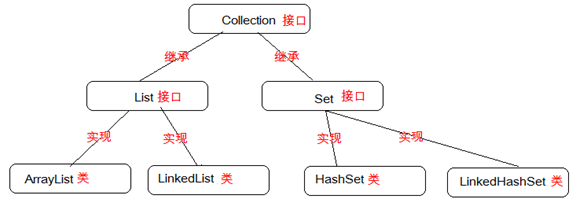
1.1 Collection接口概述
既然Collection接口是集合中的顶层接口,那么它中定义的所有功能子类都可以使用。查阅API中描述的Collection接口。Collection 层次结构中的根接口。Collection 表示一组对象,这些对象也称为 collection 的元素。一些 collection 允许有重复的元素,而另一些则不允许。一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些则是无序的。
数组的长度是固定的。集合的长度是可变的。
集合中存储的元素必须是引用类型数据
ArrayList类发现它继承了抽象类AbstractList同时实现接口List,而List接口又继承了Collection接口。Collection接口为最顶层集合接口了
Collection接口常用的子接口有:List接口、Set接口
List接口常用的子类有:ArrayList类、LinkedList类
Set接口常用的子类有:HashSet类、LinkedHashSet类
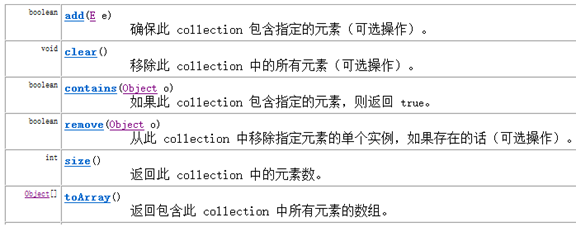
Collection的的基本方法
方式1:Collection<元素类型> 变量名 = new ArrayList<元素类型>();
方式2:Collection 变量名 = new ArrayList();
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 Collection<String> coll =new ArrayList<String>(); 3 coll.add("wrc"); 4 coll.add(new String("222")); 5 for(String a :coll){ 6 System.out.println(a); 7 } 8 }
public static void main(String[] args) { Collection<String> coll =new ArrayList<String>(); coll.add("wrc"); coll.add(new String("222")); System.out.println(coll.size()); }
Iterator迭代器
Collection集合元素的通用获取方式:在取元素之前先要判断集合中有没有元素,如果有,就把这个元素取出来,继续在判断,如果还有就再取出出来。一直把集合中的所有元素全部取出。这种取出方式专业术语称为迭代。
集合中把这种取元素的方式描述在Iterator接口中。Iterator接口的常用方法如下:

1 Collection<String> coll =new ArrayList<String>(); 2 coll.add("wrc"); 3 coll.add(new String("222"));
1 Iterator<String> it =coll.iterator(); //定义一个定时器 2 while(it.hasNext()){ //判断下一个循环,如果有就返回ture 3 System.out.println(it.next()); 4 } 5 }
1 for(Iterator<String> it =coll.iterator();it.hasNext();){ 也可以这样写 2 System.out.println(it.next()); 3 }
泛型
泛型,用来灵活地将数据类型应用到不同的类、方法、接口当中。将数据类型作为参数进行传递。
泛型的通配符
泛型是在限定数据类型,当在集合或者其他地方使用到泛型后,那么这时一旦明确泛型的数据类型,那么在使用的时候只能给其传递和数据类型匹配的类型,否则就会报错。
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 ArrayList<Person> list =new ArrayList<Person>(); //创建一个人类 3 Person p = new Person("zhang4",20); 4 list.add(p); 5 list.add(new Person("zhang3",20)); 6 list.add(new Person("wang2",30)); 7 printCollection(list); 8 ArrayList<Student> l =new ArrayList<Student>(); //创建一个学生类, 9 l.add(new Student("小明",22)); 10 l.add(new Student("小红",22)); 11 printCollection(l); 12 } 13 public static void printCollection(Collection<?> list){ //通配符用?来表示所有的,就是谁也可以调用 14 for(Iterator<?> it =list.iterator();it.hasNext();){ 15 System.out.println(it.next()); 16 } 17 }
泛型的限定
限定泛型的上限:
格式:? extends E
? 代表接收E类型或者E的子类型的元素
可以对本类和本类的子类进行规定
1 ArrayList<worker> list = new ArrayList<worker>(); 2 list.add(new worker("王2",12)); 3 printCollection(list); 4 5 6 7 } 8 public static void printCollection(Collection<? extends Person> list){ 9 for(Iterator<? extends Person> it =list.iterator();it.hasNext();){ 10 System.out.println(it.next()); 11 }
限定泛型的下限:
格式:? super E
? 代表接收E类型或者E的父类型的元素
例如,泛型限定为:? super Student
则 ? 代表接收Student类型或者Student父类型的元素
可以对本类和本类的父类进行规定