windows 系统控制台里给我提供很方便的运行的程序的方式。类似老式的dos环境。但是这种控制台的交互风格还是非常方便的。即便在现在的情况下,因为有些操作不使用图形化的界面反而会比较快捷。在控制台环境下,我们可以执行很多指令,比如“dir","ipconfig /all","ping"等。我们今天尝试做个图形化的界面,同样可以执行执行,并将执行的结果在winform窗体里显示。如下图:
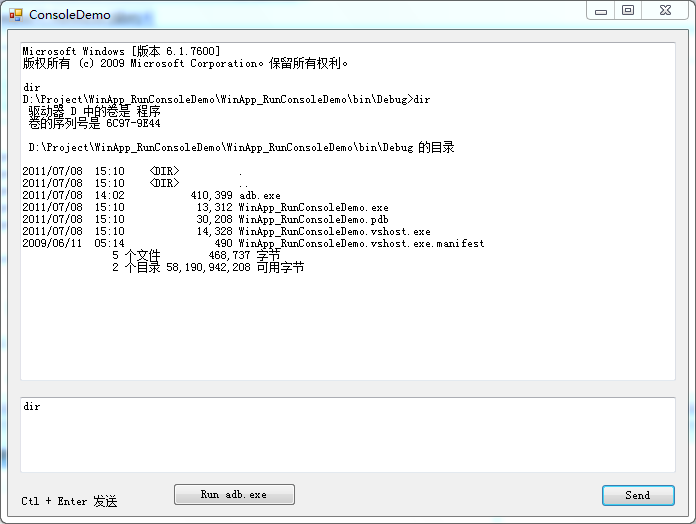
如上图所示,该窗体类似打开了一个控制台,在下方的文本框输入 "dir"指令时,会在上面提示区显示执行后的结果的内容。
这个过程是怎么实现的呢?实际上开启了一个控制台的进程,在这个进程里执行了cmd(相当于你启动一个控制台)。在我们的程序执行时,我们将 指令(比如上面输入的dir指令)发送给 这个进程,并且将这个进程的输出结果读取出来,显示在我们的winform窗体界面上。也就是说,我们开启了一个控制台,并为这个控制台做了输入,输出的重新定向,将这个控制台的输入输出的通道指向了我们的应用程序。使得我们可以将指令通过这个通道发送给控制台,并读取到控制台的输出结果。
我们是如何启动一个控制台的进程呢?代码如下:
startInfo.FileName = "cmd";
startInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
startInfo.UseShellExecute = false;
//startInfo.WindowStyle = ProcessWindowStyle.Normal;
startInfo.RedirectStandardInput = true;
startInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
startInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
startInfo.WorkingDirectory = Application.StartupPath;
_consoleProcess = Process.Start(startInfo);
在这里 构建了一个ProcessStartInfo 对象,这个对象描述了一个 启动项信息,它包括了 文件名,参数等。再调用Process.Start(startInfo)方法,来启动它。
注意上面的代码中,我们开启了它的重定向,也就是这三行代码:
startInfo.RedirectStandardInput = true;startInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
startInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
它指示了我们会对这个进程的输入,输出,错误进行重定向。
那么在,启动了一个重定向后的进程后,我们如何读取输出的内容,错误信息,和输入数据呢?
{
while (true)
{
if (_consoleProcess != null && !_consoleProcess.HasExited)
{
StreamReader sr = _consoleProcess.StandardError;
string str = sr.ReadLine();
Println(str);
}
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}));
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(delegate
{
while (true)
{
if (_consoleProcess != null && !_consoleProcess.HasExited)
{
StreamReader sr = _consoleProcess.StandardOutput;
string str = sr.ReadLine();
Println(str);
}
Thread.Sleep(10);
}
}));
如上面的代码所示,我么启动了两个线程,在这两个线程里,我们不停的读取这个进程 的 输出流,和错误流 里的数据,如果有,我们就把它显示出来。
那么如何写入数据到这个进程的输入流呢?
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(command))
{
if (_consoleProcess != null && !_consoleProcess.HasExited)
{
StreamWriter sw = _consoleProcess.StandardInput;
sw.WriteLine(command);
}
Println(command);
txtCommand.Text = "";
}
如上代码所示,我们从一个TextBox里(名字是txtCommand)读取 用户在窗体的输入框里输入的内容,然后获得 这个流的StandardInput,并将数据写过这个流内。
同时显示获得的数据内容的方法Println的实现:
/// 输出
/// </summary>
/// <param name="str"></param>
public void Println(string str)
{
this.Invoke(new MethodInvoker(delegate
{
if (str.EndsWith("\n"))
{
txtMessage.AppendText(str);
}
else
{
txtMessage.AppendText(str + "\n");
}
txtMessage.ScrollToCaret();
}));
}
至此,我们就完成了一个控制台的重定向演示。
----
下面是一些扩展内容
有时候我们会拿到一些exe文件,这些文件运行在控制台模式,必须sqlite,android里的adb等。这个时候我们需要调用这些exe来执行一些操作,而且想获得这些操作的执行结果,于是,我尝试自己封装了一个类,该类用于执行 这样的exe,并获得执行结果。代码如下:
* @名称 :
* @描述 :
* @创建人 : 张云飞
* @创建日期: 2011/7/8 15:10:14
* @修改记录:
* ----------------------------------------------------------*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace WinApp_RunConsoleDemo
{
/// <summary>
/// 指令
/// </summary>
public class Command
{
string _workDirectory;//工作文件夹,应该指向 你要执行的exe文件的所在路径
public Command()
{
}
public Command(string workDirectory)
{
_workDirectory = workDirectory;
}
//comamndString是要执行的文件名,argment是执行参数,output是执行的输出结果,errout是当错误时返回的结果。
public bool RunCommand(string comamndString, string argment, out string output, out string errout)
{
StringBuilder _result = null;
StringBuilder _error = null;
_result = new StringBuilder();
_error = new StringBuilder();
ProcessStartInfo startInfo = new ProcessStartInfo();
startInfo.FileName = comamndString;// "adb devices";
startInfo.Arguments = argment;
startInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
startInfo.UseShellExecute = false;
//startInfo.WindowStyle = ProcessWindowStyle.Normal;
startInfo.RedirectStandardInput = true;
startInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
startInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
startInfo.WorkingDirectory = _workDirectory;
Process process1 = null;
try
{
process1 = Process.Start(startInfo);
//接收错误的事件
process1.ErrorDataReceived += (object sender, DataReceivedEventArgs e) =>
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(e.Data))
{
_result.AppendLine(e.Data);
}
};
//接收数据的事件
process1.OutputDataReceived += (object sender, DataReceivedEventArgs e) =>
{
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(e.Data))
{
_error.AppendLine(e.Data);
}
};
process1.BeginErrorReadLine();
process1.BeginOutputReadLine();
//result = sr2.ReadToEnd();
//err = sr1.ReadToEnd();
process1.WaitForExit();
}
catch (Exception)
{
throw;
}
finally
{
if (process1 != null && !process1.HasExited)
{
process1.Kill();
}
}
output = _result.ToString();
errout = _error.ToString();
_error = null;
_result = null;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(errout))
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
}
}
下面是执行的测试代码:
string output;
string error;
if (cmd.RunCommand("adb.exe","devices",out output,out error))
{
MessageBox.Show("Ok:" + output);
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Error:" + error);
}
如上代码所示,我指向了一个路径“Application.StartupPath”,这个是应用程序的启动目录,我在这里将android的adb.exe拷贝到了应用程序的根目录。上面代码相当于执行了"adb devices"这个查看设备列表的指令。