10.27(04-异常处理)
1.请阅读并运行AboutException.java示例,然后通过后面的几页PPT了解Java中实现异常处理的基础知识。
import javax.swing.*;
class AboutException {
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
k=i/j;
try
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK");
}
}
}
运行结果:
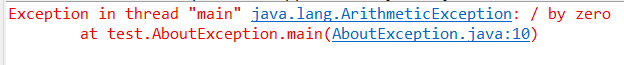
Java中的异常捕获语句
Try{
//可能发生运行错误的代码;
}
catch(异常类型 异常对象引用){
//用于处理异常的代码
}
finally{
//用于“善后” 的代码
}
Java 中所有可捕获的异常都派生自 Exception 类。
2.
多层的异常捕获:
(1)阅读以下代码(CatchWho.java),写出程序运行结果:
public class CatchWho
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
try
{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
运行结果:
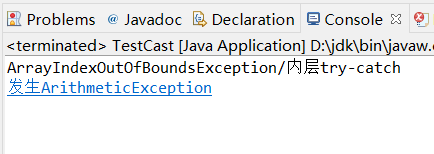
(2)写出CatchWho2.java程序运行的结果
public class CatchWho2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
try
{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
运行结果:
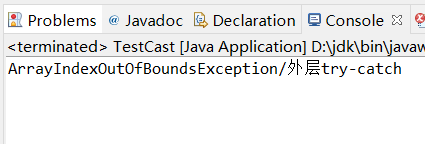
3.当有多个嵌套的try…catch…finally时,要特别注意finally的执行时机。
请先阅读 EmbedFinally.java示例,再运行它,观察其输出并进行总结。
特别注意: 当有多层嵌套的finally时,异常在不同的层次抛出 ,在不同的位置抛出,可能会导致不同的finally语句块执行顺序。
public class EmbededFinally
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int result;
try
{
System.out.println("in Level 1");
try
{
System.out.println("in Level 2");
// result=100/0; //Level 2
try
{
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally
{
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
// result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally
{
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
// result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally
{
. System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
}
运行结果:
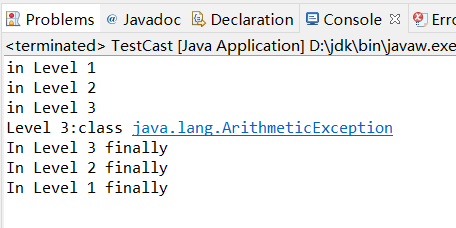
总结:try...catch语句为配对出现,程序会按着代码的顺序依次执行,当try中语句出现异常时,他会执行与当前try配对的catch语句。
4.辨析:finally语句块一定会执行吗?
请通过 SystemExitAndFinally.java示例程序回答上述问题
public class SystemExitAndFinally
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
System.out.println("in main");
throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");
//System.exit(0);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
}
运行结果:
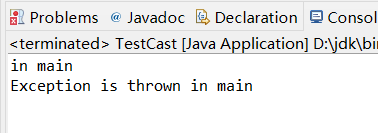
finally不会每次都执行,例如以上程序,当执行完throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");语句后便关闭了程序,System.exit(0)可以终止程序。
5.如何跟踪异常的传播路径?
当程序中出现异常时,JVM会依据方法调用顺序依次查找有关的错误处理程序。
可使用printStackTrace 和 getMessage方法了解异常发生的情况:
printStackTrace:打印方法调用堆栈。
每个Throwable类的对象都有一个getMessage方法,它返回一个字串,这个字串是在Exception构造函数中传入的,通常让这一字串包含特定异常的相关信息。
请通过 PrintExpressionStack.java示例掌握上述内容。
// UsingExceptions.java // Demonstrating the getMessage and printStackTrace // methods inherited into all exception classes. public class PrintExceptionStack { public static void main( String args[] ) { try { method1(); } catch ( Exception e ) { System.err.println( e.getMessage() + "\n" ); e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void method1() throws Exception { method2(); } public static void method2() throws Exception { method3(); } public static void method3() throws Exception { throw new Exception( "Exception thrown in method3" ); } }
运行结果:
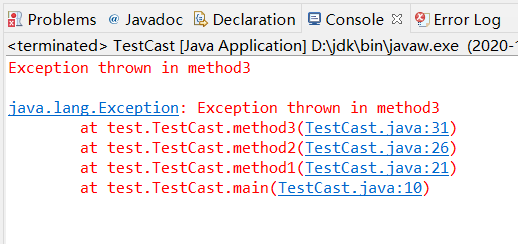
6.依据对本讲多个示例程序的分析,请自行归纳总结出Java多层嵌套异常处理的基本流程。
阅读任何一本Java教材,或者是使用互联网搜索引擎,查找有关Java多层嵌套异常处理流程的资料,看看你总结得是否全面。
7.请看以下代码,它们完全符合Java语法规范,但事实是它们不能通过编译:
public class TestThrows {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
}
}
修正代码
public class TestThrows {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws FileNotFoundException(受控的异常)
{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
}
}
解释:
throws语句表明某方法中可能出现某种(或多种)异常,但它自己不能处理这些异常,而需要由调用者来处理。
当一个方法包含throws子句时,需要在调用此方法的代码中使用try/catch/finally进行捕获,或者是重新对其进行声明,否则编译时报错。
受控与不受控的异常:
throws语句中声明的异常称为受控(checked)的异常,通常直接派生自Exception类。
RuntimeException(其基类为Exception)和Error(基类为Throwable)称为非受控的异常。这种异常不用在throws语句中声明。
CheckedExceptionDemo.java示例展示了上述两种异常的特性。
8.抛出多个受控异常的方法
一个方法可以声明抛出多个异常
int g(float h) throws OneException,TwoException
{ …… }
ThrowMultiExceptionsDemo.java示例展示了相关特性。
import java.io.*; public class ThrowMultiExceptionsDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { try { throwsTest(); } catch(IOException e) { System.out.println("捕捉异常"); } } private static void throwsTest() throws ArithmeticException,IOException { System.out.println("这只是一个测试"); // 程序处理过程假设发生异常 throw new IOException(); //throw new ArithmeticException(); } }
运行结果:
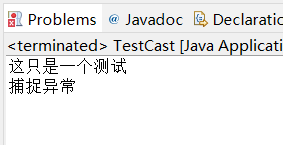
注意一个Java异常处理中的一个比较独特的地方:
当一个方法声明抛出多个异常时,在此方法调用语句处只要catch其中任何一个异常,代码就可以顺利编译。
9.子类抛出受控异常的限制
一个子类的throws子句抛出的异常,不能是其基类同名方法抛出的异常对象的父类。
OverrideThrows.java示例展示了Java的这个语法特性。
import java.io.*; public class OverrideThrows { public void test()throws IOException { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt"); } } class Sub extends OverrideThrows { //如果test方法声明抛出了比父类方法更大的异常,比如Exception //则代码将无法编译…… public void test() throws FileNotFoundException { //... } }
10.Java 7 中的新特性
Java 7 及以后的版本,允许在一个catch块中捕获多个异常。
示例代码如下:
try {
//...
throw new SocketException();
}
catch (SocketException | SecurityException | NullPointerException e) {
//exception handler
}
11.关于开发中异常处理的建议
(1)在中间层组件中抛出异常,在界面层组件中捕获异常在底层组件中捕获JVM抛出的“只有程序员能看懂的”异常,转换为中间层的业务逻辑异常,再由界面层捕获以提供有意义的信息。
自身能够处理的异常,不要再向外界抛出。
尽可能地在靠近异常发生的地方捕获并处理异常。
(2)尽可能地捕获最具体的异常类型,不要在中间层用 catch(Exception)“吃掉”所有异常
在开发阶段捕获并显示所有异常信息,发布阶段要移除部分代码,以避免“过于专业”的异常信息困扰用户,特别地,系统发布之后,不要将服务端异常的详细信息发给客户端,以免被黑客利用。
12.编写一个程序,此程序在运行时要求用户输入一个 整数,代表某门课的考试成绩,程序接着给出“不及格”、“及格”、“中”、“良”、“优”的结论。
package Test;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class dengji {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
int n=-1;
try {
System.out.print("请输入一个范围为0~100的整数:");
n=scanner.nextInt();
if(0<=n&&n<60){
System.out.println("不及格");
}
if(60<=n&&n<80) {
System.out.println("中");
}
if(80<=n&&n<90) {
System.out.println("良");
}
if(90<=n&&n<=100) {
System.out.println("优");
}
if(n<0||n>100) {
System.out.println("输入超出范围!");
}
}
catch (InputMismatchException e)
{
System.out.println("输入不是整数");
}
}
}