前言
C#1.0的委托特性使方法作为其他方法的参数来传递,而C#2.0 中提出的泛型特性则使类型可以被参数化,从而不必再为不同的类型提供特殊版本的实现方法。
另外C#2.0还提出了可空类型,匿名方法和迭代器3个优美的特性。
1,泛型
1.1 泛型是什么
泛型的英文表述是"generic", 这个单词意为通用的。从字面意思可知,泛型代表的就是"通用类型",它可以代替任意的数据类型,使类型参数化,
从而达到之实现一个方法就可以操作多种数据类型的目的。泛型是将方法实现行为与方法操作的数据类型分离,实现了代码重用。
1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main(string[] args) 4 { 5 //用int作为实际参数来促使花泛型类型 6 List<int> intList = new List<int>(); 7 //从int列表添加元素3 8 intList.Add(3); 9 10 //用string作为实际参数来初始化泛型类型 11 List<string> stringList = new List<string>(); 12 //从string列表添加元素 13 stringList.Add("wanmg-meng"); 14 } 15 }
在以上的代码中,List<T> 是.Net 类库中实现的泛型类型,T是泛型参数(可理解为形参), 如果想实例化一个泛型类型,必须传入实际的参数类型。
泛型除了可以实现代码重用外, 还提供了更好的性能和类型安全特性. 前面关于拆箱装箱讲过. 应用类型和值类型间存在着相互转换,转换的过程称为装箱和拆箱. 这对过程会引起一定的性能损失. 而泛型是避免性能损失的有效方法.
1.2全面解析泛型
在前面的泛型代码中, T就是类型参数. 无论调用类型方法还是初始化泛型实例, 都需要用真实类型来替换T. 可以将T理解为类型的一个占位符, 即告诉编译器, 在调用泛型时必须为其指定一个实际类型.
1.2.1
已构造泛型又可分为开放类型和密封类型. 其中, 开放类型是指包含类型参数的泛型,所有未绑定的泛型类型都属于开放类型; 而封闭类型则是指那些已经为每一个类型参数都传递了司机数据类型的泛型.
1 //声明开放泛型类型 2 public class DictionaryStringKey<T> : Dictionary<string, T> 3 { 4 5 } 6 class Program 7 { 8 static void Main(string[] args) 9 { 10 //Dictionary<,> 是一个开放类型, 它有两个类型参数 11 Type t = typeof(Dictionary<,>); 12 //DictionaryStringKey<int> 是一个封闭类型 13 t = typeof(DictionaryStringKey<int>); 14 } 15 }
1.2.2
泛型中的静态字段和静态函数问题
静态数据类型是属于类型的. 对于静态之端来说, 如果某个MyClass类中定义了一个静态字段X, 则不管之后创建了多少个该类的实例,也不管从该类派生出多少个实例,
都只存在一个MyClass.x字段. 但泛型类型却并非如此, 每个封闭的泛型类型中都有仅属于他自己的静态数据.
1 //泛型类型, 具有一个类型参数 2 public static class TypeWithStaticField<T> 3 { 4 //静态字段 5 public static string field; 6 //静态构造函数 7 public static void OutField() 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine(field + ":" + typeof(T).Name); 10 } 11 } 12 13 //非泛型类 14 public static class NoGenericTypeWithStaticField 15 { 16 public static string field; 17 public static void OutField() 18 { 19 Console.WriteLine(field); 20 } 21 } 22 23 class Program 24 { 25 static void Main(string[] args) 26 { 27 //使用不同类型实参来实例化泛型实例 28 TypeWithStaticField<int>.field = "一"; 29 TypeWithStaticField<string>.field = "二"; 30 TypeWithStaticField<Guid>.field = "三"; 31 32 //对于非泛型类型, 此时field只会有一个值, 每次赋值都改变了原来的值 33 NoGenericTypeWithStaticField.field = "非泛型类静态字段一"; 34 NoGenericTypeWithStaticField.field = "非泛型类静态字段二"; 35 NoGenericTypeWithStaticField.field = "非泛型类静态字段三"; 36 37 NoGenericTypeWithStaticField.OutField(); 38 39 //证明每个封闭类型都有一个静态字段 40 TypeWithStaticField<int>.OutField(); 41 TypeWithStaticField<string>.OutField(); 42 TypeWithStaticField<Guid>.OutField(); 43 Console.ReadKey(); 44 } 45 }
运行结果图:
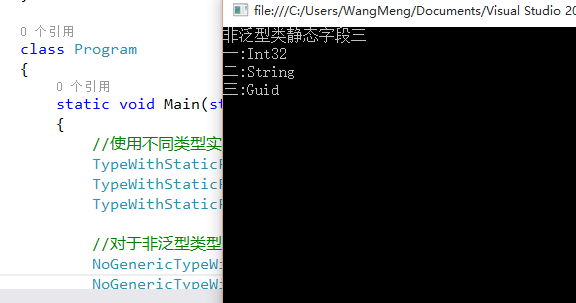
从图中可以看出每个封闭的泛型类型都有属于它自己的静态字段. 泛型暂时就写这么多, 以后遇到这方面的内容还会继续补充.
2,可空类型
2.1可空类型也是值类型, 但它是包含null值得值类型.
int? nullable = null;
解析: C# 肯定没有int?这个类型, 对于编译器而言,int?会被编译成Nullable<int>类型, 即可空类型. C# 2.0 提供和的可空类型是Nullable<int>和Nullable. (可控类型的定义是public struct Nullable<T> where T:struct, T只能为值类型)
int? value = 1 等价于==> Nullable<int> value = 1;
2.2 空合并操作符
空合并操作符即??操作符, 他会对左右两个操作数进行判断: 如果左边的数不为null,就返回左边的数; 如果左边的数位null, 就返回右边的数.
这个操作符可以用于可空类型, 也可用于引用类型,但是不能用于值类型. 因为??运算符会将其左边的数与null进行比较, 但除了可空类型外,其他的值类型是不能与null进行比较的.
可空类型的优点就是可以很方便地设置默认值,避免了通过if和else语句来进行判断, 从而简化代码函数,提高了代码的可读性:
int? nullHasValue = 1;
int x = nullHasValue ?? 12;// ??和三目运算符功能差不多, 类似于: x = nullHasValue.HasValue ? b.value : 12;
2.3 可空类型与一元或二元运算符一起使用时,只要有一个操作数为null,结果都为null;
int? d = null;
int? dd = d = 5;
Console.WriteLine(dd); //null
同理: 比较可空类型时,只要一个操作数为null,比较结果就为false。
2.4可空类型的装箱与拆箱
既然值类型存在着装箱和拆箱, 而可空类型属于值类型, 那么它自然也就存在装箱和拆箱. 当把一个可空类型赋给引用类型变量时, CLR会对可空类型对象处理.
CLR首先会检测可空类型是否为null. 如果为null, CLR将不会进行实际的装箱操作, 如果不为null,CLR则会从可空类型对象中获取值,并对该值进行装箱操作.
1 //定义一个可控类型对象nullable 2 Nullable<int> nullable = 5; 3 int? nullableWithoutValue = null; 4 5 //获得可空对象的类型, 此时返回的是System.Int32, 而不是System.Nullable<System.Int32>, 这一点需要特别注意 6 nullable.GetType();// System.Int32 7 8 //对一个为null的类型调用方法时将出现异常, 所以一般引用类型调用方法前, 最好先检查下它是否为null 9 nullableWithoutValue.GetType(); 10 11 //装箱操作 12 object obj = nullable; 13 obj.GetType();// System.Int32 14 15 //拆箱后变成非可空变量 16 int value = (int)obj; 17 18 //拆箱后变成可空类型 19 nullable = (int?)obj;
前面说了 对于没有值得可空类型调用函数时会抛出空引用异常, 但是仍然可以访问HasValue属性.
原因在于,可空类型是包含null值得可空类型, 对于向可空类型赋值这项操作来说, null是一个有效的值类型.而向引用类型赋值null值则表示空引用
表示不指向托管对中的任何对象, 所以可以访问HasValue属性.
3. 匿名方法
匿名方法就是没有名字的方法. 因为没有名字, 匿名方法只能在函数定义的时候被调用, 在其他任何情况下都不能被调用.
前面讲到委托的时候讲到 委托是后续诸多特性的基础, 匿名方法和委托有着莫大的关系. 下面用代码来说明二者之间的关系. 首先回顾委托的使用方法.
1 class Program 2 { 3 //定义投票委托 4 delegate void VoteDelegate(string name); 5 static void Main(string[] args) 6 { 7 //使用Vote方法来实例化委托对象 8 VoteDelegate voteDelegate = new VoteDelegate(new Friend().Vote); 9 //下面的方式为隐式实例化委托方式,它把方法直接赋给了委托对象 10 //VoteDelegate voteDelegate = new Friend().Vote; 11 12 //通过调用委托来回调Vote()方法, 这是隐式调用方式 13 voteDelegate("BarryWang"); 14 Console.ReadKey(); 15 } 16 17 public class Friend 18 { 19 //朋友的投票方法 20 public void Vote(string nickName) 21 { 22 Console.WriteLine("昵称为: {0}来办Wang Meng投票了", nickName); 23 } 24 } 25 }
委托是用来包装方法的类类型, 既然委托方法也是方法, 当然可以被委托类型包装了, 所以我们还可以用匿名方法的方式去实现前面的代码:
1 class Program 2 { 3 //定义投票委托 4 delegate void VoteDelegate(string name); 5 static void Main(string[] args) 6 { 7 //使用Vote方法来实例化委托对象 8 VoteDelegate voteDelegate = delegate(string nickName) 9 { 10 Console.WriteLine("昵称为: {0}来办Wang Meng投票了", nickName); 11 }; 12 13 //通过调用委托来回调Vote()方法, 这是隐式调用方式 14 voteDelegate("BarryWang"); 15 Console.ReadKey(); 16 } 17 }
从以上代码可以看出, 若使用了匿名方法, 就不再需要单独定义一个Vote方法了, 这减少了代码行数, 更有利于程序阅读.
但是匿名方法也有缺点: 不能再其他地方被调用, 即不具有重复性. 所以如果委托包装的方法相对简单, 并且该方法在其他地方的调用频率较低, 我们就可以考虑用匿名方法来实例化委托对象了.
4, 迭代器
迭代器记录了集合中的某个位置, 它使程序只能向前移动.
在C#1.0中, 一个类中要想使用foreach关键字进行遍历, 它必须实现IEnumerable或者IEnumerable<T>接口.
然而在C#2.0中, 微软提供了yield关键字来简化迭代器的实现, 这使得自定义迭代器变得容易了很多.
4.1,首先我们来看看IEnumerable、IEnumerator的区别来帮助我们理解迭代器:
先来看一下IEnumerable接口,其实看过这个接口之后,发现它其实是非常的简单,只包含一个方法GetEnumerator(),它返回一个可用于循环访问集合的IEnumerator对象,如下面代码所示:
1 public interface IEnumerable 2 { 3 // Summary: 4 // Returns an enumerator that iterates through a collection. 5 // 6 // Returns: 7 // An System.Collections.IEnumerator object that can be used to iterate through 8 // the collection. 9 [DispId(-4)] 10 IEnumerator GetEnumerator(); 11 }
那么再来看看IEnumerator中的实现方法:
这里的IEnumerator对象,其实就是另外一个接口,这个接口对象有什么呢?它是一个真正的集合访问器,没有它,就不能使用foreach语句遍历集合或数组,因为只有IEnumerator对象才能访问集合中的项,假如连集合中的项都访问不了,那么进行集合的循环遍历是不可能的事情了。那么让我们看看IEnumerator接口又定义了什么东西。

1 // Summary: 2 // Supports a simple iteration over a nongeneric collection. 3 [ComVisible(true)] 4 [Guid("496B0ABF-CDEE-11d3-88E8-00902754C43A")] 5 public interface IEnumerator 6 { 7 // Summary: 8 // Gets the current element in the collection. 9 // 10 // Returns: 11 // The current element in the collection. 12 // 13 // Exceptions: 14 // System.InvalidOperationException: 15 // The enumerator is positioned before the first element of the collection or 16 // after the last element. 17 object Current { get; } 18 19 // Summary: 20 // Advances the enumerator to the next element of the collection. 21 // 22 // Returns: 23 // true if the enumerator was successfully advanced to the next element; false 24 // if the enumerator has passed the end of the collection. 25 // 26 // Exceptions: 27 // System.InvalidOperationException: 28 // The collection was modified after the enumerator was created. 29 bool MoveNext(); 30 // 31 // Summary: 32 // Sets the enumerator to its initial position, which is before the first element 33 // in the collection. 34 // 35 // Exceptions: 36 // System.InvalidOperationException: 37 // The collection was modified after the enumerator was created. 38 void Reset(); 39 }
那么我们再来看一个真实的例子:
1 public class Person 2 { 3 public string Name { get; set; } 4 public int Age { get; set; } 5 } 6 7 public class People : IEnumerable 8 { 9 Person[] personList = new Person[4]; 10 public People() 11 { 12 personList[0] = new Person() { Name = "aehyok", Age = 25 }; 13 personList[1] = new Person() { Name = "Kris", Age = 22 }; 14 personList[2] = new Person() { Name = "Leo", Age = 21 }; 15 personList[3] = new Person() { Name = "Niki", Age = 23 }; 16 } 17 18 public IEnumerator GetEnumerator() 19 { 20 return this.personList.GetEnumerator(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 class Program 25 { 26 static void Main(string[] args) 27 { 28 People p = new People(); 29 30 //第一种遍历Person的方式 31 foreach (Person person in p) 32 { 33 Console.WriteLine("Name {0} : Age {1}", person.Name, person.Age); 34 } 35 36 //第二种遍历方式 37 IEnumerator i = p.GetEnumerator(); 38 while (i.MoveNext()) 39 { 40 Person person = (Person)i.Current; 41 Console.WriteLine("Name {0} : Age {1}", person.Name, person.Age); 42 } 43 44 Console.ReadKey(); 45 } 46 }
从上面我们知道IEnumerator接口定义了一个Current属性,MoveNext和Reset两个方法,这是多么的简约。既然IEnumerator对象是一个访问器。那至少应该有一个Current属性,来获取当前集合中的项吧。MoveNext方法只是将游标的内部位置向前移动(就是移到一下个元素而已),要想进行循环遍历,不向前移动一下怎么行呢?
通过注释也可以明确的发现他们的用处。
4.2, 使用yield自定义迭代器
直接看code的实现形式吧:

1 //使用yield自定义实现迭代器 2 class Program 3 { 4 static void Main(string[] args) 5 { 6 //创建一个对象 7 Friends friendCollection = new Friends(); 8 //Friends实现了IEnumerable,所以可以使用foreach语句进行遍历 9 foreach (Friend f in friendCollection) 10 { 11 Console.WriteLine(f.Name); 12 } 13 Console.ReadKey(); 14 } 15 } 16 17 //朋友类 18 public class Friend 19 { 20 private string name; 21 public string Name 22 { 23 get { return name; } 24 set { name = value; } 25 } 26 public Friend(string name) 27 { 28 this.name = name; 29 } 30 } 31 32 //朋友集合 33 public class Friends : IEnumerable 34 { 35 private Friend[] friendArray; 36 37 public Friends() 38 { 39 friendArray = new Friend[] 40 { 41 new Friend("张三"), 42 new Friend("李四"), 43 new Friend("王五") 44 }; 45 } 46 47 //索引器 48 public Friend this[int index] 49 { 50 get { return friendArray[index]; } 51 } 52 53 public int Count 54 { 55 get { return friendArray.Length; } 56 } 57 58 //C#2.0简化了迭代器的实现 59 public IEnumerator GetEnumerator() 60 { 61 for (int i = 0; i < friendArray.Length; i++) 62 { 63 //在C#2.0中, 只需要使用下面的语句就可以实现一个迭代器 64 yield return friendArray[i]; 65 66 //这里使用yield 简化了IEnumerator GetEnumerator中的Current() MoveNext() Reset() 方法的实现 67 } 68 } 69 }
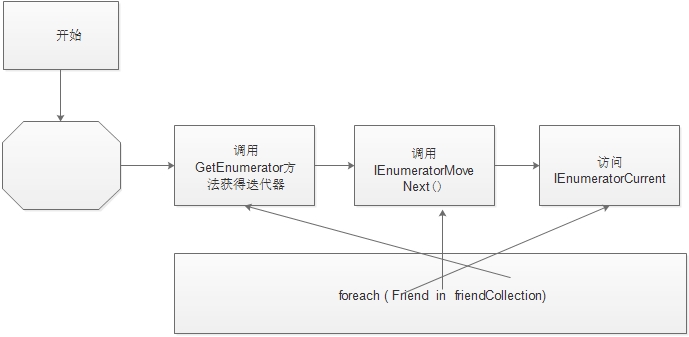
4.3迭代器的执行过程图解
PS: 这两天比较闲 便更新的比较频繁. 写完这个系列也等于把这本书又重新读了一遍, 仍有不少的收获. 勉励自己多读书, 多记录, 加油! 2016/01/20
