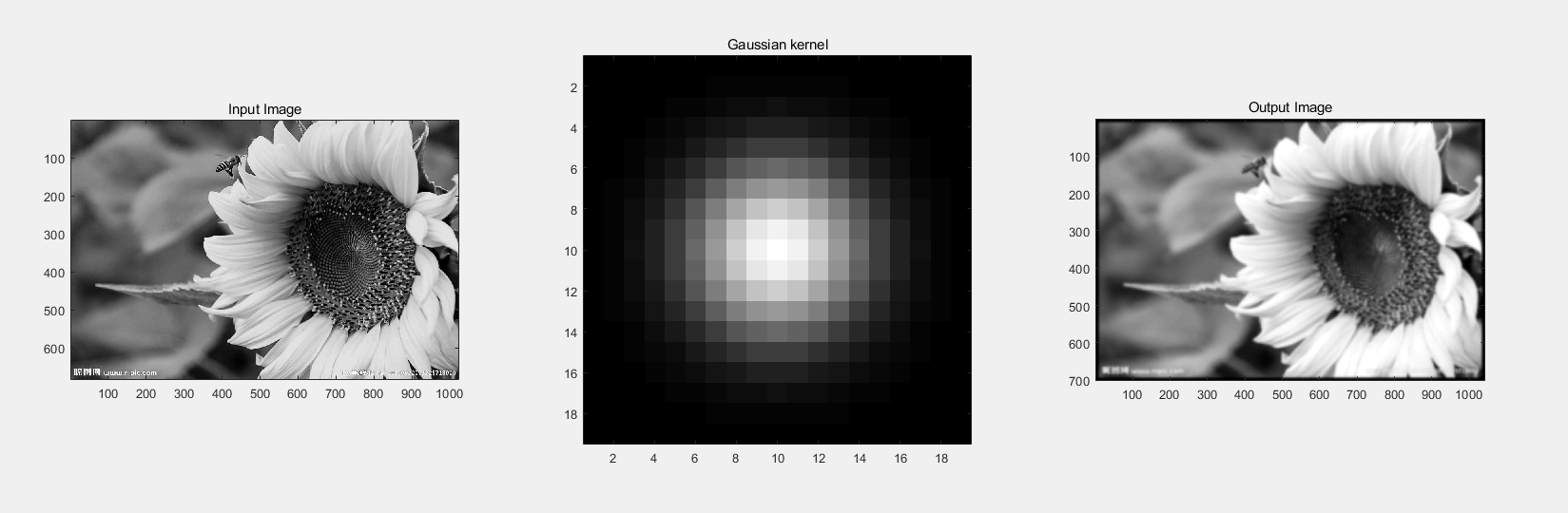
卷积就是滤波操作,将中心点与其邻域加权相加,得到的值就是中心点的新值。滤波之后的中心点的像素值用它周围的点的像素值的加权平均代替,使得边界变得更加模糊(低通滤波)
高斯核
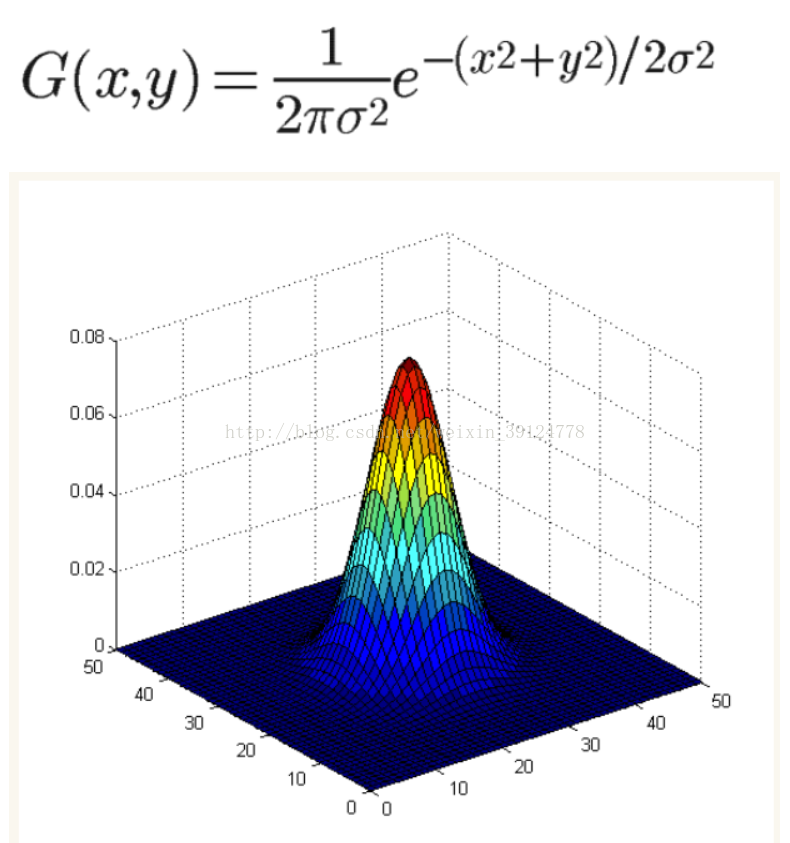
高斯核的函数图像是一个正态分布钟形线,坐标越趋近中心点,值就越大,反之越小。也就是说离中心点越近权值就越大,离中心点越远,权值就越小。
高斯核函数公式中的xy是滤波器的点坐标,计算出来的值是滤波器上的值,也就是图像上每个点对应的权重,用滤波器与原图像滚动相乘,也就得到了最终的处理结果。
p=imread('data/1.jpg'); imshow(p); g1=rgb2gray(p); imshow(g1); %g1=imadjust(g,[0.4,0.6],[0,1]); %g2=imcomplement(g); %g3= imadjust(g, stretchlim(g), []); %imshow(g3) sigma = 3; % you can set the sigma yourself Wx = floor(3*sigma); % Wx 的确定是根据gaussian函数的分布集中在【Mu-3Sigma, Mu+3sigma]内 x = -Wx:Wx; g = exp(-(x.^2)/(2*sigma^2)); kernel = conv2( g, g'); %I = imread( 'cameraman.gif' ); I = double( g1 ); Ig = conv2(I, kernel); %Use kernel to convolution with Input image figure(1); subplot(1,3,1); imagesc(I); axis image; colormap(gray); title('Input Image'); subplot(1,3,2); imagesc(kernel); axis image; colormap(gray); title('Gaussian kernel'); subplot(1,3,3); imagesc(Ig); axis image; colormap(gray); title('Output Image');