一、基础理解
- Hard Margin SVM 和 Soft Margin SVM 都是解决线性分类问题,无论是线性可分的问题,还是线性不可分的问题;
- 和 kNN 算法一样,使用 SVM 算法前,要对数据做标准化处理;
- 原因:SVM 算法中设计到计算 Margin 距离,如果数据点在不同的维度上的量纲不同,会使得距离的计算有问题;
- 例如:样本的两种特征,如果相差太大,使用 SVM 经过计算得到的决策边界几乎为一条水平的直线——因为两种特征的数据量纲相差太大,水平方向的距离可以忽略,因此,得到的最大的 Margin 就是两条虚线的垂直距离;
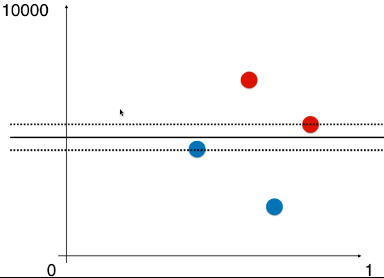
- 只有不同特征的数据的量纲一样时,得到的决策边界才没有问题;
二、例
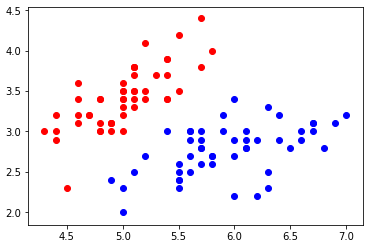
1)导入并绘制数据集
-
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets iris = datasets.load_iris() X = iris.data y = iris.target X = X[y<2, :2] y = y[y<2] plt.scatter(X[y==0, 0], X[y==0, 1], color='red') plt.scatter(X[y==1, 0], X[y==1, 1], color='blue') plt.show()
2)LinearSVC(线性 SVM 算法)
- LinearSVC:该算法使用了支撑向量机的思想;
- 数据标准化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler standardScaler = StandardScaler() standardScaler.fit(X) X_standard = standardScaler.transform(X)
- 调用 LinearSVC
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC svc = LinearSVC(C=10**9) svc.fit(X_standard, y)
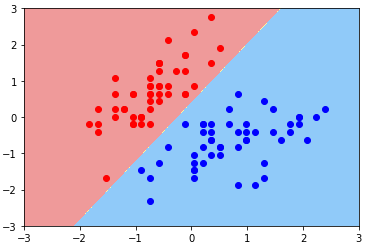
- 导入绘制决策边界的函数,并绘制模型决策边界:Hard Margin SVM 思想
def plot_decision_boundary(model, axis): x0, x1 = np.meshgrid( np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1,1), np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1,1) ) X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()] y_predict = model.predict(X_new) zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape) from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9']) plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) plot_decision_boundary(svc, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3]) plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0, 0], X_standard[y==0, 1], color='red') plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1, 0], X_standard[y==1, 1], color='blue') plt.show()
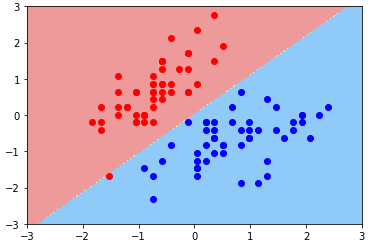
- 绘制决策边界:Soft Margin SVM 思想
svc2 = LinearSVC(C=0.01) svc2.fit(X_standard, y) plot_decision_boundary(svc2, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3]) plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0, 0], X_standard[y==0, 1], color='red') plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1, 0], X_standard[y==1, 1], color='blue') plt.show()
3)绘制支撑向量所在的直线
- svc.coef_:算法模型的系数,有两个值,因为样本有两种特征,每个特征对应一个系数;
- 系数:特征与样本分类结果的关系系数;
- svc.intercept_:模型的截距,一维向量,只有一个数,因为只有一条直线;
- 系数:w = svc.coef_
- 截距:b = svc.intercept_
- 决策边界直线方程:w[0] * x0 + w[1] * x1 + b = 0
- 支撑向量直线方程:w[0] * x0 + w[1] * x1 + b = ±1
- 变形:
- 决策边界:x1 = -w[0]/w[1] * x0 - b/w[1]
- 支撑向量:x1 = -w[0]/w[1] * x0 - b/w[1] ± 1/w[1]
-
修改绘图函数
# 绘制:决策边界、支撑向量所在的直线 def plot_svc_decision_boundary(model, axis): x0, x1 = np.meshgrid( np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], int((axis[1]-axis[0])*100)).reshape(-1,1), np.linspace(axis[2], axis[3], int((axis[3]-axis[2])*100)).reshape(-1,1) ) X_new = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()] y_predict = model.predict(X_new) zz = y_predict.reshape(x0.shape) from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap custom_cmap = ListedColormap(['#EF9A9A','#FFF59D','#90CAF9']) plt.contourf(x0, x1, zz, linewidth=5, cmap=custom_cmap) w = model.coef_[0] b = model.intercept_[0] plot_x = np.linspace(axis[0], axis[1], 200) up_y = -w[0]/w[1] * plot_x - b/w[1] + 1/w[1] down_y = -w[0]/w[1] * plot_x - b/w[1] - 1/w[1] # 将 plot_x 与 up_y、down_y 的关系以折线图的形式表示出来 # 此处有一个问题:up_y和down_y的结果可能超过了 axis 中 y 坐标的范围,需要添加一个过滤条件: # up_index:布尔向量,元素 True 表示,up_y 中的满足 axis 中的 y 的范围的值在 up_y 中的引索; # down_index:布尔向量,同理 up_index; up_index = (up_y >= axis[2]) & (up_y <= axis[3]) down_index = (down_y >= axis[2]) & (down_y <= axis[3]) plt.plot(plot_x[up_index], up_y[up_index], color='black') plt.plot(plot_x[down_index], down_y[down_index], color='black')
-
绘图:Hard Margin SVM
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3]) plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0, 0], X_standard[y==0, 1], color='red') plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1, 0], X_standard[y==1, 1], color='blue') plt.show()
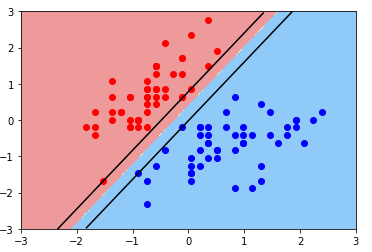
-
绘图:Soft Margin SVM
plot_svc_decision_boundary(svc2, axis=[-3, 3, -3, 3]) plt.scatter(X_standard[y==0, 0], X_standard[y==0, 1], color='red') plt.scatter(X_standard[y==1, 0], X_standard[y==1, 1], color='blue') plt.show()
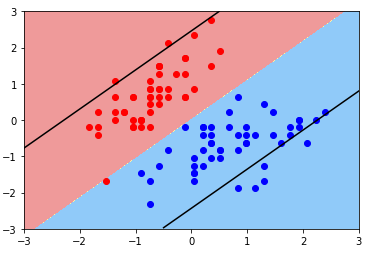
- 现象:Margin 非常大,中间容错了很多样本点;
- 原因:C 超参数过小,模型容错空间过大;
- 方案:调参;