SpringMVC是三层架构中的控制层部分,有过JavaWEB开发经验的同学一定很熟悉它的使用了。这边有我之前整理的SpringMVC相关的链接:
看过之后大致对springmvc有一个了解,但对于真正完全掌握springmvc还差得远,本篇博客主要针对的是springmvc的注解开发,传统的项目使用spingmvc避免不了地需要在web.xml里配置前端控制器等等,想要在项目中优雅地去掉这些配置,还得学习如何使用万能的注解来代替这些配置。
Servlet3.0整合SpringMVC
一.原理分析
1) 首先需要导入pom依赖gav:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>4.3.11.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
2) web容器启动
1.web容器启动的时候会扫描每个jar包下的META-INF/services/javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer文件
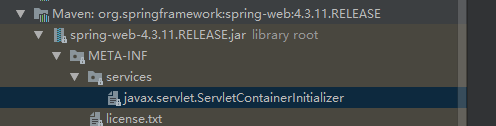
2.加载这个文件指定类的org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer
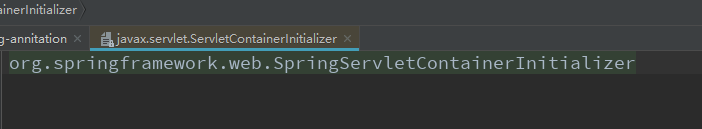
3.Spring的应用一启动会加载感兴趣的WebApplicationInitializer接口下的所有组件
4.并且为WebApplicationInitializer组件创建对象(非接口、非抽象类)
@HandlesTypes({WebApplicationInitializer.class})
public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer {
public SpringServletContainerInitializer() {
}
public void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList();
Iterator var4;
if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) {
var4 = webAppInitializerClasses.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Class<?> waiClass = (Class)var4.next();
if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) {
try {
initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer)waiClass.newInstance());
} catch (Throwable var7) {
throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", var7);
}
}
}
}
if (initializers.isEmpty()) {
servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath");
} else {
servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath");
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers);
var4 = initializers.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
WebApplicationInitializer initializer = (WebApplicationInitializer)var4.next();
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}
}
}
5.WebApplicationInitializer的子类
AbstractContextLoaderInitializer:创建根容器,createRootApplicationContext();
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer:
创建一个web的ioc容器,createServletApplicationContext();
创建了DispacherServlet:createDispacherServlet();
将创建的DispacherServlet添加到ServletContext中
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer:注解方式配置的DispacherServlet初始化器
创建根容器createRootApplicationContext()
创建一个webioc容器createServletApplicationContext()
总结:要以注解方式来启动SpringMVC,实现配置类的方式,需要继承AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,实现抽象方法指定的DispacherServlet的配置信息。
二.整合SpringMVC
经过上述分析,我们来试着整合SpringMVC。
1.创建一个类来继承AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
//在web容器启动的时候创建对象,调用方法来初始化容器以及前端控制器 public class MyWebAppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { /** * 获取根容器的配置(类似于之前监听器配置spring的配置文件) * <listener> * <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> * </listener> * *<context-param> * <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> * <param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext-*.xml</param-value> 。 * </context-param> * * * **/ @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class[]{RootConig.class}; } /** * 获取web容器的配置类(类似于springmvc的配置文件)(前端控制器)子容器 * @return */ @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class[]{AppConfig.class}; } /** * 获取DispatcherServlet的映射信息 * * {"/"}:拦截所有请求包括静态资源(xx.js,xx.png),不包括*.jsp * {"/*"}:拦截所有请求,包括*.jsp,jsp页面是tomcat的jsp引擎解析的 * @return */ @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[]{"/"}; } }
2.创建根容器的配置
//Spring的容器不扫描Controller,交给SpringMvc扫描 @ComponentScan(value = "com.wang",excludeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})}) public class RootConig { }
3.创建web容器的配置类
//SpringMVC只扫描Controller,子容器 //useDefaultFilters=false 禁用默认的过滤规则 @ComponentScan(value = "com.wang",includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})},useDefaultFilters = false) public class AppConfig { }
4.将配置类加入到AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer的子类中


5.创建Controller,Service类测试
@Controller public class HelloController { @Autowired private MyHelloService myHelloService; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/myhello") public String hello(){ return myHelloService.sayHello(); } }
@Service public class MyHelloService { public String sayHello(){ return "hello"; } }
启动应用,访问"/myhello"请求,若能正常访问到该请求,说明上述配置类生效。
三.定制SpringMVC
1). @EnableWebMVC:开启SpringMVC定制配置功能相当于<mvc:annotation-driven/>

2). 配置组件(视图解析器、视图映射、静态资源映射、拦截器)
@ComponentScan(value = "com.wang",includeFilters = {@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class})},useDefaultFilters = false) @EnableWebMvc public class AppConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { /** * 路径映射规则 * @param pathMatchConfigurer */ @Override public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer pathMatchConfigurer) { } /** * 视图解析器 * @param registry */ @Override public void configureViewResolvers(ViewResolverRegistry registry) { //默认所有的页面都从"/WEB-INF/*.jsp" //registry.jsp(); registry.jsp("/WEB-INF/views/",".jsp"); } /** * 配置静态资源访问,将springmvc处理不了的请求交给springmvc,开启后可以访问静态资源(*.js,*.jpg,...) * @param defaultServletHandlerConfigurer */ @Override public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer defaultServletHandlerConfigurer) { defaultServletHandlerConfigurer.enable();//相当于开启了default-servlet-handler <mvc:default-servlet-handler/> } /** * 添加拦截器 * @param registry */ @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { registry.addInterceptor(new MyInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/success"); } }