参考资料:
[1]:http://www.voidcn.com/article/p-huucvank-dv.html
题意:
题意就是找一个连续的子区间,使它的和的绝对值最接近target。
题解:
这题的做法是先预处理出前缀和,然后对前缀和进行排序,再用尺取法贪心的去找最合适的区间。
要注意的是尺取法时首尾指针一定不能相同,因为这时区间相减结果为0,但实际上区间为空,这是不存在的,可能会产生错误的结果。
处理时,把(0,0)这个点也放进数组一起排序,比单独判断起点为1的区间更方便。
还有ans初始化的值INF一定要大于t的最大值。
最后说说这个题最重要的突破口,对前缀和排序。为什么这么做是对的呢?
因为这题是取区间的和的绝对值,所以所以用sum[r]-sum[l] 和 sum[l]-sum[r]是没有区别的。
这样排序后,把原来无序的前缀和变成有序的了,就便于枚举的处理,并且不影响最终结果。
以上分析来自参考资料[1]。
AC代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define P pair<int ,int > 6 const int maxn=1e5+10; 7 8 int n,k; 9 P p[maxn]; 10 11 bool cmp(P _a,P _b){ 12 return _a.second < _b.second; 13 } 14 void Solve(int t) 15 { 16 int l=0,r=1; 17 int resL=p[l].first,resR=p[r].first;//先假设区间[1,p[1].first]为解 18 int resSum=p[r].second-p[l].second; 19 while(r <= n) 20 { 21 int curSum=p[r].second-p[l].second; 22 if(abs(curSum-t) < abs(resSum-t))//判断是否可以更新 resSum 23 { 24 resSum=curSum; 25 resL=p[l].first; 26 resR=p[r].first; 27 } 28 if(curSum < t)//如果当前区间值过小,增大当前值 29 r++; 30 else if(curSum > t)//如果当前区间值过大,减小当前值 31 l++; 32 else 33 break; 34 if(l == r) 35 r++; 36 } 37 if(resL > resR) 38 swap(resL,resR); 39 printf("%d %d %d ",resSum,resL+1,resR);//while()循环中做区间减法时始终左边界一直被减掉 40 } 41 int main() 42 { 43 // freopen("C:\Users\lenovo\Desktop\in.txt\poj2566.txt","r",stdin); 44 while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&k),n != 0 || k != 0) 45 { 46 int sum=0; 47 for(int i=1;i <= n;++i) 48 { 49 int val; 50 scanf("%d",&val); 51 sum += val; 52 p[i]=P(i,sum); 53 } 54 p[0]=P(0,0); 55 sort(p,p+n+1,cmp); 56 while(k--) 57 { 58 int t; 59 scanf("%d",&t); 60 Solve(t); 61 } 62 } 63 return 0; 64 }
我的理解:
为什么对前缀和用尺取法是正确的呢?
定义 pair<int ,int > 型变量 p[ maxn ];
p[ i ].first : 右边界;
p[ i ].second : 前 p[ i ].first 项和;
将 p 按前缀和从小到大排序后,如图所示:
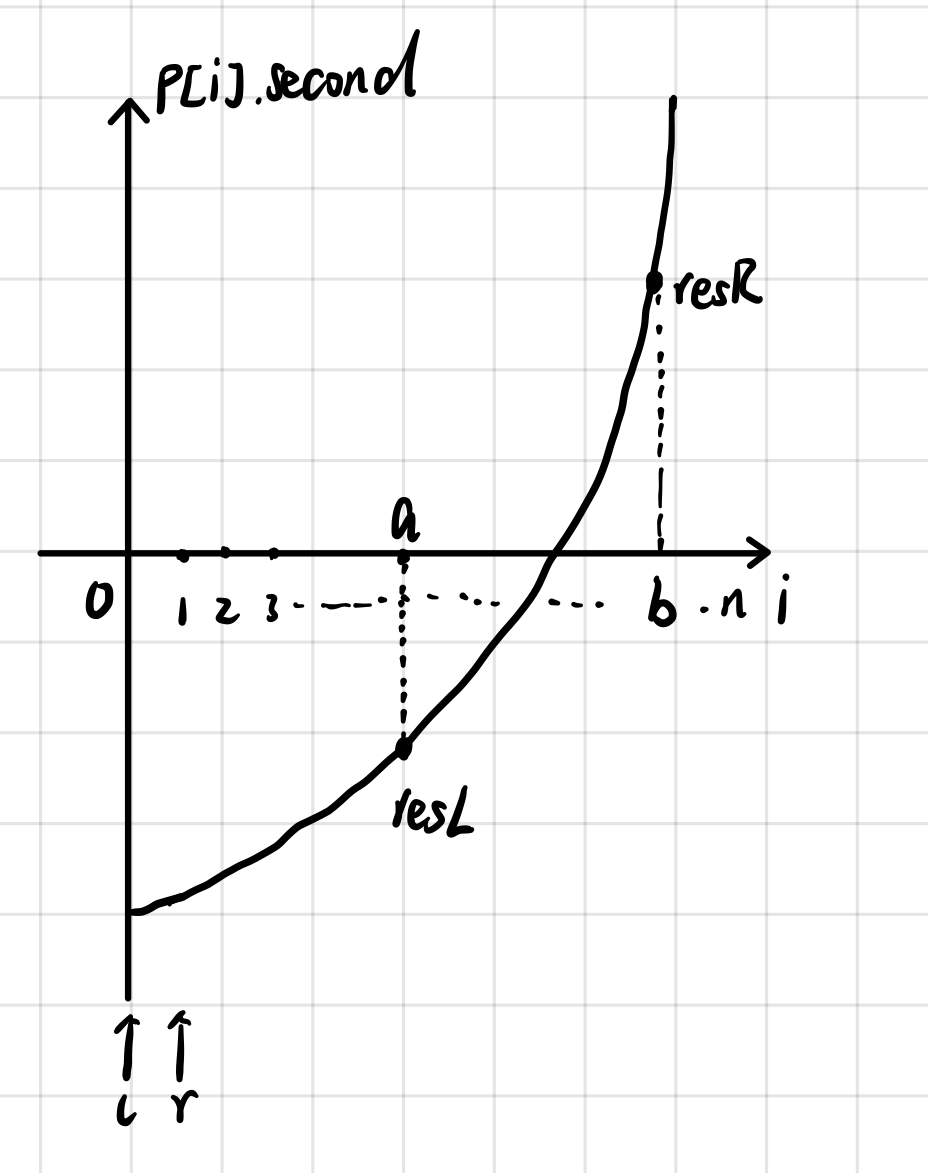
纵坐标 : 排序后的前缀和
假设 ( p[b].second-p[a].second ) 距 t 最近 , resSum = p[b].second-p[a].second;
问题1:当 R 来到区间(a,b)时,L 有可能超过 a 吗?
答案:不会。
分析如下:当 a < R < b , L = a 时, 令 curSum=p[R].second-p[L].second;
易得 curSum < resSum;
根据 Solve() 中 while() 循环的代码,只由当 curSum > target 时,才会使 L++;
假设 curSum > target , 则 resSum > curSum > target,那么答案就为 curSum 所标示的区间而不是resSum 所表示的区间,与假设不符;
故当 L = a , a < R < b 时,curSum < target ,直到 R 来到 b 。
问题2:当 L < a 时,R 有可能超过 b 吗?
答案:不会。
分析如下:当 L < a , R = b 时,令 curSum=p[R].second-p[L].second;
易得 curSum > resSum;
根据 Solve() 中 while() 循环的代码,只由当 curSum < target 时,才会使R++;
假设 curSum < target , 则 resSum < curSum < target,那么答案就为 curSum 所标示的区间而不是resSum 所表示的区间,与假设不符;
故当 R = b , L < a 时,curSum > target ,直到 L 来到 a 。
综上所述,L,R一定会来到答案所对应的区间。
问题3:为什么要加入 (0,0)点?
根据Solve()中的while()循环可知,curSum求的是L,R区间的差集(大-小)的和,如果答案的左区间为 1 呢?
不加入 (0,0) 点就永远也不可能使某两区间的差集(大-小)包含 1 .
或者说可以另用一重循环判断,感觉加入 (0,0)点更美观,哈哈哈。
