LinkedList是基于链表结构的一种List,在分析LinkedList源码前有必要对链表结构进行说明。
1.链表的概念
链表是由一系列非连续的节点组成的存储结构,简单分下类的话,链表又分为单向链表和双向链表,而单向/双向链表又可以分为循环链表和非循环链表,下面简单就这四种链表进行图解说明。
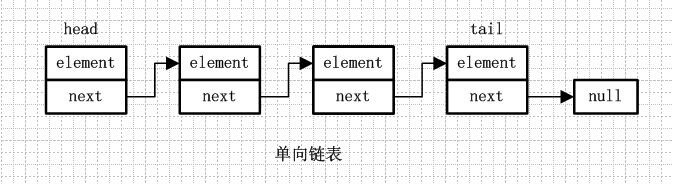
1.1.单向链表
单向链表就是通过每个结点的指针指向下一个结点从而链接起来的结构,最后一个节点的next指向null。
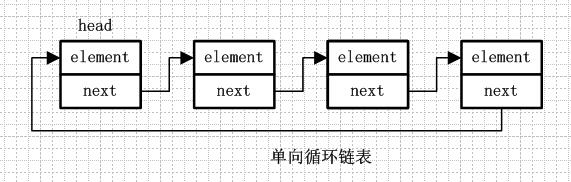
1. 2.单向循环链表
单向循环链表和单向列表的不同是,最后一个节点的next不是指向null,而是指向head节点,形成一个“环”。
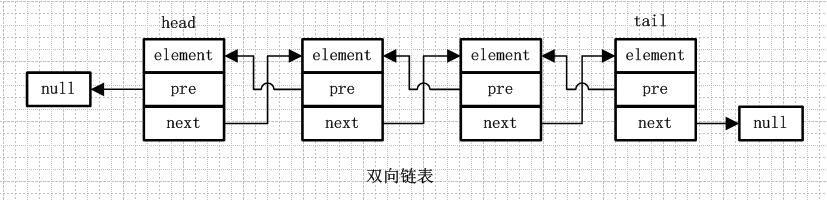
1. 3.双向链表
从名字就可以看出,双向链表是包含两个指针的,pre指向前一个节点,next指向后一个节点,但是第一个节点head的pre指向null,最后一个节点的tail指向null。
1. 4.双向循环链表
双向循环链表和双向链表的不同在于,第一个节点的pre指向最后一个节点,最后一个节点的next指向第一个节点,也形成一个“环”。而LinkedList就是基于双向循环链表设计的。
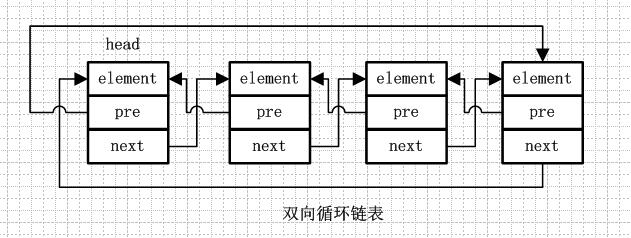
更形象的解释下就是:双向循环链表就像一群小孩手牵手围成一个圈,第一个小孩的右手拉着第二个小孩的左手,第二个小孩的左手拉着第一个小孩的右手。。。最后一个小孩的右手拉着第一个小孩的左手。
ok,链表的概念介绍完了,下面进入写注释和源码分析部分,但是在这之前还是要提醒一句,不是啰嗦哦,链表操作理解起来比数组困难了不少,所以务必要理解上面的图解,如果源码解析过程中遇到理解困难,请返回来照图理解。
2.定义
同样先来看看LinkedList 的定义部分,
|
1
2
3
|
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable |
可以看出LinkedList 继承AbstractSequentialList 抽象类,实现了List,Deque,Cloneable,Serializable 几个接口,AbstractSequentialList 继承 AbstractList,是对其中方法的再抽象,其主要作用是最大限度地减少了实现受“连续访问”数据存储(如链接列表)支持的此接口所需的工作,简单说就是,如果需要快速的添加删除数据等,用AbstractSequentialList抽象类,若是需要快速随机的访问数据等用AbstractList抽象类(详细说明会在iterator 分析中进行解释)。
Deque 是一个双向队列,也就是既可以先入先出,又可以先入后出,再直白一点就是既可以在头部添加元素又在尾部添加元素,既可以在头部获取元素又可以在尾部获取元素。看下Deque的定义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> { void addFirst(E e); boolean offerFirst(E e); boolean offerLast(E e); E removeFirst(); E removeLast(); E pollFirst(); E pollLast(); E getFirst(); E getLast(); E peekFirst(); E peekLast(); boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o); boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o); // *** Queue methods *** boolean add(E e); boolean offer(E e); E remove(); E poll(); E element(); E peek(); // *** Stack methods *** void push(E e); E pop(); // *** Collection methods *** boolean remove(Object o); boolean contains(Object o); public int size(); Iterator<E> iterator(); Iterator<E> descendingIterator();} |
3.底层存储
明白了上面的链表概念,以及LinkedList是基于双向循环链表设计的,下面在具体来看看LinkedList的底层存储实现方式。
|
1
2
|
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);private transient int size = 0; |
LinkedList中提供了上面两个属性,其中size和ArrayList中一样用来计数,表示list的元素数量,而header则是链表的头结点,Entry则是链表的节点对象。
private static class Entry<E> {
E element; // 当前存储元素
Entry<E> next; // 下一个元素节点
Entry<E> previous; // 上一个元素节点
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) {
this.element = element;
this.next = next;
this.previous = previous;
}
}
Entry为LinkedList 的内部类,其中定义了当前存储的元素,以及该元素的上一个元素和下一个元素。结合上面双向链表的示意图很容易看懂。
4.构造方法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
/** * 构造一个空的LinkedList . */ public LinkedList() { //将header节点的前一节点和后一节点都设置为自身 header.next = header. previous = header ; } /** * 构造一个包含指定 collection 中的元素的列表,这些元素按其 collection 的迭代器返回的顺序排列 */ public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); } |
需要注意的是空的LinkedList构造方法,它将header节点的前一节点和后一节点都设置为自身,这里便说明LinkedList 是一个双向循环链表,如果只是单存的双向链表而不是循环链表,他的实现应该是这样的:
|
1
2
3
4
|
public LinkedList() { header.next = null; header. previous = null;} |
非循环链表的情况应该是header节点的前一节点和后一节点均为null(参见链表图解)。
5.增加
增加方法的代码读起来比较不容易理解,需要的时候请结合链表图解。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/** * 将一个元素添加至list尾部 */ public boolean add(E e) { // 在header前添加元素e,header前就是最后一个结点啦,就是在最后一个结点的后面添加元素e addBefore(e, header); return true; } /** * 在指定位置添加元素 */ public void add(int index, E element) { // 如果index等于list元素个数,则在队尾添加元素(header之前),否则在index节点前添加元素 addBefore(element, (index== size ? header : entry(index))); } private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) { // 用entry创建一个要添加的新节点,next为entry,previous为entry.previous,意思就是新节点插入entry前面,确定自身的前后引用, Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous); // 下面修改newEntry的前后节点的引用,确保其链表的引用关系是正确的 // 将上一个节点的next指向自己 newEntry. previous.next = newEntry; // 将下一个节点的previous指向自己 newEntry. next.previous = newEntry; // 计数+1 size++; modCount++; return newEntry;} |
到这里可以发现一点疑虑,header作为双向循环链表的头结点是不保存数据的,也就是说hedaer中的element永远等于null。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
/** * 添加一个集合元素到list中 */ public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { // 将集合元素添加到list最后的尾部 return addAll(size , c); } /** * 在指定位置添加一个集合元素到list中 */public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { // 越界检查 if (index < 0 || index > size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: "+index+ ", Size: "+size ); Object[] a = c.toArray(); // 要插入元素的个数 int numNew = a.length ; if (numNew==0) return false; modCount++; // 找出要插入元素的前后节点 // 获取要插入index位置的下一个节点,如果index正好是lsit尾部的位置那么下一个节点就是header,否则需要查找index位置的节点 Entry<E> successor = (index== size ? header : entry(index)); // 获取要插入index位置的上一个节点,因为是插入,所以上一个点击就是未插入前下一个节点的上一个 Entry<E> predecessor = successor. previous; // 循环插入 for (int i=0; i<numNew; i++) { // 构造一个节点,确认自身的前后引用 Entry<E> e = new Entry<E>((E)a[i], successor, predecessor); // 将插入位置上一个节点的下一个元素引用指向当前元素(这里不修改下一个节点的上一个元素引用,是因为下一个节点随着循环一直在变) predecessor. next = e; // 最后修改插入位置的上一个节点为自身,这里主要是为了下次遍历后续元素插入在当前节点的后面,确保这些元素本身的顺序 predecessor = e; } // 遍历完所有元素,最后修改下一个节点的上一个元素引用为遍历的最后一个元素 successor. previous = predecessor; // 修改计数器 size += numNew; return true;} |
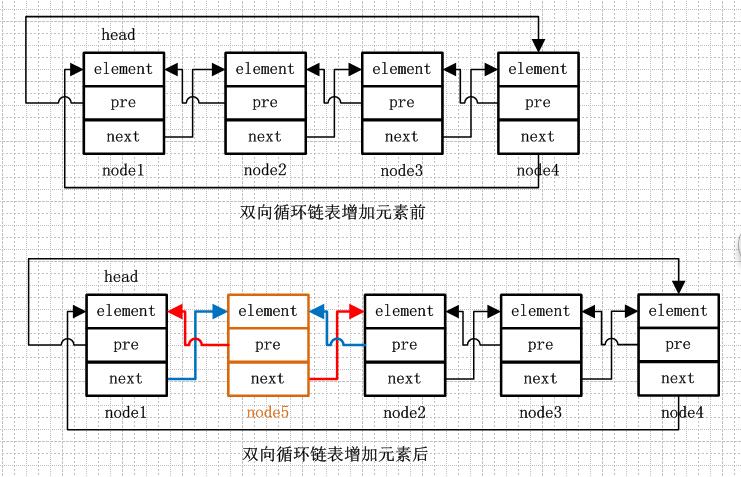
增加方法的代码理解起来可能有些困难,但是只要理解了双向链表的存储结构,掌握增加的核心逻辑就可以了,这里总结一下往链表中增加元素的核心逻辑:1.将元素转换为链表节点,2.增加该节点的前后引用(即pre和next分别指向哪一个节点),3.前后节点对该节点的引用(前节点的next指向该节点,后节点的pre指向该节点)。现在再看下就这么简单么,就是改变前后的互相指向关系(看图增加元素前后的变化)。
其实删除也是一样的对不对?下面看看删除方法的实现。
PS:不要问我entry()方法是怎么回事,这里先不讲,打我也不讲。。。
6.删除
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
/** * 删除第一个匹配的指定元素 */ public boolean remove(Object o) { // 遍历链表找到要被删除的节点 if (o==null) { for (Entry<E> e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) { if (e.element ==null) { remove(e); return true; } } } else { for (Entry<E> e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) { if (o.equals(e.element )) { remove(e); return true; } } } return false;}private E remove(Entry<E> e) { if (e == header ) throw new NoSuchElementException(); // 被删除的元素,供返回 E result = e. element; // 下面修正前后对该节点的引用 // 将该节点的上一个节点的next指向该节点的下一个节点 e. previous.next = e.next; // 将该节点的下一个节点的previous指向该节点的上一个节点 e. next.previous = e.previous; // 修正该节点自身的前后引用 e. next = e.previous = null; // 将自身置空,让gc可以尽快回收 e. element = null; // 计数器减一 size--; modCount++; return result;} |
上面对于链表增加元素总结了,一句话就是“改变前后的互相指向关系”,删除也是同样的道理,由于节点被删除,该节点的上一个节点和下一个节点互相拉一下小手就可以了,注意的是“互相”,不能一厢情愿。
7.修改
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
/** * 修改指定位置索引位置的元素 */ public E set( int index, E element) { // 查找index位置的节点 Entry<E> e = entry(index); // 取出该节点的元素,供返回使用 E oldVal = e. element; // 用新元素替换旧元素 e. element = element; // 返回旧元素 return oldVal;} |
set方法看起来简单了很多,只要修改该节点上的元素就好了,但是不要忽略了这里的entry()方法,重点就是它。
8.查询
终于到查询了,终于发现了上面经常出现的那个方法entry()根据index查询节点,我们知道数组是有下标的,通过下标操作天然的支持根据index查询元素,而链表中是没有index概念呢,那么怎么样才能通过index查询到对应的元素呢,下面就来看看LinkedList是怎么实现的。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/** * 查找指定索引位置的元素 */ public E get( int index) { return entry(index).element ; } /** * 返回指定索引位置的节点 */private Entry<E> entry( int index) { // 越界检查 if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException( "Index: "+index+ ", Size: "+size ); // 取出头结点 Entry<E> e = header; // size>>1右移一位代表除以2,这里使用简单的二分方法,判断index与list的中间位置的距离 if (index < (size >> 1)) { // 如果index距离list中间位置较近,则从头部向后遍历(next) for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) e = e. next; } else { // 如果index距离list中间位置较远,则从头部向前遍历(previous) for (int i = size; i > index; i--) e = e. previous; } return e;} |
现在知道了,LinkedList是通过从header开始index计为0,然后一直往下遍历(next),直到到底index位置。为了优化查询效率,LinkedList采用了二分查找(这里说的二分只是简单的一次二分),判断index与size中间位置的距离,采取从header向后还是向前查找。
到这里我们明白,基于双向循环链表实现的LinkedList,通过索引Index的操作时低效的,index所对应的元素越靠近中间所费时间越长。而向链表两端插入和删除元素则是非常高效的(如果不是两端的话,都需要对链表进行遍历查找)。
9.是否包含
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
|
/** * Returns <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element. * More formally, returns <tt>true</tt> if and only if this list contains * at least one element <tt>e</tt> such that * <tt>(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))</tt>. * * @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested * @return <tt> true</tt> if this list contains the specified element */ public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) != -1; } /** * Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the lowest index <tt>i</tt> such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, * or -1 if there is no such index. * * @param o element to search for * @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element */ public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o==null) { for (Entry e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) { if (e.element ==null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Entry e = header .next; e != header; e = e.next ) { if (o.equals(e.element )) return index; index++; } } return -1; } /** * Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element * in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element. * More formally, returns the highest index <tt>i</tt> such that * <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>, * or -1 if there is no such index. * * @param o element to search for * @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in * this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element */ public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { int index = size ; if (o==null) { for (Entry e = header .previous; e != header; e = e.previous ) { index--; if (e.element ==null) return index; } } else { for (Entry e = header .previous; e != header; e = e.previous ) { index--; if (o.equals(e.element )) return index; } } return -1; } |
和public boolean remove(Object o) 一样,indexOf查询元素位于容器的索引位置,都是需要对链表进行遍历操作,当然也就是低效了啦。
10.判断容量
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
/** * Returns the number of elements in this list. * * @return the number of elements in this list */ public int size() { return size ; } /** * {@inheritDoc} * * <p>This implementation returns <tt>size() == 0 </tt>. */ public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; } |
和ArrayList一样,基于计数器size操作,容量判断很方便。
到这里LinkedList就分析完了,不对好像还差些什么对不对?是什么呢,就是最开始说的Deque双端队列,明白了链表原理和LinkedList的基本crud操作,Deque的LinkedList实现就已经是so easy了,我们简单看下。
11.LinkedList实现的Deque双端队列
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
|
/** * Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list. * * @param e the element to add * @return <tt> true</tt> (as specified by {@link Queue#offer}) * @since 1.5 */ public boolean offer(E e) { return add(e);}/** * Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list * @return the head of this list, or <tt>null </tt> if this list is empty * @since 1.5 */public E poll() { if (size ==0) return null; return removeFirst();}/** * Removes and returns the first element from this list. * * @return the first element from this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty */public E removeFirst() { return remove(header .next);}/** * Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list. * @return the head of this list, or <tt>null </tt> if this list is empty * @since 1.5 */public E peek() { if (size ==0) return null; return getFirst();}/** * Returns the first element in this list. * * @return the first element in this list * @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty */public E getFirst() { if (size ==0) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return header .next. element;}/** * Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other * words, inserts the element at the front of this list. * * <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}. * * @param e the element to push * @since 1.6 */public void push(E e) { addFirst(e);}/** * Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list. * * @param e the element to add */public void addFirst(E e) { addBefore(e, header.next );} |
看看Deque 的实现是不是很简单,逻辑都是基于上面讲的链表操作的,对于队列的一些概念我不打算在这里讲,是因为后面队列会单独拿出来分析啦,这里只要理解基于链表实现的list内部是怎么操作的就可以啦。。。
LinkedList 完!