Python的其他方法
1 __str__方法
- 触发时机: 使用print(对象)或者str(对象)的时候触发
- 功能: 查看对象信息
- 参数: 一个self接受当前对象
- 返回值: 必须返回字符串类型
基本用法
创建一个基本的类
class Cat():
gift = "catch mouse"
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def cat_info(self):
strvar = "This object is {},and cat can catch {} normally".format(self.name,self.gift)
return strvar
tom = Cat("Tom")
res = tom.cat_info()
print (res)
print (tom)
使用__str__定义属性查看
class Cat():
gift = "catch mouse"
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def cat_info(self):
strvar = "This object is {},and cat can catch {} normally".format(self.name,self.gift)
return strvar
def __str__(self):
return "strcgdfas" #必须要返回一个字符串
tom = Cat("Tom")
res = tom.cat_info()
print (res)
print (tom)
不返回字符串报错
class Cat():
gift = "catch mouse"
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def cat_info(self):
strvar = "This object is {},and cat can catch {} normally".format(self.name,self.gift)
return strvar
def __str__(self):
return 1234
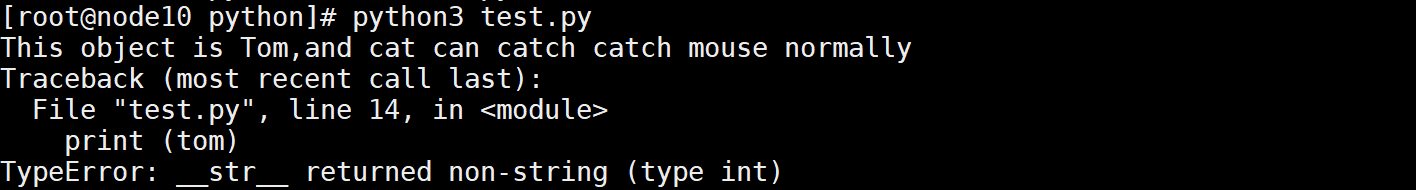
tom = Cat("Tom")
res = tom.cat_info()
print (res)
print (tom)
执行
可与i调用函数,世界返回信息
class Cat():
gift = "catch mouse"
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def cat_info(self):
strvar = "This object is {},and cat can catch {} normally".format(self.name,self.gift)
return strvar
def __str__(self):
return self.cat_info()
tom = Cat("Tom")
res = tom.cat_info()
print (res)
print (tom)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py This object is Tom,and cat can catch catch mouse normally This object is Tom,and cat can catch catch mouse normally
2 __repr__方法
- 触发时机: 使用repr(对象)的时候触发
- 功能: 查看对象,与魔术方法__str__相似
- 参数: 一个self接受当前对象
- 返回值: 必须返回字符串类型
实例
class Mouse():
gift = "make holes"
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def mouse_info(self):
strvar = "This object is {},and mouse can {} normally".format(self.name,self.gift)
return strvar
def __repr__(self):
return self.mouse_info()
jerry = Mouse("Jerry")
res = repr(jerry)
print (res)
print (jerry) #这里是因为相当于执行__str__ = __repr__,把一个函数赋给另一个函数,在底层自己实现,把删除当做变量名使用
#也可以强转,效果一样
res = str(jerry)
print (res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py This object is Jerry,and mouse can make holes normally This object is Jerry,and mouse can make holes normally This object is Jerry,and mouse can make holes normally
把函数当作变量名使用
def func():
print("只是一个函数")
func2 = 5
func2 = func
func2()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 只是一个函数
3 __bool__ 魔术方法
类似的还有如下等等(了解):
__complex__(self) 被complex强转对象时调用
__int__(self) 被int强转对象时调用
__float__(self) 被float强转对象时调用
- 触发时机:使用bool(对象)的时候自动触发
- 功能:强转对象
- 参数:一个self接受当前对象
- 返回值:必须是布尔类型
class MyClass():
def __bool__(self):
return False
obj = MyClass()
res = bool(obj)
print (res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py False
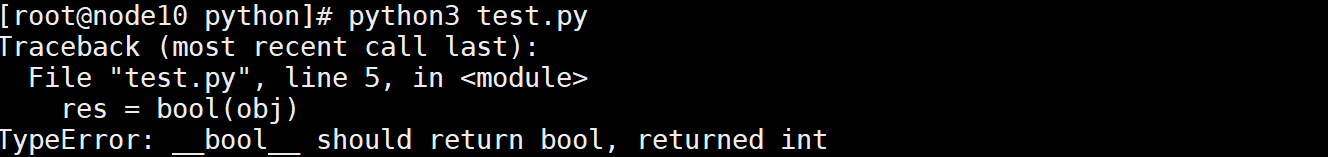
不是布尔值,使用数字报错
class MyClass():
def __bool__(self):
return 1
obj = MyClass()
res = bool(obj)
print (res)
执行
4 __add__ 魔术方法
与之相关的__radd__ 反向加法 类似的还有如下等等(了解): __sub__(self, other) 定义减法的行为:- __mul__(self, other) 定义乘法的行为: __truediv__(self, other) 定义真除法的行为:/
- 触发时机:使用对象进行运算相加的时候自动触发
- 功能:对象运算
- 参数:二个对象参数
- 返回值:运算后的值
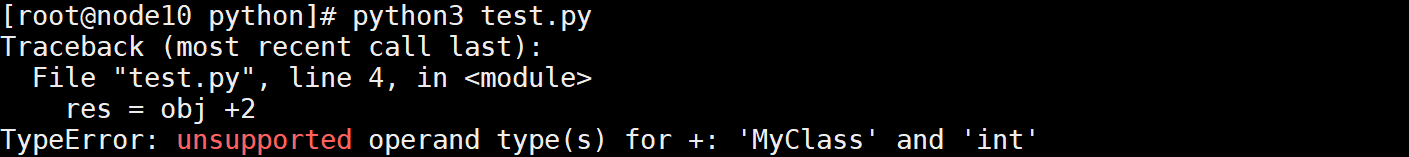
对象直接相加不支持
class MyClass():
pass
obj = MyClass()
res = obj +2
执行
使用__add__和__radd__方法
class MyClass():
def __init__(self,num):
self.num = num
def __add__(self,other):
# self 自动接收对象,other是另外一个值
# 当对象在+加号左侧的时候,自动触发
return self.num *3 +other
#当对象在+的右侧,自动触发
def __radd__(self,other):
return self.num*2+other
obj = MyClass(5)
res = obj +2
print (res)
res = 3 + obj
print (res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 17 13
对象加对象
class MyClass():
def __init__(self,num):
self.num = num
def __add__(self,other):
# self 自动接收对象,other是另外一个值
# 当对象在+加号左侧的时候,自动触发
return self.num *3 +other
#当对象在+的右侧,自动触发
def __radd__(self,other):
return self.num*2+other
obj1 = MyClass(5)
res = obj1 +2
print (res)
obj2 = MyClass(3)
res = 3 + obj2
print (res)
res = obj1 + obj2
print (res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 17 9 21
执行过程
obj1在加号的左侧,先执行add方法 res = obj1 + obj2 self接收的是obj1对象other接收的是obj2对象 return self.num + other相当于 obj1.num*3 + obj2 = 15 + obj2 res = 15 + obj2 对象obj2在+号右侧,触发radd self接收对象obj2,other节后对象15 eturn self.num + other相当于obj2.num*2+ 15 =3*2 + 15 =21 return 21 res = 21
5 __len__ 魔术方法
- 触发时机:使用len(对象)的时候自动触发
- 功能:用于检测对象中或者类中成员个数
- 参数:一个self接受当前对象
- 返回值:必须返回整型
给你一个对象,算出该对象所归属的类里面有几个自定义成员.
listvar = [1,2,3,4,5]
res = len(listvar)
print(res)
class MyClass():
pty1 = 1
pty2 = 2
__pty3 = 3
__pty4 = 4
def func():
pass
def func2():
pass
def __func3():
pass
def __func4():
pass
res = MyClass.__dict__
print (res)
obj = MyClass()
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py
5
{'__module__': '__main__',
'pty1': 1, 'pty2': 2,
'_MyClass__pty3': 3,
'_MyClass__pty4': 4,
'func': <function MyClass.func at 0x7fcaf74880d0>,
'func2': <function MyClass.func2 at 0x7fcaf7488158>,
'_MyClass__func3': <function MyClass.__func3 at 0x7fcaf74881e0>,
'_MyClass__func4': <function MyClass.__func4 at 0x7fcaf7488268>,
'__dict__': <attribute '__dict__' of 'MyClass' objects>,
'__weakref__': <attribute '__weakref__' of 'MyClass' objects>, '__doc__': None}
使用len方法
listvar = [1,2,3,4,5]
res = len(listvar)
print(res)
class MyClass():
pty1 = 1
pty2 = 2
__pty3 = 3
__pty4 = 4
def func():
pass
def func2():
pass
def __func3():
pass
def __func4():
pass
def __len__(self):
res = MyClass.__dict__
#以__开头和以__结尾的都不要使用not
lst = [i for i in res if not ( i.startswith("__") and i.endswith("__")) ]
# print(lst)
return len(lst)
res = MyClass.__dict__
obj = MyClass()
res = len(obj)
print(res)
执行
[root@node10 python]# python3 test.py 5 8
