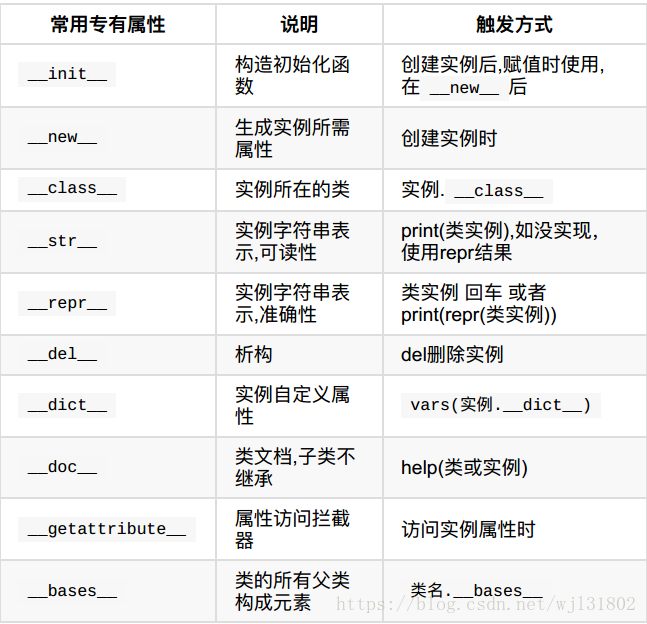
动态的创建类
类也是对象,可以再运行时动态的创建他们。
def choose_class(name):
if name == 'foo':
class Foo(object):
pass
return Foo #返回的是类,不是类的实例
else:
class Bar(object):
pass
return Bar
MyClass = choose_class('foo')
print MyClasstype功能1.测一个数据的类型2.元类,创建类
Person = type("Person",(),{"num":0})
p1=Person()
print(p1.num)
type(类名,由父类名称组成的元祖(针对继承的情况,可以为空),包含属性的字典(名称和值))
type("Cat",(Animal,),{})类装饰器
是个接口约束,必须接受一个callable对象作为参数,然后返回一个callable对象。
__call__方法,原来的装饰器是先创建一个函数,再创建一个函数,让函数名指向新函数;现在相当于是让函数名指向对象,对象里有个属性指向原来函数。
class Test(object):
def __init__(self,func):
print("---初始化---")
print("func name is %s"%func.__name__)
self.__func = func
def __call__(self):
print("---装饰器中的功能----")
self.__func()
@Test
def test():
print("---test---")
元类
类也是对象,python中一切皆为对象,可以在运行时动态创建类,跟其他对象一样。
动态创建类的方法1.
def choose_class(name):
if name == 'foo':
class Foo(object):
pass
return Foo #返回的是类,不是类的实例
else:
class Bar(object):
pass
return Bar
MyClass = choose_class('foo')
#print MyClass #函数返回的是类,不是类的实例
print MyClass() #可以通过这个类创建类实例,也就是对象动态创建类的方法2 用type type也可以
type作为内建函数,可以让你知道一个对象的类型是什么
print(type(1))#结果是<class 'int'>type 另外一个功能:动态的创建类
type(类名,由父类名称组成的元祖(针对继承的情况,可以为空),包含属性的字典(名称和值))
注意:type的第二个参数,元祖中是父类的名字,而不是字符串,不加引号,添加的属性是类属性,不是实例属性
Test2 = type("Test2",(),{}) #定义一个Test2类
Foo = type('Foo',(),{'bar':True})
#相当于
class Foo(object):
bar = True
#添加方法
def echo_bar(self):
print(self.bar)
FooChild = type('FooChild',(Foo,){'echo_bar':echo_bar})
#echo_bar不加‘’相当于函数的引用,加‘’相当于普通的值
hasattr(Foo,'echo_bar')#判断Foo类中,是否有echo_bar这个属性
---》False
hasattr(FooChild,'echo_bar')#判断Foochild类中,是否有echo_bar这个属性
---》True元类
创建这些类的类,类的类。 type就是python的内建元类。
__metaclass__属性,元类的属性 先找父类的,再找内建的,最后再找元类的
def upper_attr(future_class_name,future_class_parents,future_class_attr):
#遍历字典属性,把不是__开头的属性名字变为大写
newAttr = {}
for name,value in future_class_attr.items():
if not name.startswith("__"):
newAttr[name.upper()] = value
#调用type创建一个类
return type(future_class_name,future_class_parents,newAttr)
class Foo(object,metaclass = upper_attr):
bar = 'bip'
print(hasattr(Foo,'bar'))
print(hasattr(Foo,'BAR'))一般不用元类
python的垃圾回收机制
1.小整数对象池 对小整数的定义是[-5,257),优化速度,避免为整数频繁申请和销毁内存空间
2.大整数对象池 每一个大整数,均创建一个新的对象
3.intern机制 共享机制 单个单词只占用一个“Helloworld”所占的内存空间,靠引用计数去维护何时释放。
Garbage Collection GC垃圾回收
解决垃圾回收的机制 以引用计数为主,标记-清除和分代收集为辅的策略
隔代回收
使用链表追踪活跃的对象,称之为零代链表,每创建一个值,都会将其加入零代链表。随后循环遍历上面的每个对象,检查相互引用的对象,根据规则减掉其引用计数,释放回收内存空间。剩下的活跃的对象移入新的链表:一代链表。解释器会标记过程,被分配对象的计数值与被释放对象的计数值之前的差异累计超过GC阈值时,启动收集机制,释放浮动的垃圾,将剩下的对象移动到一代链表。
gc.get_count()
gc.get_threshold()
(700,10,10) #如果剩余数量大于700,就开始清理零代链表,清10次零代再清一代,清10次1代再清理2代导致引用计数+1的情况:1.对象被创建a=10 2.对象被引用 b=a 3.对象作为参数传到函数func(a) 4.对象作为元素存到列表list[a,a]
导致引用计数-1的情况 : 1.对象的别名被显性摧毁del a 2.对象的别名被赋予新的对象a=20 3.对象离开作用域,如局部变量使用完 4.对象所在的容器被销毁
查看引用计数
import sys
a = 'hello world'
sys.getrefcount(a)gc模块处理不了的情况
循环引用的类都有__del__方法,项目避免定义del
内建属性
__getattribute__的坑
class Person(object):
def __getattribute__(self,obj):
print("---test---")
if obj.startswith("a"):
return "hahha"
else:
return self.test
def test(self):
print("heihei")
t=Person()
t.a
t.b #return self.test对象的属性,需要再调用__getattribute__的方法,产生递归调用,没有判断什么时候退出,最后崩了
#注意:以后不要在__getattribute__方法中调用self.xxx内建函数
range python2里面range(start,stop,step)返回列表,xrange返回一个迭代值,节省空间,python3中range返回迭代值,若要得到列表,用list函数
map函数
#函数需要一个参数
map(lambda x:x*x,[1,2,3])
#结果为[1,4,9]
#函数需要两个参数
map(lambda x,y:x+y,[1,2,3],[4,5,6])
#结果为[5,7,9]
def f1(x,y):
return (x,y)
l1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
l2 = ['sun','M','T','W','T','F','S']
l3 = map(f1,l1,l2)
print(list(l3))filter函数
会对制定序列执行过滤操作
filter(...)
filter(function or None,sequence) ->list,tuple or string
对序列中每个元素调用function函数,最后返回的结果包含调用结果为True的元素,返回值类型和参数sequence类型相同。
filter(lambda x:x%2,[1,2,3,4])
[1,3]reduce函数
会对参数序列中元素进行累积,python3里面reduce函数被放置在functools模块里,用的话需要先引入
from functools import reduce
reduce(...)
reduce(function, sequence[, initial]) ->value
reduce(lambda x, y: x+y, [1,2,3,4,5])
计算过程((((1+2)+3)+4)+5)
上次调用function结果作为参数再次调用functionsorted函数
sorted(...)
sorted(iterable, cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) -->new集合set
1.去重
a = [11,223,45,656,76,23,11,45,667,77,43,22,2,3,3]
b = set(a)
b
{2, 3, 11, 76, 45, 77, 43, 656, 22, 23, 667, 223}
a = list(b)
a2. union(联合)、intersection(交)、difference(差)、sysmmetric_difference(对称差集)等数学运算
a = 'abcdef'
b = set(a)
b
A = 'bdf'
B = set(A)
B
b&B
b|B
b-B #b减去b&B的部分
b^B #对称差集functools
工具函数
partial函数(偏函数)
把一个函数的某些参数设置默认值,返回一个新的函数,调用新函数会更简单。
import functools
def showarg(*args, **kw):
print(args)
print(kw)
p1 = functools.partial(showarg, 1,2,3)
p1()
p1(4,5,6)
p1(a='python', b='itcast')
p2=functools.partial(showarg, a=3, b='linux')
p2()
p2(1,2)
p2(a='python', b='itcast')
wraps函数
一般的装饰器会产生一个问题,被装饰后,函数名和函数的doc发生改变,对测试结果有些影响
def note(func):
'note function'
def wrapper():
"wrapper function"
print("note something")
return func()
return wrapper
@note
def test():
"test function"
print("I am test")
test()
print(test.__doc__)
结果
note something
I am test
wrapper function所以python的functools 包中提供了一个叫wraps的装饰器消除这样的副作用
import functools
def note(func):
'note function'
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper():
"wrapper function"
print("note something")
return func()
return wrapper
@note
def test():
"test function"
print("I am test")
test()
print(test.__doc__)
运行结果
note something
I am test
test function模块进阶
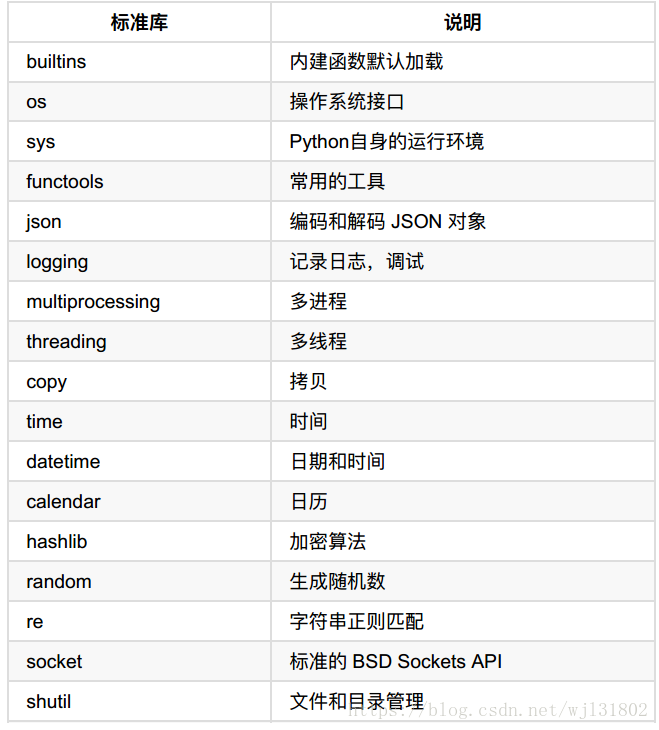
标准模块(默认常用的)
json杰森
hashlib 哈希
import hashlib
m = hashlib.md5()
print(m)
m.update(b'itcast')
print(m.hexdigest())
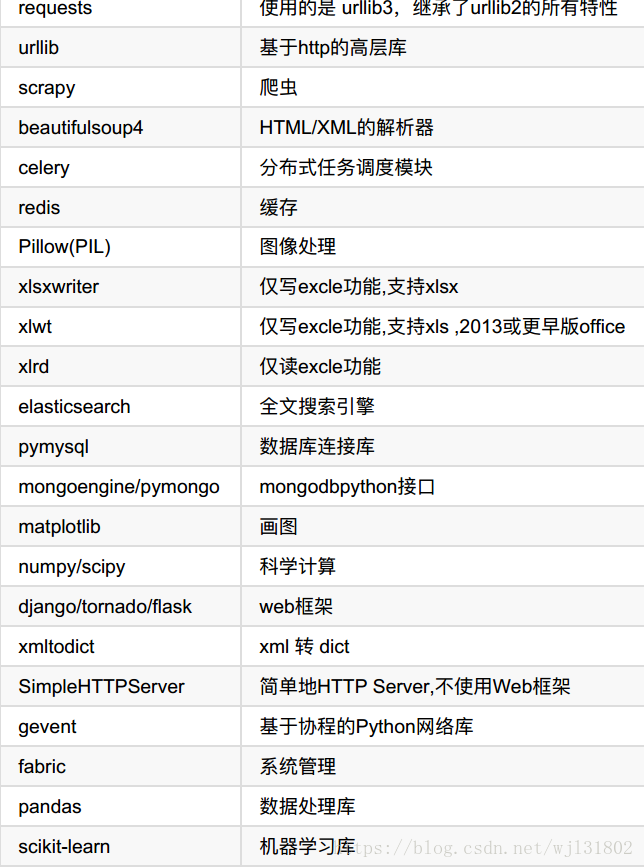
常用的扩展库