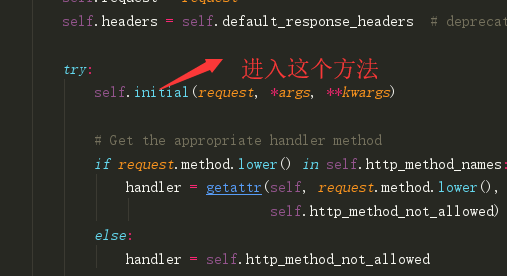
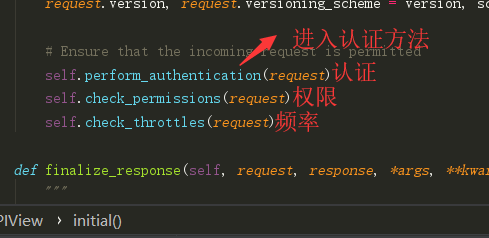
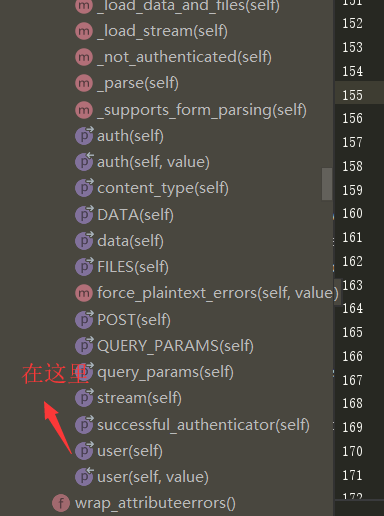
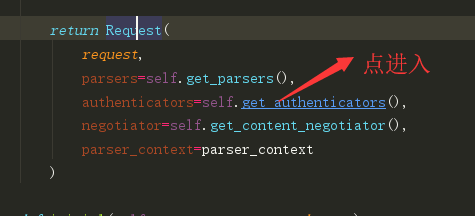
0|1一、认证组件的作用
在一个程序中有一些功能是需要登录才能使用的,原生Django中的auth组件可以用来解决这个认证问题,drf框架中也有对应的认证组件来解决这个问题。
- models.py
from django.db import models # Create your models here. class User(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=16) pwd = models.CharField(max_length=16) class TokenUser(models.Model): token = models.CharField(max_length=256) user = models.OneToOneField(to='User',null=True,on_delete=models.SET_NULL,db_constraint=False) class Book(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=16) price = models.IntegerField() publish_date = models.DateField()
- myserializer.py 序列化
from rest_framework import serializers from app01 import models class BookSerializer(serializers.ModelSerializer): class Meta: model = models.Book fields = '__all__' def validate(self, attrs): return attrs
0|1二、自定义版登录验证组件
- urls.py
"""blog_test URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.conf.urls import url, include 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01.views import BooksView, BookView,Login urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^Login/$', Login.as_view()), url(r'^Books/$', BooksView.as_view()), url(r'^Books/(?P<pk>d+)/$', BookView.as_view()), ]
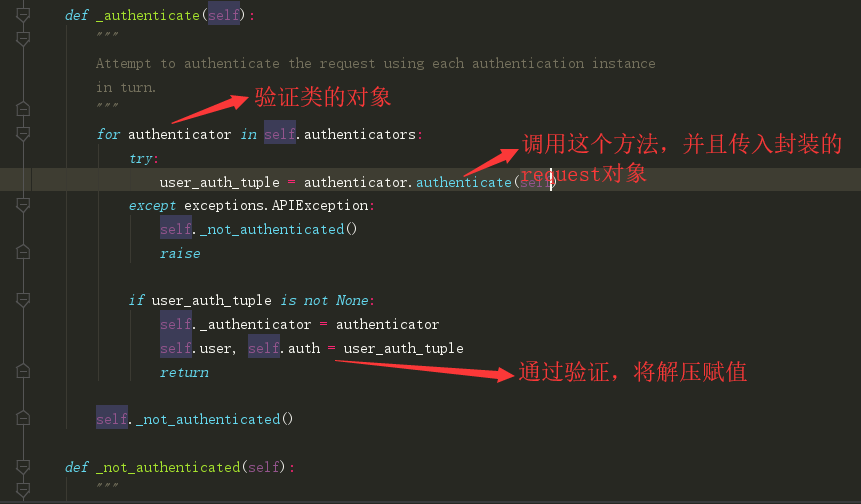
- myauth.py 自定义验证类
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from app01.models import TokenUser from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed class MyAuthentication(): #验证过程 def authenticate(self, request): token = request.GET.get('token') token_user = TokenUser.objects.filter(token=token).first() if token_user: return token_user.user,token else: raise AuthenticationFailed('你还未登录,请先登录') def authenticate_header(self, request): pass
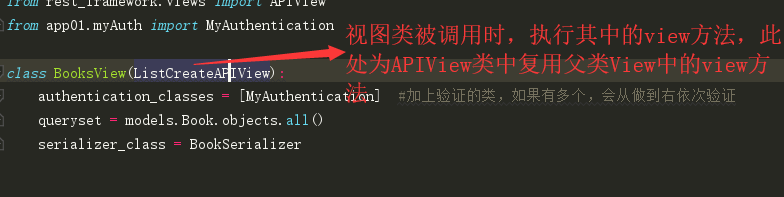
- views.py 视图类
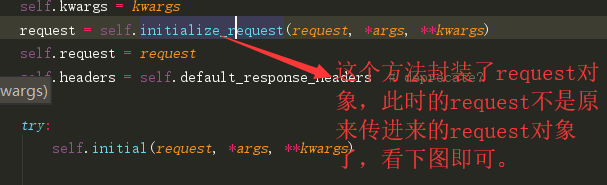
from django.shortcuts import render from rest_framework.response import Response # Create your views here. from rest_framework.generics import ListCreateAPIView,RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView from app01 import models from app01.myserializer import BookSerializer from rest_framework.views import APIView from app01.myAuth import MyAuthentication class BooksView(ListCreateAPIView): authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication] #加上验证的类,如果有多个,会从做到右依次验证 queryset = models.Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer class BookView(RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView): authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication] queryset = models.Book.objects.all() serializer_class = BookSerializer import uuid #登录 class Login(APIView): def post(self,request): name = request.data.get('name') pwd = request.data.get('pwd') user = models.User.objects.filter(name=name,pwd=pwd).first() if user: token = uuid.uuid4() models.TokenUser.objects.update_or_create(user=user,defaults={"token":token}) response = {"status":100,"message":"登录成功"} else: response = {"status": 200, "message": "登录失败"} return Response(response)
结果:登录后会在数据库中生成一个token,用get请求将其发送,观察各个请求的结果。
结果1:
结果2:
0|1三、继承BaseAuthentication的类的登录验证组件
- myauth.py
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication from app01.models import TokenUser from rest_framework.exceptions import AuthenticationFailed class MyAuthentication(): #验证过程 def authenticate(self, request): token = request.GET.get('token') token_user = TokenUser.objects.filter(token=token).first() if token_user: return token_user.user,token else: raise AuthenticationFailed('你还未登录,请先登录')
其他代码一致
0|1四、认证组件的使用方式
1.局部使用:在需要使用登录验证的视图类中写上变量 authentication_classes= [ 验证类名,]
2.全局使用:在settings.py配置文件中,加入 REST_FRAMEWORK = {‘DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES’:'验证类的具体位置例如(app01.myauth.MyAuthenyicatin)'}
3.全局使用,局部禁用:在全局使用的基础上,在不需要验证的视图类中,将变量 authentication_classes 改为 [ ] 即 authentication_classes = [ ]