public class MyCollection {
private String[]array;
private List<String>list;
private Set<String>set;
Map<String,String>map;
Properties properties;
public String[] getArray() {
return array;
}
public void setArray(String[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public List<String> getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Set<String> getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
public Map<String, String> getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map<String, String> map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
}
<bean id="map" class="cn.happy.spring03xmldi.MyCollection">
<property name="map">
<map>
<!-- map中的每一项entry=key+value -->
<entry key="1" value="11"></entry>
<entry key="2" value="22"></entry>
<entry key="3">
<value>33</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
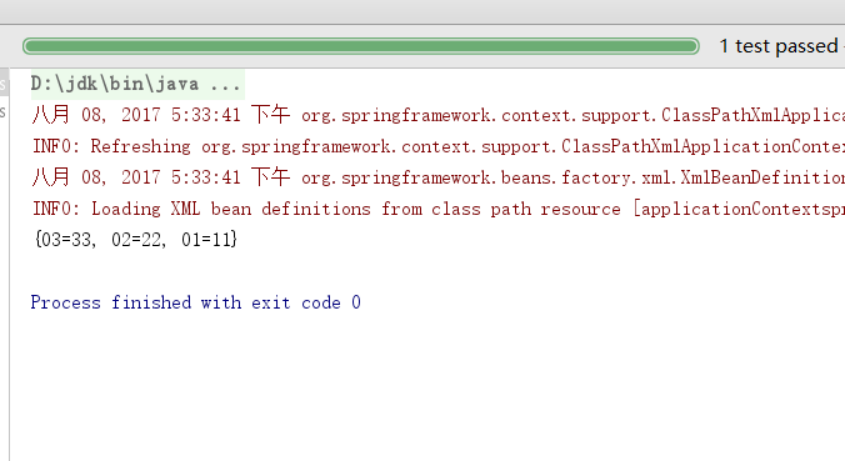
测试
public void test02(){
ApplicationContext ct= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContextspring03xmldl.xml");
MyCollection collection=(MyCollection)ct.getBean("map");
System.out.println(collection.getMap());
}