1. 语法:
try{
//需要执行的代码
}catch(e){
//错误处理 e程序遇到错误时的报错信息
}
2.惰性函数:
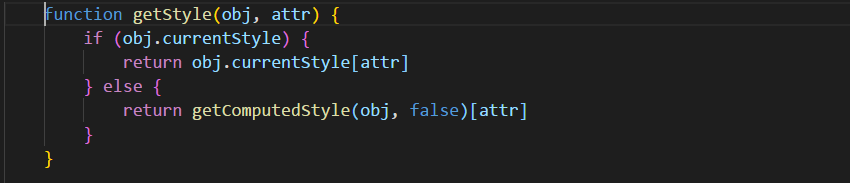
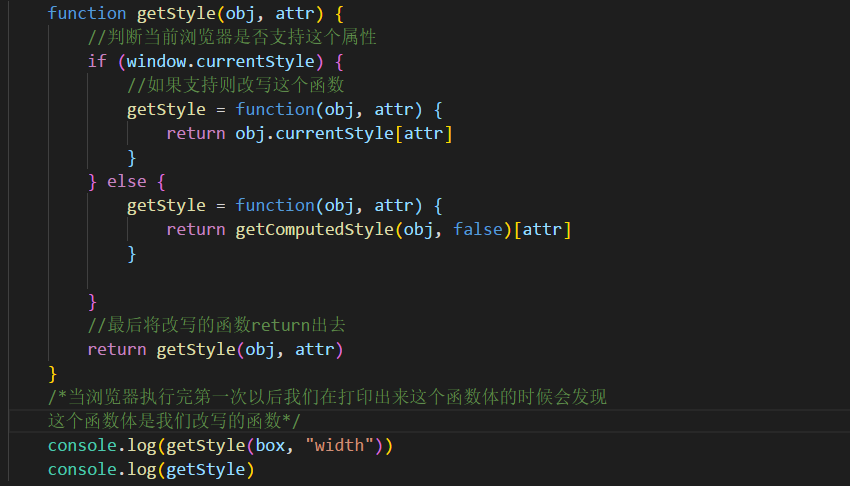
函数在第一次被调用时会根据某些条件进行分支处理,在分支中重新定义函数,以后每次在进行调用函数时,不再进行判断
惰性函数:
3.设计模式
何为设计模式?
* 具有某种重复性规律的方案,就是设计过程中可以反复使用的、可以解决特定问题的设计方法。
* 设计模式是针对特定上下文的特定问题的解决方案,这种解决方案被抽象化、模版化,就是设计模式。
* 是一种解决问题的思维,而并非某种特定的方法。
(1)单例模式
添加的静态属性的方法:
function CreateModel(){
if(!CreateModel.instance){ //添加静态属性
CreateModel.instance = {
init : function(){
this.eventBind();
},
create : function(){
var newDiv = document.createElement('div');
newDiv.className = 'box';
document.body.appendChild(newDiv);
},
eventBind : function(){
document.addEventListener('click',this.create.bind(this));
}
}
}
return CreateModel.instance;
}
new CreateModel().init();
function CreateModel(){
if(!CreateModel.instance){ //添加静态属性
CreateModel.instance = {
init : function(){
this.eventBind();
},
create : function(){
var newDiv = document.createElement('div');
newDiv.className = 'box';
document.body.appendChild(newDiv);
},
eventBind : function(){
document.addEventListener('click',this.create.bind(this));
}
}
}
return CreateModel.instance;
}
new CreateModel().init();
闭包的写法:
var createDiv = (function(){
var newDiv
return function(){
if(!newDiv){
return newDiv = document.createElement('div');
}
}
})()
var newDiv
return function(){
if(!newDiv){
return newDiv = document.createElement('div');
}
}
})()
console.log(createDiv());
console.log(createDiv() == createDiv());
console.log(createDiv() == createDiv());