Heterogeneous Face Attribute Estimation: A Deep Multi-Task Learning Approach
2017.11.28
Introduction:
人脸属性的识别在社会交互,提供了非常广泛的信息,包括:the person’s identity, demographic (age, gender, and race), hair style, clothing, etc. 基于人脸属性识别的场景也越来越多,如:(i)video Surveillance;
(ii)face retrieval;(iii)social media。尽管最近在属性识别上取得了很大的进展,但是,大部分 prior works 限制在预测单个属性(如:age),或者 针对每一个属性学习一个 model,进行识别。为了解决上述的局限性,已经有很多工作在尝试 joint 的预测多个属性【见文章引用 19-23】。但是这些方法都有或多或少的不足:
1. The approaches in [19], [20], [22] used the same features for estimating all the attributes without considering the attribute heterogeneity.
2. The sumproduct network (SPN) adopted in [21] for modeling attribute correlations may not be feasible because of the exponentially growing number of attribute group combinations.
3. The cascade network in [23] also required learning a separate Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier for each face attribute, and is not an end-to-end learning approach.

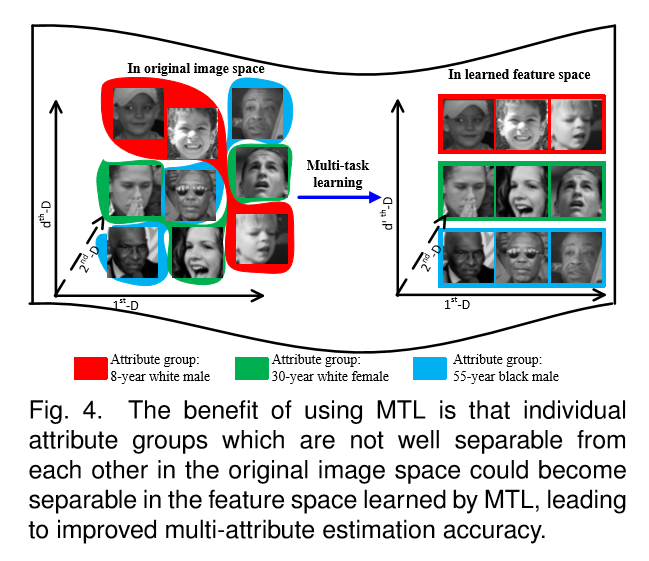
图一展示了人脸属性的相关性以及多样性。属性之间关系要么是 pos 要么是 neg。与此同时,单个属性可以是多样的(根据 data type 或者 scale,以及 semantic meaning)。这种属性相关性以及多样性应该被编码到 属性预测模型中去(Such attribute correlation and heterogeneity should be considered in designing face attribute estimation models.)。
Proposed Algorithm:
本文提出一种 Deep Multi-Task Learning (DMTL) approach 来 Jointly 的预测单张图像中的多个属性。所提出的方法,是受到现有方法的启发,但是在一个网络中,考虑到 attribute correlation 以及 attribute heterogeneity。所提出的 DMTL 有前期的共享特征提取阶段,以及 特定类型的特征学习来进行多个属性的预测。共享的特征学习自然地探索了多个 task 之间的相关性,可以更加鲁棒以及有效的进行特征的表达。
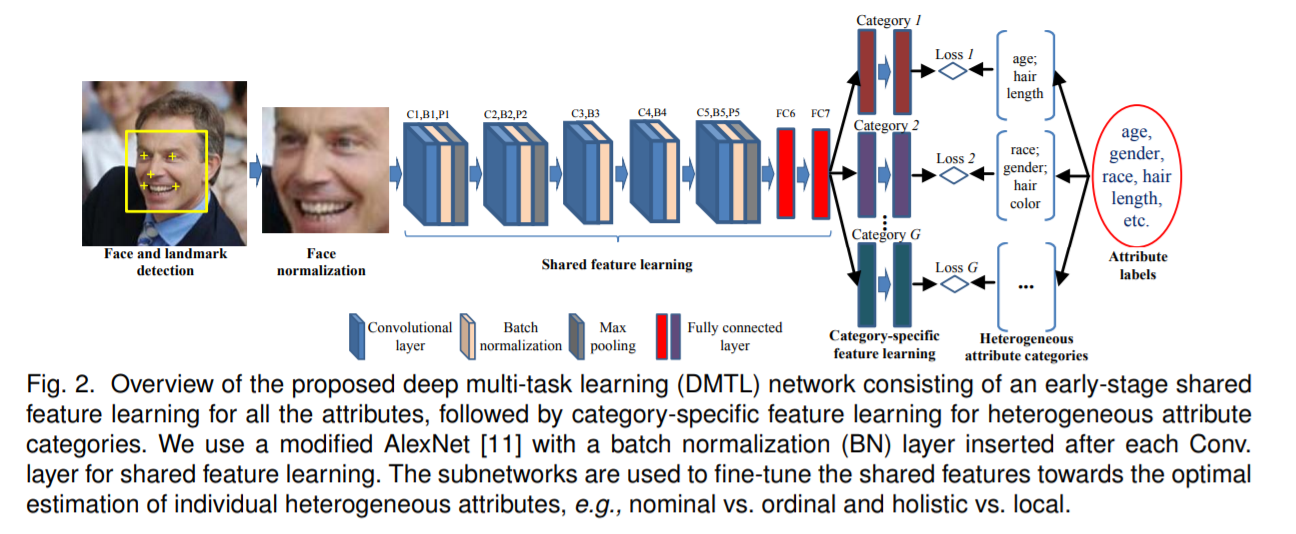
Main Contributions:
(i) an efficient multi-task learning (MTL) method for joint estimation of a large number of face attributes;
(ii) modeling both attribute correlation and attribute heterogeneity in a single network;
(iii) studying the generalization ability of the proposed approach under cross-database testing scenarios;
(iii) compiling the LFW+ database2 with face images in the wild (LFW), and heterogeneous demographic attributes (age, gender, and race) via crowdsourcing.
Proposed Approach:
1. Deep Multi-task Learning :
本文的目标是,用一个联合的预测模型,同时预测多个人脸属性。当大量 face attributes 给特征学习效率上带来挑战的同时,他们也提供了结合属性内部关系的机会(leveraging the attribute inter-correlations to obtain informative and robust feature representation)。例如,CelebA dataset 中的各个属性之间就有很强的 correlation,如下图所示:
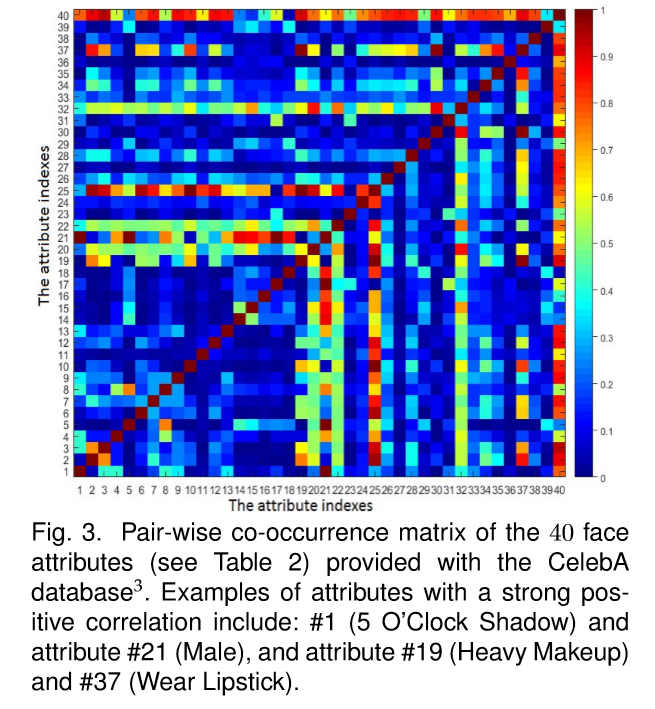
那么,采用 多任务的框架来学习这个东西,就变的特别直觉了。但是,外观变换的出现 以及 the heterogeneity of individual attributes, 从 face image space 到 attribute space 的映射,通常是 nonlinear。所以, the joint attribute estimation model 应该可以捕获到复杂和综合的非线性变换。CNN model 是一种有效的处理 MTL 以及 nonlinear transformation learning 的方法。所以,我们选择基于 CNN 的 多任务框架来完成该任务:
一个传统的 DMTL model 进行联合的属性预测可以 formulated by minimizing the regularization error function:
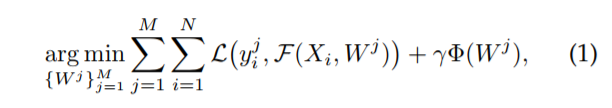
上述 model 就是:重构 loss + 正则化项的标准做法。但是这种方法不是最优的,因为属性之间的关系并没有考虑到,而属性的预测应该共享某些 feature。这也是被其他 paper 所支持的【34】。但是,公式 1 当中的表达方式,并没有显示的强调了 a large portion of feature sharing during MTL。我们将上述表达式改为下面的形式:
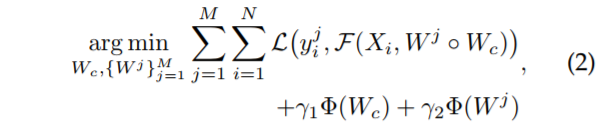
其中,Wc 控制了人脸属性共享的 feature,Wj 控制了共享 feature 的更新。Specifically, as shown in Fig. 2, a face image is first projected to a high-level representation through a shared deep network (Wc) consisting of a cascade of complex non-linear mappings, and then refined by shallow subnetworks ({Wj}M j=1) towards individual attribute estimation tasks。
Heterogeneous Face Attributes Estimation:
尽管上述 DMTL 在特征学习过程中用到了 attribute correlations,the attribute heterogeneity 仍然需要考虑。单个 face Attribute 的异质性曾经被提出过,但没有受到足够多的关注。原因是如下两个方面:
1. many of the public-domain face databases are labeled with a single attribute, the requirement of designing corresponding models becomes no longer urgent ;
2. many of the published methods choose to learn a separate model for each face attribute; model learning for individual attributes does not face the attribute heterogeneity problem.
我们分别对待每一个 异质的属性类别(the heterogeneous attribute categories),但是每一个类别的 attributes 都希望能够共享 feature learning 以及 classification model。为了完成这个,我们重写了目标函数:

其中,G 是异质属性类别的个数。
将大量属性进行几个 heterogeneous categories 的划分,依赖于 prior knowledge。此处,我们从 data type and scale (i.e. ordinal vs. nominal) 以及 semantic meaning (i.e. holistic vs. local) 考虑 face attribute heterogeneities,然后解释我们的 特定类别的建模,来进行这些 heterogeneous attribute categories。
Nominal vs. ordinal attributes .

