向量和矩阵
什么是矩阵/向量?
Vectors and matrix are just collections of ordered numbers that represent something: movements in space, scaling factors, pixel brightness, etc. We'll define some common uses and standard operations on them.
向量:列向量/行向量
用处:
- Vectos can represented an offset in 2D or 3D space; points are just vectors from the origion
- data(pixels, gradient at an image key point)can be treated as a vector
矩阵:在python中图像被表示为像素亮度矩阵, grayscale(m*n), color(m*n*3)
算术运算:
- addition
- scaling
- norm: vector/matrix

- inner prodcut/dot product of vectors
- product of matrix
- transpose
- determinant
通常任何满足以下四种性质的函数都可以作为范数:
- 非负性
- 正定性
- 齐次性
- 三角不等式
特殊矩阵
- 单位阵
- 对角阵
- 对称阵
- 反对阵矩阵
变换矩阵
矩阵可以用来对向量进行变换
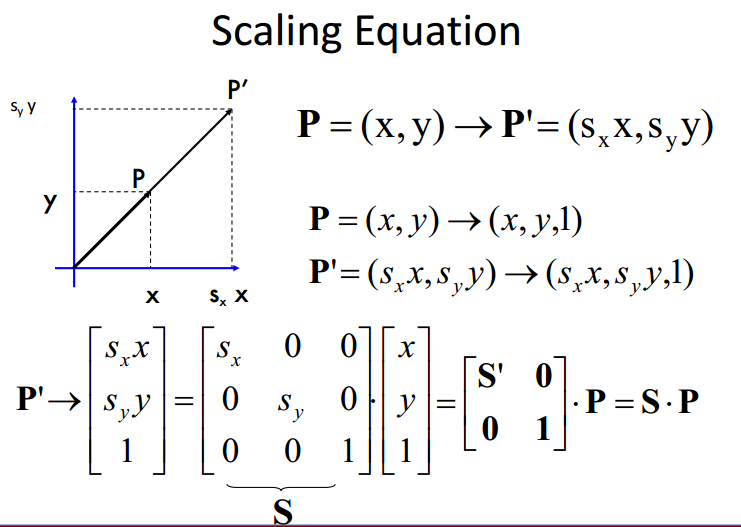
- scaling
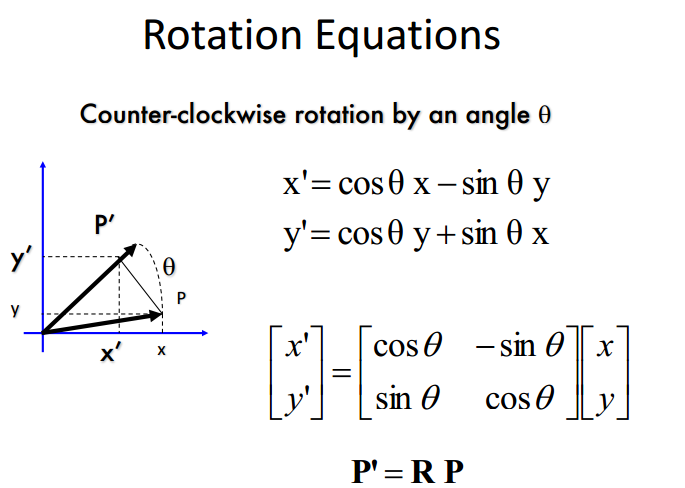
- rotation
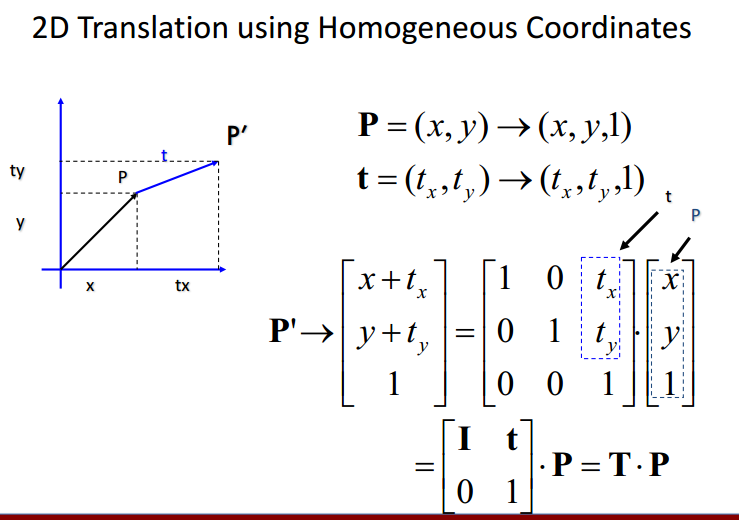
齐次系统/齐次坐标:
变换矩阵最右列被加到原有向量中
这里有时候会用到前面看的仿射矩阵affine matrix 的知识(见参考资料):
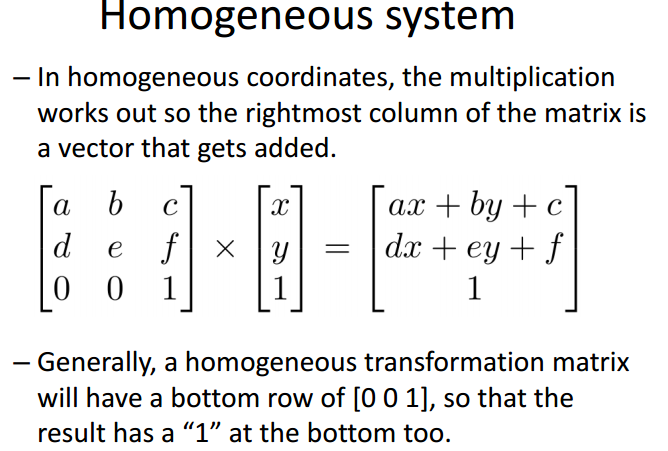
平移(translation):
缩放(scaling)
旋转(rotation)
平移旋转缩放

矩阵的逆
如果A的逆存在,A是可逆的或者是非奇异的non-singular; 否则是不可逆或者是奇异的.
伪逆(pseudoinverse):在计算大型矩阵逆的时候,会伴随这浮点数问题,而且不是每个矩阵都有逆
np.linalg(A,B) to solve AX = B
如果没有具体解, 返回最近的一个解
如果有多个解,返回最小的那个解
矩阵的阶
the rank of a transforamtion matrix tells you hwo many dimensions it transforms a vector to.
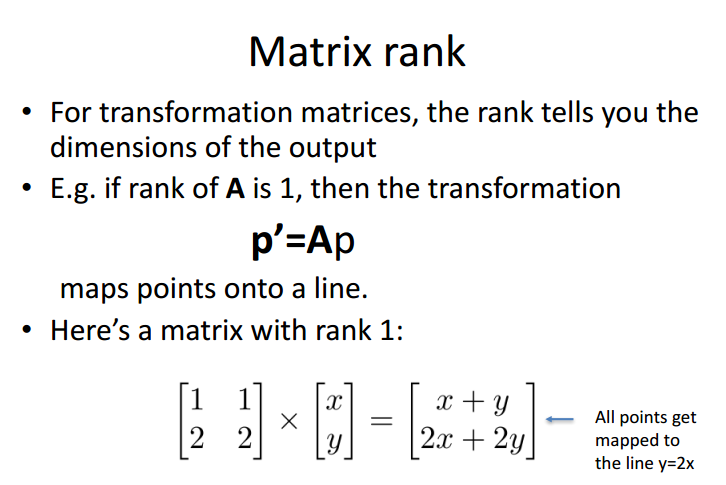
满秩; m*m 矩阵,阶数为m
阶数 < 5, 奇异矩阵,逆不存在
非方阵没有逆
特征值和特征向量
what is eigenvector?
An eigenvector x of a linear transformation A is a non-zero vector that when A is applied to it, does not change direction. And only scales the eigenvector by the scalar value lambda, called an eigenvalue.
$$Ax = lambda x$$
$Ax = (lambda I)x, ightarrow (lambda I - A)x = 0$, $x$ is non-zero, thus, $|(lambda I - A)| = 0$
性质:
- $tr(A) = sum_{i=1}^n lambda_i$
- $|A| = prod_{i=1}^n lambda_i$
- the rank of A is equal to the number of non-zero eigenvalues of A
- the eigenvalues of a diagonal matrix $D = diag(d_1,...d_n)$ are just the diagonal entries $d_1, ..., d_n$
分形理论(spectral theroy)

对角化(diagonalization)
如果n*n矩阵有n个线性独立的特征向量,则它是可对角化的
如果n*n矩阵有n个不同的特征值,则它是可对角化的
对应着不同特征值的特征向量是线性独立的
所有的特征向量方程可以写为:
$$AV = VD$$
$V in R^{n*n}$ V的列是A的特征向量,D为对角矩阵,对应着值为A的特征值. 如果A可以写为:$A = VDV^{-1}$则A可对角化

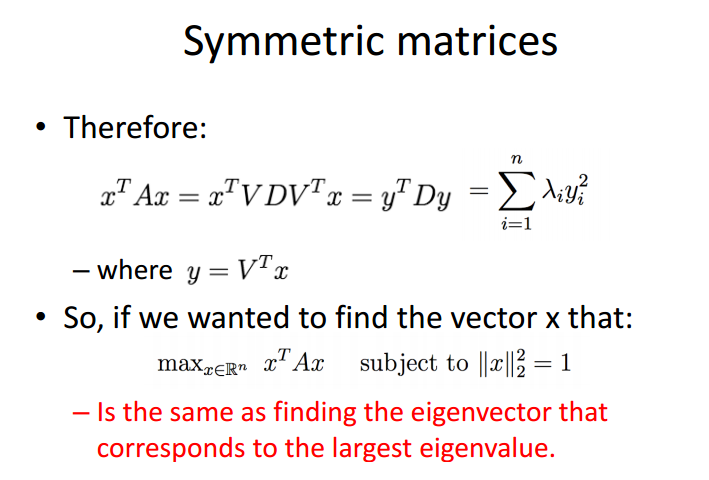
特征值特征向量和对称对阵
对称矩阵的性质:$A^{-1} = A^T$, A所有的特征值都是实数,A所有的特征向量都是正交的.
Some applications of eigenvlues: PageRank, Schrodinger's equation, PCA
矩阵代数
矩阵梯度:
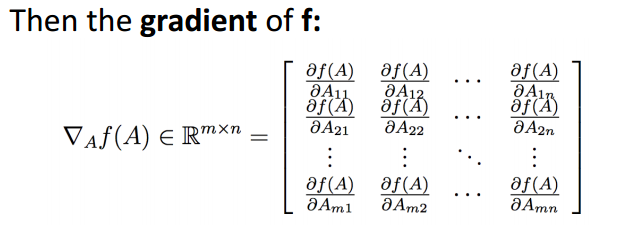
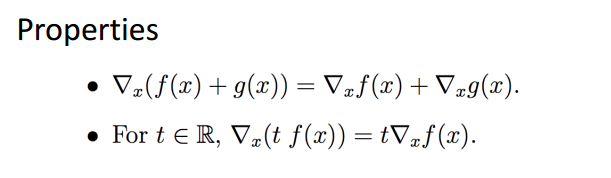
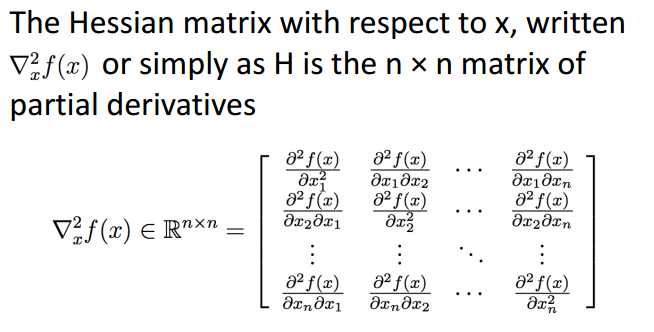
Hessian Matrix
参考资料:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/framework/winforms/advanced/how-to-rotate-reflect-and-skew-images