一、环境
pycharm tensorflow1.15 python3.7 sklearn
二、波士顿房价预测实验

from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression, SGDRegressor, Ridge, LogisticRegression from sklearn.datasets import load_boston from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error #from sklearn.externals import joblib from sklearn.metrics import r2_score from sklearn.neural_network import MLPRegressor import pandas as pd import numpy as np lb = load_boston() x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(lb.data, lb.target, test_size=0.2) # 为数据增加一个维度,相当于把[1, 5, 10] 变成 [[1, 5, 10],] y_train = y_train.reshape(-1, 1)#列数为1 y_test = y_test.reshape(-1, 1) # 进行标准化 std_x = StandardScaler()#标准化数据 x_train = std_x.fit_transform(x_train)#对数据进行某种统一处理 x_test = std_x.transform(x_test) std_y = StandardScaler() y_train = std_y.fit_transform(y_train) y_test = std_y.transform(y_test) # 正规方程预测 lr = LinearRegression()#线性回归 lr.fit(x_train, y_train) print("r2 score of Linear regression is",r2_score(y_test,lr.predict(x_test))) #岭回归 from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeCV cv = RidgeCV(alphas=np.logspace(-3, 2, 100))#样本数据集 cv.fit (x_train , y_train) print("r2 score of Linear regression is",r2_score(y_test,cv.predict(x_test))) #梯度下降 sgd = SGDRegressor()#最大迭代次数 sgd.fit(x_train, y_train)#用训练器数据拟合分类器模型 print("r2 score of Linear regression is",r2_score(y_test,sgd.predict(x_test)))
三、鸢尾花分类

from sklearn import datasets import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from sklearn import tree # Iris数据集是常用的分类实验数据集, # 由Fisher, 1936收集整理。Iris也称鸢尾花卉数据集, # 是一类多重变量分析的数据集。数据集包含150个数据集, # 分为3类,每类50个数据,每个数据包含4个属性。 # 可通过花萼长度,花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度4个属性预测鸢尾花卉属于(Setosa,Versicolour,Virginica)三个种类中的哪一类。 # 载入数据集 iris = datasets.load_iris()#数据集 iris_data = iris['data'] iris_label = iris['target'] iris_target_name = iris['target_names'] X = np.array(iris_data) Y = np.array(iris_label) print(X) # 训练 clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=3) clf.fit(X, Y) # 这里预测当前输入的值的所属分类 print('类别是', iris_target_name[clf.predict([[12, 1, -1, 10]])[0]])
实验截图:

四、特征处理(标准化、归一化、正则化)
4.1

from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler from matplotlib import gridspec import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt cps = np.random.random_integers(0, 100, (100, 2)) ss = StandardScaler()#标准化归一化 std_cps = ss.fit_transform(cps)#对数据进行某种统一处理 gs = gridspec.GridSpec(5, 5)#创建区域,参数5,5的意思就是每行五个,每列五个,最后就是一个5×5的画布 fig = plt.figure()#创建画布 ax1 = fig.add_subplot(gs[0:2, 1:4])#在画布上创建不同的区域 ax2 = fig.add_subplot(gs[3:5, 1:4]) ax1.scatter(cps[:, 0], cps[:, 1])#标准化 ax2.scatter(std_cps[:, 0], std_cps[:, 1]) plt.show()
实验截图:
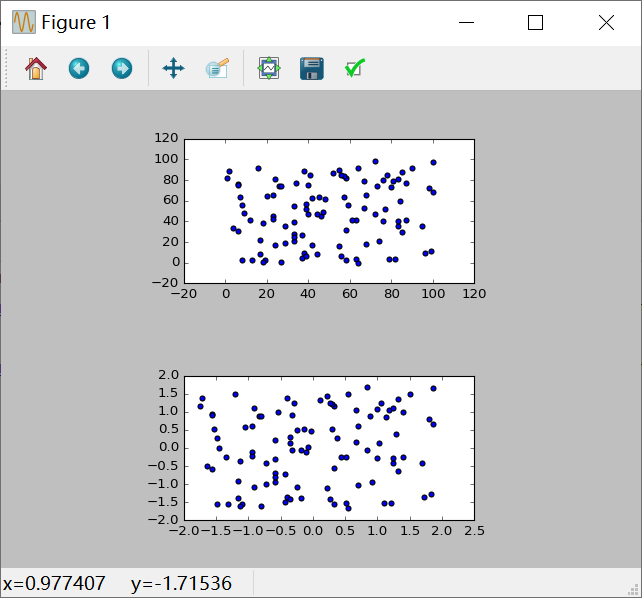
4.2

from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler import numpy as np data = np.random.uniform(0, 100, 10)[:, np.newaxis]#从零位对浮点数组做舍入 mm = MinMaxScaler()#归一化特征到一定区间 mm_data = mm.fit_transform(data)#对数据进行某种统一处理 origin_data = mm.inverse_transform(mm_data)#将标准化后的数据转换为原始数据。 print('data is ',data) print('after Min Max ',mm_data) print('origin data is ',origin_data)
实验截图:
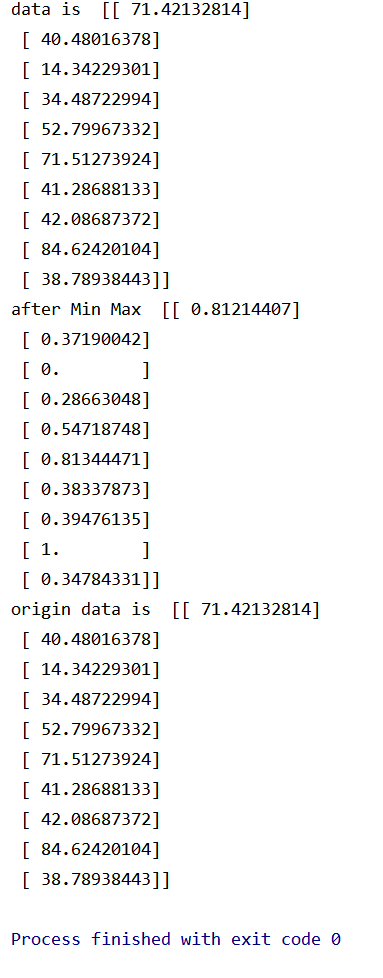
4.3

X = [[1, -1, 2], [2, 0, 0], [0, 1, -1]] # 使用L2正则化 from sklearn.preprocessing import normalize l2 = normalize(X, norm='l2')#数据预处理 print('l2:', l2) # 使用L1正则化 from sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer normalizerl1 = Normalizer(norm='l1')#对每个样本的每一个元素都除以该样本的L1范数. l1 = normalizerl1.fit_transform(X) print('l1:', l1)
实验截图:

五、交叉验证

from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split,cross_val_score,cross_validate # 交叉验证所需的函数 from sklearn.model_selection import KFold,LeaveOneOut,LeavePOut,ShuffleSplit # 交叉验证所需的子集划分方法 from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold,StratifiedShuffleSplit # 分层分割 from sklearn.model_selection import GroupKFold,LeaveOneGroupOut,LeavePGroupsOut,GroupShuffleSplit # 分组分割 from sklearn.model_selection import TimeSeriesSplit # 时间序列分割 from sklearn import datasets # 自带数据集 from sklearn import svm # SVM算法 from sklearn import preprocessing # 预处理模块 from sklearn.metrics import recall_score # 模型度量 iris = datasets.load_iris() # 加载数据集 print('样本集大小:',iris.data.shape,iris.target.shape) # ===================================数据集划分,训练模型========================== X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, test_size=0.4, random_state=0) # 交叉验证划分训练集和测试集.test_size为测试集所占的比例 print('训练集大小:',X_train.shape,y_train.shape) # 训练集样本大小 print('测试集大小:',X_test.shape,y_test.shape) # 测试集样本大小 clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=1).fit(X_train, y_train) # 使用训练集训练模型 print('准确率:',clf.score(X_test, y_test)) # 计算测试集的度量值(准确率) # 如果涉及到归一化,则在测试集上也要使用训练集模型提取的归一化函数。 scaler = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit(X_train) # 通过训练集获得归一化函数模型。(也就是先减几,再除以几的函数)。在训练集和测试集上都使用这个归一化函数 X_train_transformed = scaler.transform(X_train) clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=1).fit(X_train_transformed, y_train) # 使用训练集训练模型 X_test_transformed = scaler.transform(X_test) print(clf.score(X_test_transformed, y_test)) # 计算测试集的度量值(准确度) # ===================================直接调用交叉验证评估模型========================== clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear', C=1) scores = cross_val_score(clf, iris.data, iris.target, cv=5) #cv为迭代次数。 print(scores) # 打印输出每次迭代的度量值(准确度) print("Accuracy: %0.2f (+/- %0.2f)" % (scores.mean(), scores.std() * 2)) # 获取置信区间。(也就是均值和方差) # ===================================多种度量结果====================================== scoring = ['precision_macro', 'recall_macro'] # precision_macro为精度,recall_macro为召回率 scores = cross_validate(clf, iris.data, iris.target, scoring=scoring,cv=5, return_train_score=True) sorted(scores.keys()) print('测试结果:',scores) # scores类型为字典。包含训练得分,拟合次数, score-times (得分次数) # ==================================K折交叉验证、留一交叉验证、留p交叉验证、随机排列交叉验证========================================== # k折划分子集 kf = KFold(n_splits=2) for train, test in kf.split(iris.data): print("k折划分:%s %s" % (train.shape, test.shape)) break # 留一划分子集 loo = LeaveOneOut() for train, test in loo.split(iris.data): print("留一划分:%s %s" % (train.shape, test.shape)) break # 留p划分子集 lpo = LeavePOut(p=2) for train, test in loo.split(iris.data): print("留p划分:%s %s" % (train.shape, test.shape)) break # 随机排列划分子集 ss = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=3, test_size=0.25,random_state=0) for train_index, test_index in ss.split(iris.data): print("随机排列划分:%s %s" % (train.shape, test.shape)) break # ==================================分层K折交叉验证、分层随机交叉验证========================================== skf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3) #各个类别的比例大致和完整数据集中相同 for train, test in skf.split(iris.data, iris.target): print("分层K折划分:%s %s" % (train.shape, test.shape)) break skf = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=3) # 划分中每个类的比例和完整数据集中的相同 for train, test in skf.split(iris.data, iris.target): print("分层随机划分:%s %s" % (train.shape, test.shape)) break # ==================================组 k-fold交叉验证、留一组交叉验证、留 P 组交叉验证、Group Shuffle Split========================================== X = [0.1, 0.2, 2.2, 2.4, 2.3, 4.55, 5.8, 8.8, 9, 10] y = ["a", "b", "b", "b", "c", "c", "c", "d", "d", "d"] groups = [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3] # k折分组 gkf = GroupKFold(n_splits=3) # 训练集和测试集属于不同的组 for train, test in gkf.split(X, y, groups=groups): print("组 k-fold分割:%s %s" % (train, test)) # 留一分组 logo = LeaveOneGroupOut() for train, test in logo.split(X, y, groups=groups): print("留一组分割:%s %s" % (train, test)) # 留p分组 lpgo = LeavePGroupsOut(n_groups=2) for train, test in lpgo.split(X, y, groups=groups): print("留 P 组分割:%s %s" % (train, test)) # 随机分组 gss = GroupShuffleSplit(n_splits=4, test_size=0.5, random_state=0) for train, test in gss.split(X, y, groups=groups): print("随机分割:%s %s" % (train, test)) # ==================================时间序列分割========================================== tscv = TimeSeriesSplit(n_splits=3) TimeSeriesSplit(max_train_size=None, n_splits=3) for train, test in tscv.split(iris.data): print("时间序列分割:%s %s" % (train, test))
