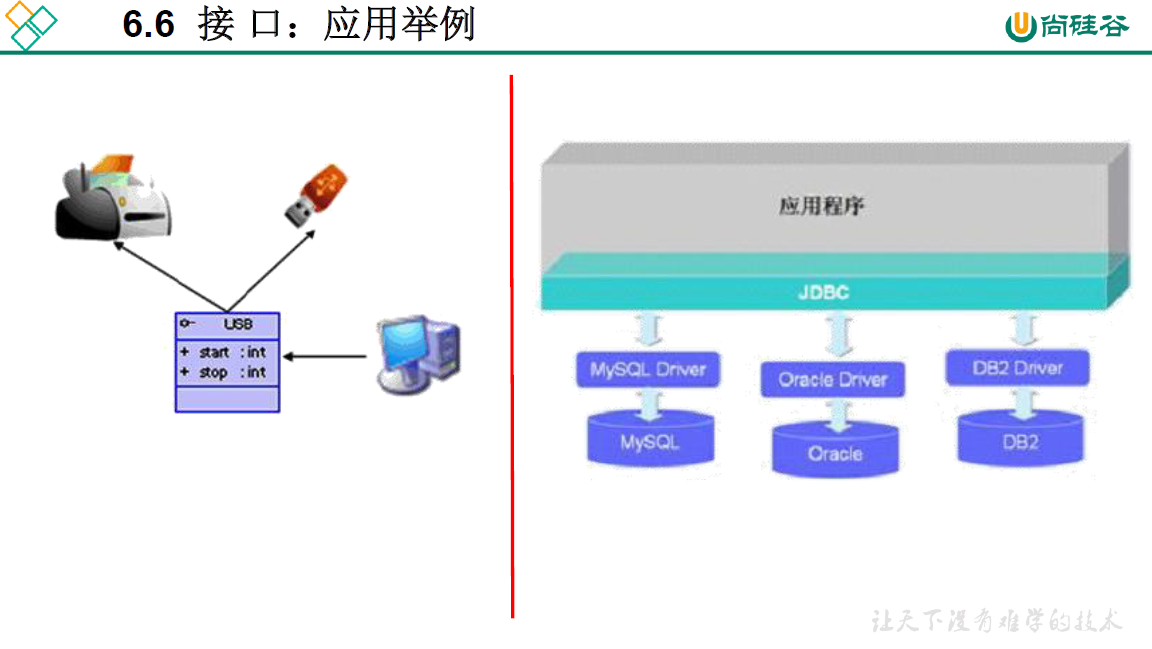
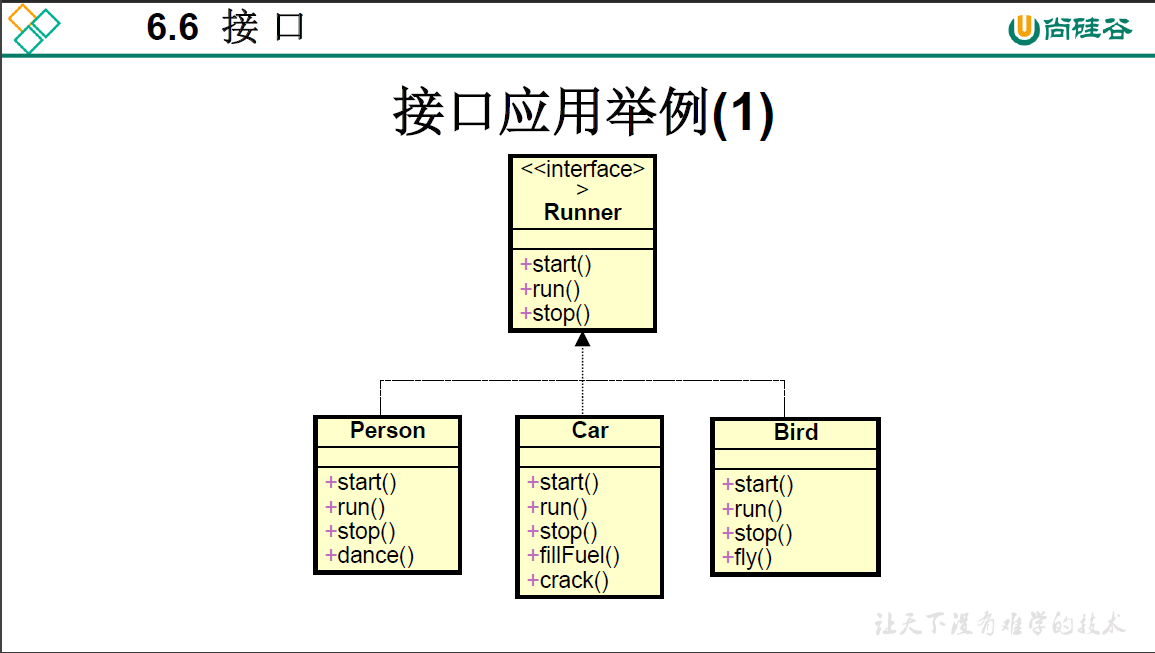
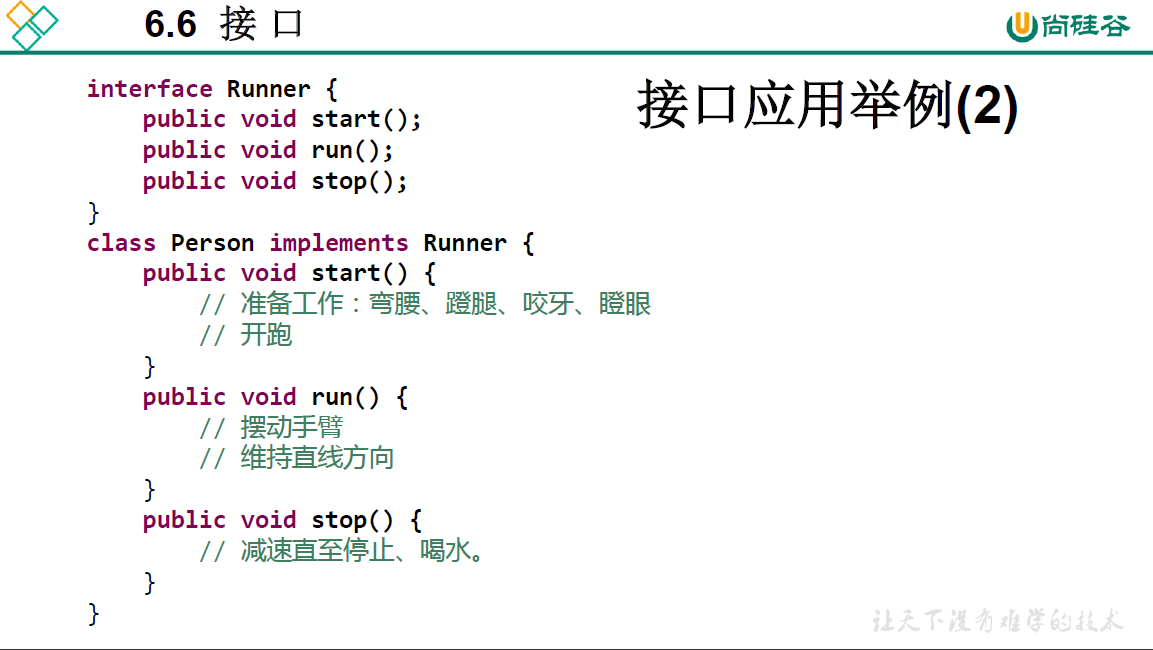
package oop.third;
/*
* 接口的使用
* 1. 接口使用上也满足多态性
* 2. 接口,实际上就是定义了一种规范
* 3. 开发中,体会面向接口编程!
*
*/
public class USBTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PersonalComputer pc = new PersonalComputer();
Printer p = new Printer();
pc.transferData(p);
}
}
class PersonalComputer{
public void transferData(USB usb) {
usb.start();
System.out.println("start transfer data");
usb.stop();
}
}
interface USB{
//常量:定义了长、宽、最大最小的传输速度
void start();
void stop();
}
class Flash implements USB{
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("USB start work");
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("USB stop work");
}
}
class Printer implements USB{
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("printer start work") ;
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("printer stop work") ;
}
}
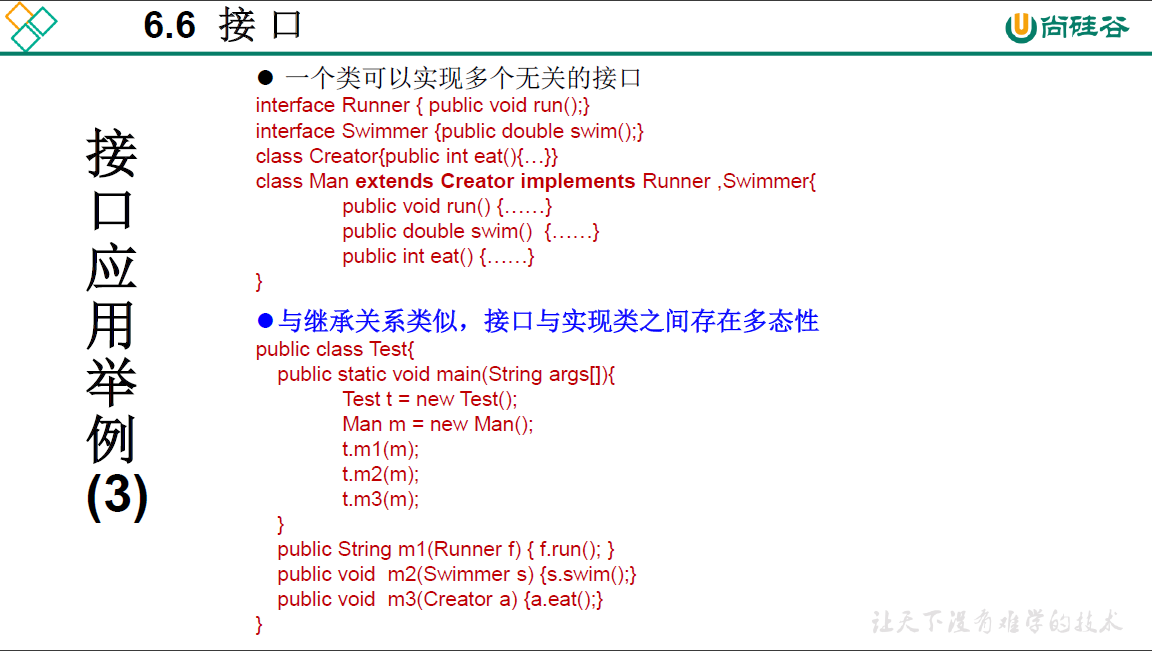
创建接口匿名实现类的对象的4种方式
package oop.third;
/*
* 创建接口匿名实现类的对象的4种方式
*
*/
public class USBTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PersonalComputer pc = new PersonalComputer();
//1. 创建了接口的非匿名实现类的非匿名对象
Printer p = new Printer();
pc.transferData(p);
//2. 创建了接口的非匿名实现类的匿名对象
pc.transferData(new Flash());
//3. 创建了接口的匿名实现类的非匿名对象
USB phone = new USB() {
@Override
public void start() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void stop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
pc.transferData(phone);
//4. 创建了接口的匿名实现类的匿名对象
pc.transferData(new USB() {
@Override
public void start() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void stop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
});
}
}
class PersonalComputer{
public void transferData(USB usb) {
usb.start();
System.out.println("start transfer data");
usb.stop();
}
}
interface USB{
//常量:定义了长、宽、最大最小的传输速度
void start();
void stop();
}
class Flash implements USB{
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("USB start work");
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("USB stop work");
}
}
class Printer implements USB{
@Override
public void start() {
System.out.println("printer start work") ;
}
@Override
public void stop() {
System.out.println("printer stop work") ;
}
}

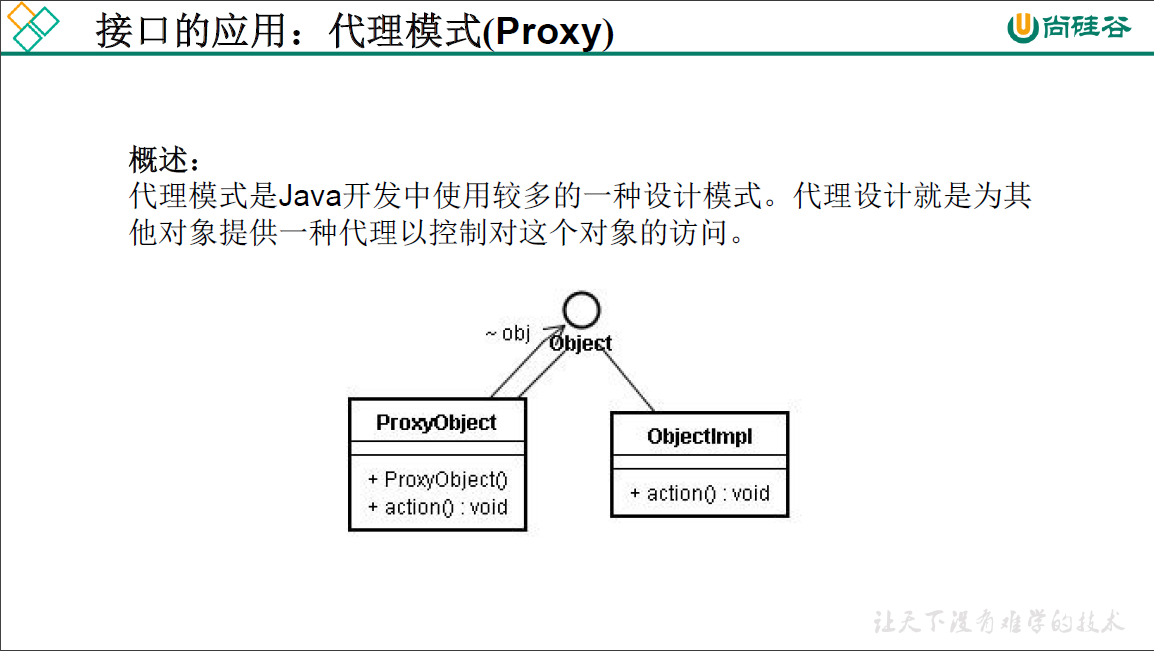
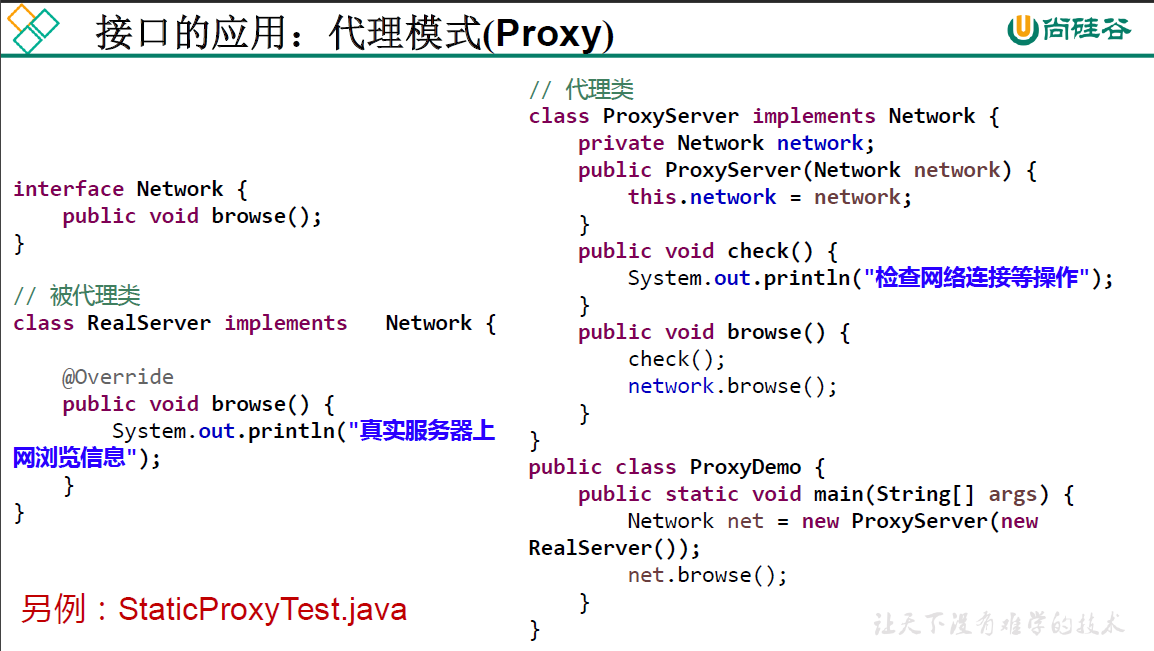

package oop.third;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Network net = new ProxyServer(new RealServer());
net.browse();
}
}
// 接口
interface Network{
public void browse();
}
//被代理类
class RealServer implements Network{
@Override
public void browse() {
System.out.println("the real server browse the information");
}
}
//代理类
class ProxyServer implements Network{
private Network network;
public ProxyServer(Network network) {
this.network = network;
}
public void check() {
System.out.println("check the network connection and so on");
}
// 方法的实际执行通过被代理类
@Override
public void browse() {
check();
network.browse();
}
}
面试题1
package oop.third;
public class InterfaceInterview {
public static void main(String[] args) {
E e = new E();
e.px();
}
}
interface B{
int x = 0;
}
class C{
int x = 1;
}
class E extends C implements B{
public void px() {
// System.out.println(x); //不能这样写,编译器不能确定是哪一个x
System.out.println(super.x); // 1
System.out.println(B.x); // 0
}
}
面试题2
package oop.third;
public class InterfaceInterview1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
interface Playable{
void play();
}
interface Bounceable{
void play();
}
interface Rollable extends Playable, Bounceable{
Ball ball = new Ball("PingPang");
}
class Ball implements Rollable{
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public Ball(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//此处的paly() 方法同时重写了Playable和Bounceable中的paly()方法
public void play() {
ball = new Ball("football"); // final 修饰的变量不能被再赋值
System.out.println(ball.getName());
}
}

CompareObject接口
package oop.exercise.exer14;
public interface CompareObject {
public int compareTo(Object o);
}
Circle类
package oop.exercise.exer14;
public class Circle {
private double radius;
public Circle() {
}
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
}
ComparableCircle类
package oop.exercise.exer14;
public class ComparableCircle extends Circle implements CompareObject{
public ComparableCircle(double radius) {
super(radius);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (this == o)
return 0;
if (o instanceof ComparableCircle) {
ComparableCircle c = (ComparableCircle) o;
if (this.getRadius() > c.getRadius())
return 1;
else if (this.getRadius() == c.getRadius())
return 0;
else
return -1;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据类型不匹配");
}
}
}
ComparableCirclTest 主方法入口
package oop.exercise.exer14;
public class ComparableCircleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ComparableCircle comp1 = new ComparableCircle(4.3);
ComparableCircle comp2 = new ComparableCircle(5.3);
System.out.println(comp1.compareTo(comp2));
}
}
************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
Rectangle类
package oop.exercise.exer14;
public class Rectangle {
private double width;
private double height;
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(double width, double height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public double findArea() {
return width * height;
}
}
ComparableRectangle类
package oop.exercise.exer14;
public class ComparableRectangle extends Rectangle implements CompareObject{
public ComparableRectangle() {
}
public ComparableRectangle(double width, double height) {
super(width, height);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if (this == o)
return 0;
if (o instanceof ComparableRectangle) {
ComparableRectangle c = (ComparableRectangle) o;
if (this.findArea() > c.findArea())
return 1;
else if (this.findArea() == c.findArea())
return 0;
else
return -1;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据类型不匹配");
}
}
}


package oop.third;
/* 知识点1: 接口中定义的静态方法,只能通过接口来调用。
* 知识点2: 通过实现类的对象,可以调用接口中的默认方法, 如果实现类重写了接口中的默认方法,调用时,仍然调用的是重写以后的方法
* 知识点3: 如果子类(或实现类)继承的父类和实现的接口中声明了同名同参数的方法,
* 那么子类在没有重写此方法的情况下,默认调用的是父类中的同名同参数的方法。--->类优先原则
* 知识点4: 如果实现类实现了多个接口,而这多个接口中定义了同名同参数的默认方法,//那么在实现类没有重写此方法的情况下,报错。-->接口冲突。
* 如:class SubClass implements CompareA, CompareB
* 知识点5: 如何在子类(或实现类)的方法中调用父类、接口中被重写的方法
*/
public class Java8Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//知识点1: 接口中定义的静态方法,只能通过接口来调用
CompareA.methd1();
//通过实现类的对象,可以调用接口中的默认方法,
SubClass sc = new SubClass();
sc.method2(); // 如果实现类重写了接口中的默认方法,调用时,仍然调用的是重写以后的方法
sc.method3();
sc.ordinaryMethod();
}
}
//接口CompareA
interface CompareA{
//静态方法
public static void methd1(){
System.out.println("CompareA: beijing");
}
// 默认方法
public default void method2() {
System.out.println("CompareA: shanghai");
}
default void method3() {
System.out.println("CompareA : tokyo");
}
}
//接口CompareB
interface CompareB{
default void method3() {
System.out.println("CompareA : kyoto");
}
}
class SuperClass{
public void method3() {
System.out.println("CompareA : Berlin");
}
}
class SubClass extends SuperClass implements CompareA, CompareB{
public void method2() {
System.out.println("CompareA : NewYork");
}
@Override
public void method3() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("CompareB : London");
}
//知识点5: 如何在子类(或实现类)的方法中调用父类、接口中被重写的方法
public void ordinaryMethod() {
method3(); //调用subclass类中重写的methd3()方法
super.method3(); // 调用的是父类中声明的method3()方法
//调用接口中的默认方法
CompareA.super.method3();
CompareB.super.method3();
}
}
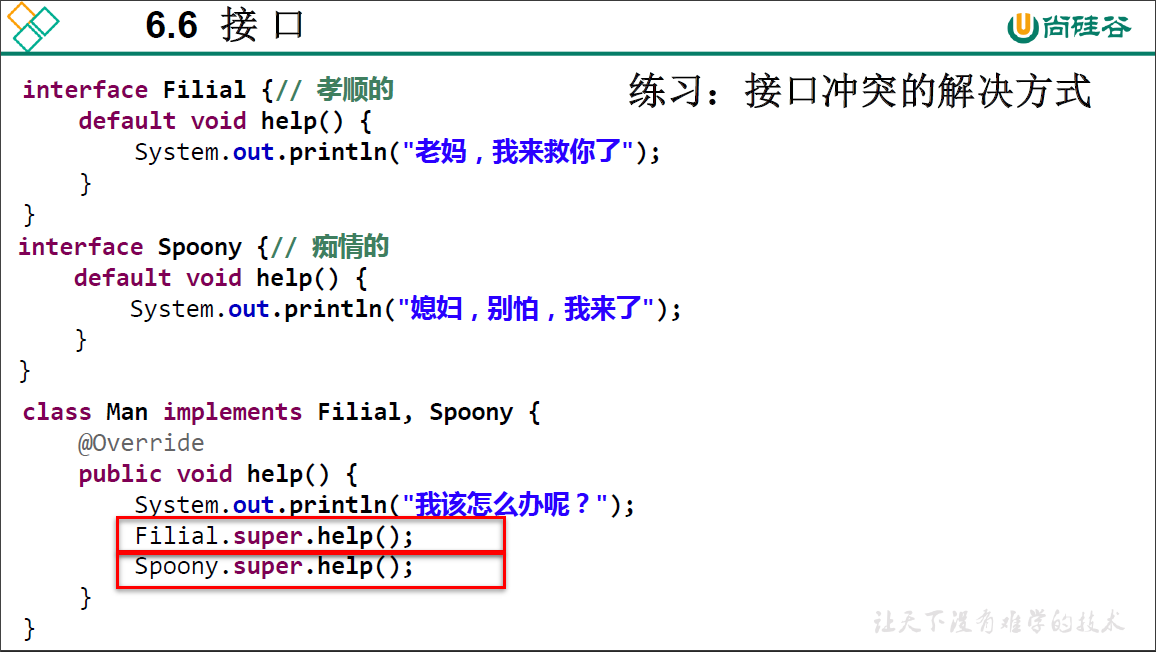
package oop.exercise.exer14;
public class InterfaceConflictTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Man m = new Man();
m.help();
}
}
interface Filial{
default void help() {
System.out.println("mother, I will help you");
}
}
interface Spoony{
default void help() {
System.out.println("wife, I will help you");
}
}
class Man implements Filial, Spoony{
//相当于同时实现了Filial和Spoony接口中的help()方法
public void help() {
System.out.println("what should I do ?");
Filial.super.help();
Spoony.super.help();
}
}
输出结果:
what should I do ?
mother, I will help you
wife, I will help you
6-7类的内部成员之五: 内部类








InnerClassTest
package oop.third;
/*
* 类的内部成员之五:内部类
* 1. Java中允许将一个类A声明在另一个类B中,则类A就是内部类,类B称为外部类
*
* 2. 内部类的分类:成员内部类(静态、非静态)MS局部内部类(方法内、代码块内、构造器内)
*
* 3. 成员内部类:
* 一方面,作为外部类的成员:
* > 调用外部类的结构
* > 可以被static修饰
* > 可以被4种不同的权限修饰
* 另一方面,作为一个类:
* > 类内可以定义属性、方法、构造器等
* > 可以被final修饰,表示此类不能被继承。言外之意,不使用final,就可以被继承
* > 可以被abstract修饰
*
* 4. 关注如下的3个问题
* 4.1 如何实例化成员内部类的对象
* 4.2 如何在成员内部类中区分调用外部类的结构
* 4.3 开发中局部内部类的使用
* 4.4 开发中局部内部类的使用,见《InnerClassTest1.java》
*
*/
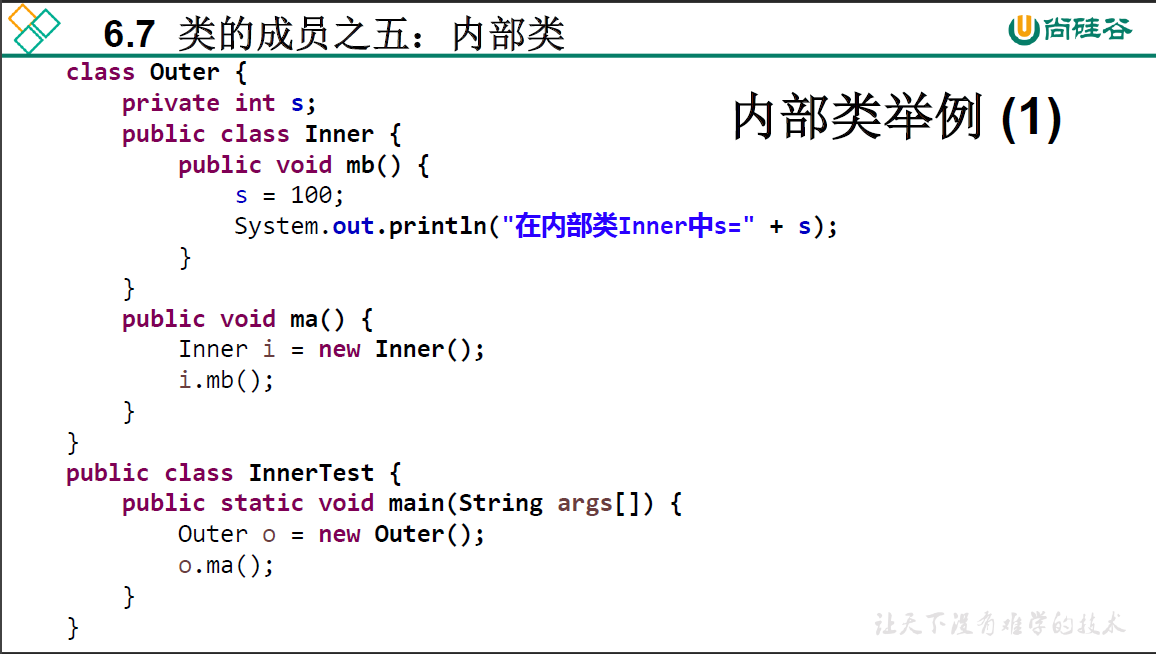
public class InnerClassTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建Dog实例(静态的成员内部类):
People.Dog dog = new People.Dog();
dog.show();
// 创建Bird实例(非静态的成员内部类)∶
People p = new People();
People.Bird bird = p.new Bird();
bird.sing();
System.out.println("***************************");
bird.display("jack");
}
}
class People{
String name = "People";
public void eat() {
System.out.println("people eat rice");
}
//静态成员内部类
static class Dog{
String name = "Dog";
int age;
public void show() {
System.out.println("kala is a dog");
}
// eat(); // 静态成员内部类不能调用外部类的非静态方法
}
//非静态成员内部类
class Bird{
String name = "Bird";
public Bird() {
}
public void sing() {
System.out.println("bird can sing");
People.this.eat(); //调用外部内的非静态方法
}
public void display(String name) {
System.out.println(name); // 方法的形参
System.out.println(this.name); // 内部类的属性
System.out.println(People.this.name); // 外部类的属性
}
}
}
InnerClassTest1
package oop.third;
public class InnerClassTest1 {
//返回一个实现了Comparable接口的类的对象
//创建一个实现了Comparable接口的类:局部内部类
//方式—:
// public static Comparable getComparable() {
// class MyComparable implements Comparable{
//
// @Override
// public int compareTo(Object o) {
// return 0;
// }
// }
// return new MyComparable();
// }
//方式二:匿名类的匿名对象
public static Comparable getComparable() {
return new Comparable(){
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
return 0;
}
};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparable c = getComparable();
System.out.println(c.getClass()); //InnerClassTest1$1MyComparable
}
}

package oop.exercise.exer15;
public class InnerClassExer {
public InnerClassExer() {
Inner s1 = new Inner();
s1.a = 10;
Inner s2 = new Inner();
s2.a = 20;
InnerClassExer.Inner s3 = new InnerClassExer.Inner();
System.out.println(s3.a);
}
class Inner{
public int a = 5;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InnerClassExer ic = new InnerClassExer();
Inner r = ic.new Inner();
System.out.println(r.a);
}
}
//输出结果
5
5
复习题
1. abstract能修饰哪些结构?修饰以后,有什么特点? 类、方法。
- 类不能实例化,提供子类
- 抽象方法,只定义了一种功能的标准。具体的执行,需要子类去实现。
2. 接口是否能继承接口? 抽象类是否能实现(implements)接口? 抽象类刹是否能继承非抽象的类?
能,能,能
3. 声明抽象类,并包含抽象方法。测试类中创建一个继承抽象类的匿名子类的对象。
abstract class AA{
public abstract void m();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AA a = new AA(){
@Override
public void m(){
System.out.println();
}
};
a.m();
}
普通类也可以使用类的匿名子类对象
class AA{
public void m();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
AA a = new AA(){
@Override
public void m(){
System.out.println();
}
};
a.m();
}
4. 抽象类和接口有哪些共同点和区别?
-
相同点: 不能实例化,都可以被继承
-
不同点:
抽象类: 有构造器。
接口: 不能声明构造器多继承vs单继承
5.如何创建静态成员内部类和非静态成员内部类的对象?
Person static Dog Bird
Person.Dog dog = new Person.Dog();
Person p = new Person();
Person.Bird bird = p.new Bird();