Linux中断子系统
Linux中断子系统是个很大的话题,如下面的思维导图所示,包含硬件、驱动、中断上半部、中断下半部等等。本文着眼于中断控制器(PIC),特别是级联中断控制器驱动部分,对驱动的设计和调试要点进行分析总结。
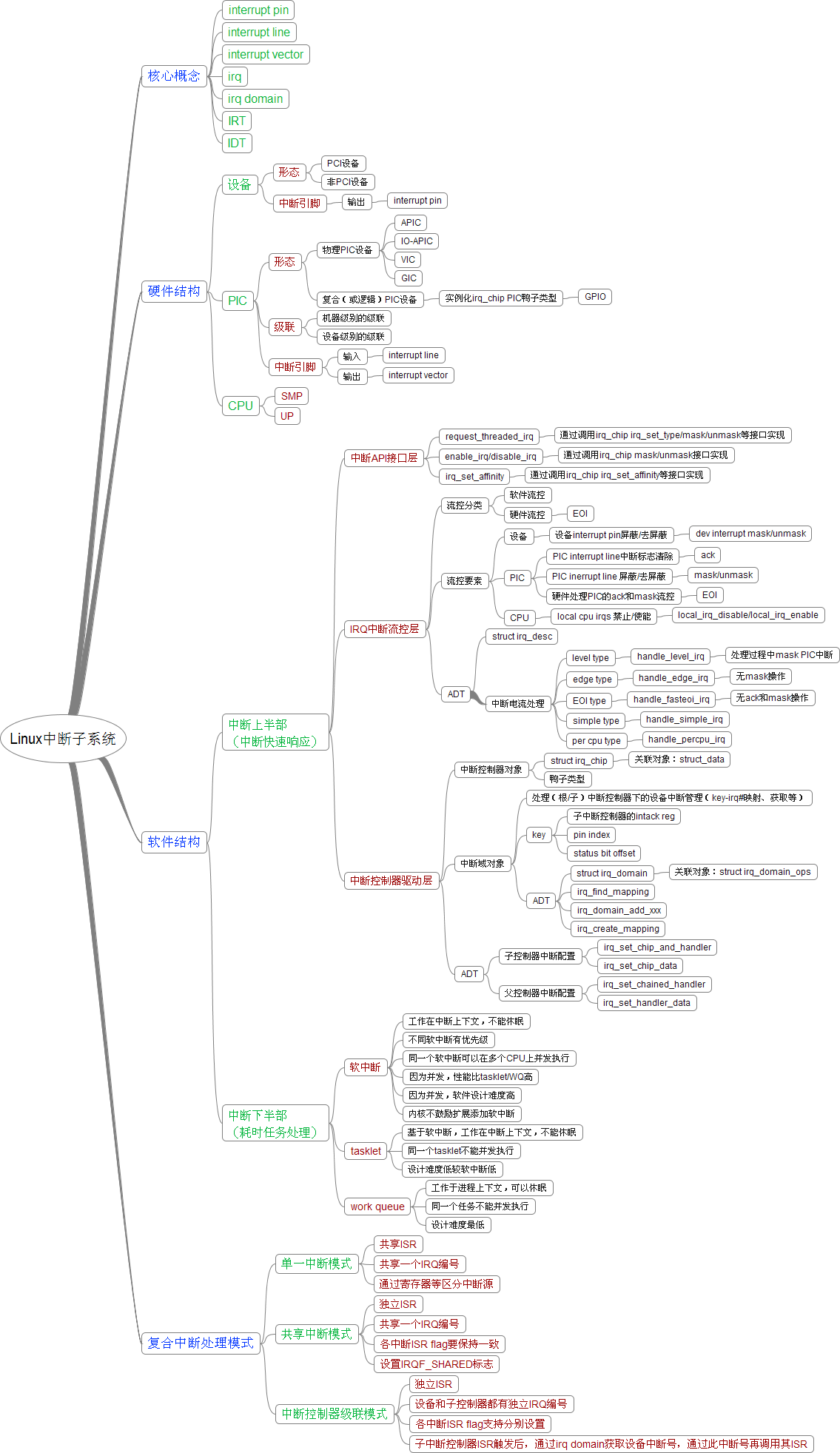
级联中断控制器驱动
中断控制器的核心对象是irq_chip,其提供了很多接口,一般情况下不需要全部实现。下面是几个类似的接口的差别介绍:
- irq_enable:在中断注册或使能时调用,一般在使能中断前需要清除中断状态。
- irq_disable:在中断注销或关闭时调用,一般在关闭中断前不清除中断状态。
- irq_mask_ack:在进入中断处理函数前调用,一般在屏蔽中断前需要清除中断源信号。
- irq_unmask:在退出中断处理函数后调用,一般在去屏蔽中断前不清除清除中断源信号。
级联中断控制器的初始化流程

中断控制器的级联如上图所示。级联中断控制器的初始化流程分为2部分:根中断控制器的初始化和子中断控制器的初始化。
根中断控制器相关部分
- 根据irq获取根PIC的irt;
- 将irt/irq的映射关系配置到根PIC的IRT表寄存器;
- 初始化根PIC的irq_chip接口对象;
- 调用irq_set_chip_and_handler设置根PIC irq的irq_chip及其handler;
- 调用irq_set_chip_data设置根PIC irq_chip接口调用时的环境对象;
子中断控制器相关部分
- 初始化子PIC的irq_chip接口对象;
- 映射子PIC io mem空间,以便后续访问其寄存器;
- 获取PIC的irq domain的irq基值,并调用irq_domain_add_xxx获取子PIC的中断域空间;
- 调用irq_set_chip_and_handler设置子PIC irq的irq_chip及其handler;
- 调用irq_set_chip_data设置子PIC irq_chip接口调用时的环境对象;
- 获取根PIC的irq;
- 调用irq_set_chained_handler设置根PIC irq handler;
- 调用irq_set_handler_data设置根PIC irq handler调用时的环境对象;
级联中断控制器的中断处理流程
首先,CPU只能感知到root PIC的中断,当root PIC的中断触发后,进入root irq handler,在handler中找到触发中断的sub irq,并调用其handler进行中断处理。换句话说,root irq的handler是root PIC的中断路由功能的软件扩展。
找到sub irq的方法依赖sub PIC具体硬件实现,以GPIO中断控制器的root irq handler为例,其方法如下:
- 调用chained_irq_enter,mask_ack root irq;
- 获取gpio 中断pin脚使能情况;
- 读取gpio interrupt status寄存器,判断此gpio 中断使能pin脚是否触发了中断;
- 通过irq_find_mapping获取此gpio pin对应的irq#;
- 通过generic_handle_irq调用 sub irq handler来进行gpio中断处理;
- 调用chained_irq_exit,unmask root irq。
中断控制器驱动调试要点
- 根据中断控制器特点,仔细设计irq_chip的接口。那么哪些需要实现,哪些又不需要是需要仔细考虑;
- root irq的handler要用chained_irq_enter/chained_irq_exit进行保护;
- 理顺中断触发时序。比如设备、子PIC的中断状态、中断源信号等中断标记清除顺序,以此来决定在哪些irq_chip接口中清除中断标记;
- 一般来说,对于任何中断设备,在使能中断前需要清除中断状态,避免垃圾中断干扰。
附关键数据结构
/**
* struct irq_chip - hardware interrupt chip descriptor
*
* @name: name for /proc/interrupts
* @irq_startup: start up the interrupt (defaults to ->enable if NULL)
* @irq_shutdown: shut down the interrupt (defaults to ->disable if NULL)
* @irq_enable: enable the interrupt (defaults to chip->unmask if NULL)
* @irq_disable: disable the interrupt
* @irq_ack: start of a new interrupt
* @irq_mask: mask an interrupt source
* @irq_mask_ack: ack and mask an interrupt source
* @irq_unmask: unmask an interrupt source
* @irq_eoi: end of interrupt
* @irq_set_affinity: set the CPU affinity on SMP machines
* @irq_retrigger: resend an IRQ to the CPU
* @irq_set_type: set the flow type (IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL/etc.) of an IRQ
* @irq_set_wake: enable/disable power-management wake-on of an IRQ
* @irq_bus_lock: function to lock access to slow bus (i2c) chips
* @irq_bus_sync_unlock:function to sync and unlock slow bus (i2c) chips
* @irq_cpu_online: configure an interrupt source for a secondary CPU
* @irq_cpu_offline: un-configure an interrupt source for a secondary CPU
* @irq_suspend: function called from core code on suspend once per chip
* @irq_resume: function called from core code on resume once per chip
* @irq_pm_shutdown: function called from core code on shutdown once per chip
* @irq_print_chip: optional to print special chip info in show_interrupts
* @flags: chip specific flags
*/
struct irq_chip {
const char *name;
unsigned int (*irq_startup)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_shutdown)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_enable)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_disable)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_ack)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_mask)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_mask_ack)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_unmask)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_eoi)(struct irq_data *data);
int (*irq_set_affinity)(struct irq_data *data, const struct cpumask *dest, bool force);
int (*irq_retrigger)(struct irq_data *data);
int (*irq_set_type)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int flow_type);
int (*irq_set_wake)(struct irq_data *data, unsigned int on);
void (*irq_bus_lock)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_bus_sync_unlock)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_cpu_online)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_cpu_offline)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_suspend)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_resume)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_pm_shutdown)(struct irq_data *data);
void (*irq_print_chip)(struct irq_data *data, struct seq_file *p);
unsigned long flags;
};
/**
* struct irq_data - per irq and irq chip data passed down to chip functions
* @irq: interrupt number
* @hwirq: hardware interrupt number, local to the interrupt domain
* @node: node index useful for balancing
* @state_use_accessors: status information for irq chip functions.
* Use accessor functions to deal with it
* @chip: low level interrupt hardware access
* @domain: Interrupt translation domain; responsible for mapping
* between hwirq number and linux irq number.
* @handler_data: per-IRQ data for the irq_chip methods
* @chip_data: platform-specific per-chip private data for the chip
* methods, to allow shared chip implementations
* @msi_desc: MSI descriptor
* @affinity: IRQ affinity on SMP
*
* The fields here need to overlay the ones in irq_desc until we
* cleaned up the direct references and switched everything over to
* irq_data.
*/
struct irq_data {
unsigned int irq;
unsigned long hwirq;
unsigned int node;
unsigned int state_use_accessors;
struct irq_chip *chip;
struct irq_domain *domain;
void *handler_data;
void *chip_data;
struct msi_desc *msi_desc;
cpumask_var_t affinity;
};
/**
* struct irq_desc - interrupt descriptor
* @irq_data: per irq and chip data passed down to chip functions
* @kstat_irqs: irq stats per cpu
* @handle_irq: highlevel irq-events handler
* @preflow_handler: handler called before the flow handler (currently used by sparc)
* @action: the irq action chain
* @status: status information
* @core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it: core internal status information
* @depth: disable-depth, for nested irq_disable() calls
* @wake_depth: enable depth, for multiple irq_set_irq_wake() callers
* @irq_count: stats field to detect stalled irqs
* @last_unhandled: aging timer for unhandled count
* @irqs_unhandled: stats field for spurious unhandled interrupts
* @lock: locking for SMP
* @affinity_hint: hint to user space for preferred irq affinity
* @affinity_notify: context for notification of affinity changes
* @pending_mask: pending rebalanced interrupts
* @threads_oneshot: bitfield to handle shared oneshot threads
* @threads_active: number of irqaction threads currently running
* @wait_for_threads: wait queue for sync_irq to wait for threaded handlers
* @dir: /proc/irq/ procfs entry
* @name: flow handler name for /proc/interrupts output
*/
struct irq_desc {
struct irq_data irq_data;
unsigned int __percpu *kstat_irqs;
irq_flow_handler_t handle_irq;
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_PREFLOW_FASTEOI
irq_preflow_handler_t preflow_handler;
#endif
struct irqaction *action; /* IRQ action list */
unsigned int status_use_accessors;
unsigned int core_internal_state__do_not_mess_with_it;
unsigned int depth; /* nested irq disables */
unsigned int wake_depth; /* nested wake enables */
unsigned int irq_count; /* For detecting broken IRQs */
unsigned long last_unhandled; /* Aging timer for unhandled count */
unsigned int irqs_unhandled;
u64 random_ip;
raw_spinlock_t lock;
struct cpumask *percpu_enabled;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
const struct cpumask *affinity_hint;
struct irq_affinity_notify *affinity_notify;
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_PENDING_IRQ
cpumask_var_t pending_mask;
#endif
#endif
unsigned long threads_oneshot;
atomic_t threads_active;
wait_queue_head_t wait_for_threads;
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
#endif
int parent_irq;
struct module *owner;
const char *name;
} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
--EOF--