一、运算符
运算按种类可分为算数运算、比较运算、逻辑运算、赋值运算、成员运算、身份运算、位运算。
算数运算
以下假设变量:a=10,b=2

比较运算
以下假设变量:a=10,b=20
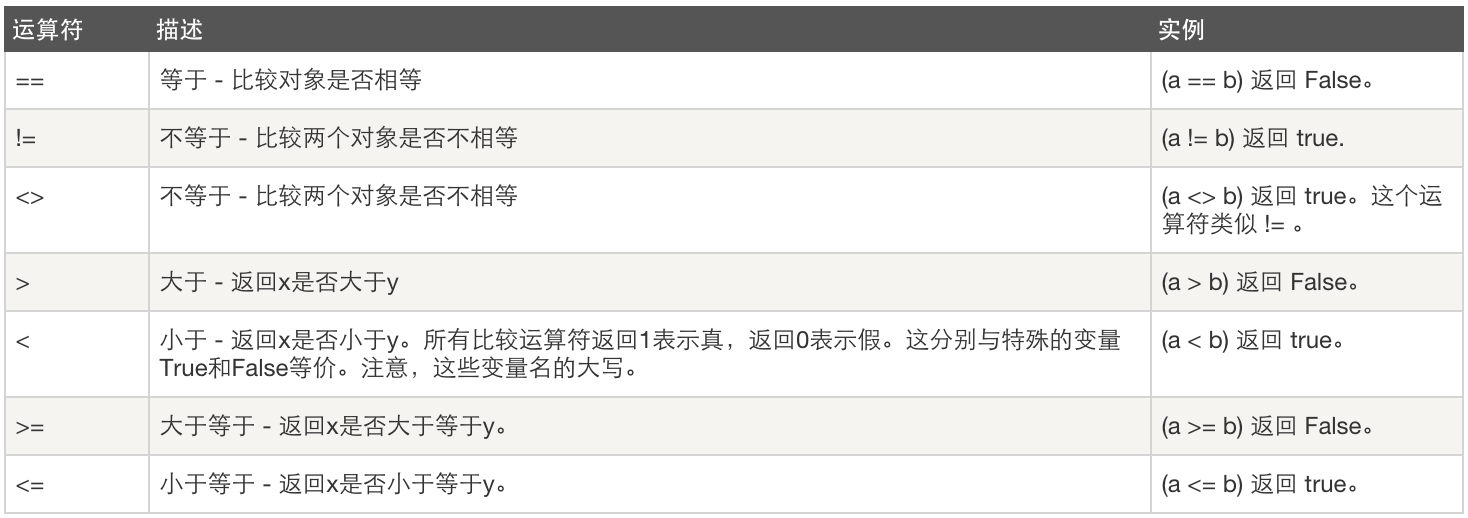
赋值运算
以下假设变量:a=10,b=20(其中=,+=,-=用得比较多)

逻辑运算
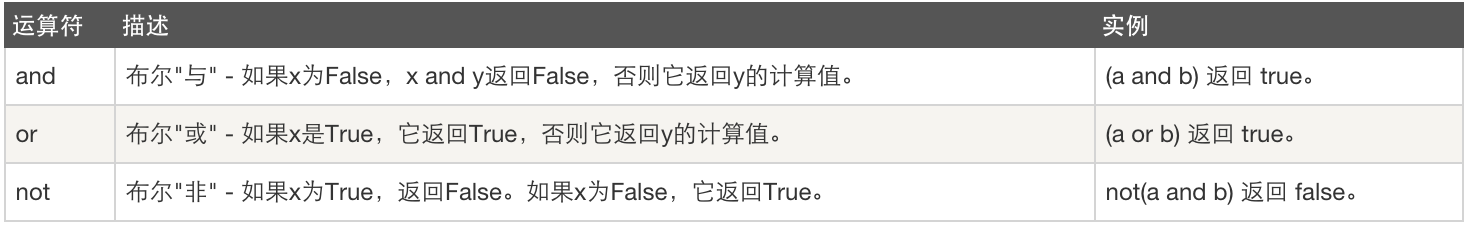
重点:
首先,‘and’、‘or’和‘not’的优先级是not>and>or。
and :x and y 返回的结果是决定表达式结果的值。如果 x 为真,则 y 决定结果,返回 y ;如果 x 为假,x 决定了结果为假,返回 x。
or :x or y 跟 and 一样都是返回决定表达式结果的值。
not : 返回表达式结果的“相反的值”。如果表达式结果为真,则返回false;如果表达式结果为假,则返回true。
>>> 4 and 3 3 >>> 3 and 4 4 >>> 4 or 3 4 >>> 3 or 4 3 >>> True or False and False True >>> (True or False) and False False
二、流程控制
if...else 语句
if 条件: 满足条件执行代码 else: if条件不满足就走这段 AgeOfOldboy = 48 if AgeOfOldboy > 50 : print("Too old, time to retire..") else: print("还能折腾几年!")
多分支
age_of_oldboy = 48 guess = int(input(">>:")) if guess > age_of_oldboy : print("猜的太大了,往小里试试...") elif guess < age_of_oldboy : print("猜的太小了,往大里试试...") else: print("恭喜你,猜对了...")
重点:
Python的缩进有以下几个原则:
1、顶级代码必须顶行写,即如果一行代码本身不依赖于任何条件,那它必须不能进行任何缩进
2、同一级别的代码,缩进必须一致
3、官方建议缩进用4个空格
While 循环
count = 0 while count <= 100 : #只要count<=100就不断执行下面的代码 print("loop ", count ) count +=1 #每执行一次,就把count+1,要不然就变成死循环,因为count一直是0
结果:
loop 0 loop 1 loop 2 loop 3 .... loop 98 loop 99 loop 100
注意:避免出现死循环,while 是只要后边条件成立(也就是条件结果为真)就一直执行。
循环中止语句(continue , break)
break用于完全结束一个循环,跳出循环体执行循环后面的语句
count = 0 while count <= 100 : #只要count<=100就不断执行下面的代码 print("loop ", count) if count == 5: break count +=1 #每执行一次,就把count+1,要不然就变成死循环,因为count一直是0 print("-----out of while loop ------") 输出 loop 0 loop 1 loop 2 loop 3 loop 4 loop 5 -----out of while loop ------
continue和break有点类似,区别在于continue只是终止本次循环,接着还执行后面的循环,break则完全终止循环
count = 0 while count <= 100 : count += 1 if count > 5 and count < 95: #只要count在6-94之间,就不走下面的print语句,直接进入下一次loop continue print("loop ", count) print("-----out of while loop ------") 输出 loop 1 loop 2 loop 3 loop 4 loop 5 loop 95 loop 96 loop 97 loop 98 loop 99 loop 100 loop 101 -----out of while loop ------
while ... else ..
当while 循环正常执行完,中间没有被break 中止的话,就会执行else后面的语句
count = 0 while count <= 5 : count += 1 print("Loop",count) else: print("循环正常执行完") print("-----out of while loop ------") 输出 Loop 1 Loop 2 Loop 3 Loop 4 Loop 5 Loop 6 循环正常执行完 -----out of while loop ------
如果执行过程中被break啦,就不会执行else的语句。
for循环
for循环主要用于循环取值 student=['egon','虎老师','lxxdsb','alexdsb','wupeiqisb'] i=0 while i < len(student): print(student[i]) i+=1 for item in student: print(item) for item in 'hello': print(item) dic={'x':444,'y':333,'z':555} for k in dic: print(k,dic[k]) for i in range(1,10,3): print(i) for i in range(10): print(i) student=['egon','虎老师','lxxdsb','alexdsb','wupeiqisb'] for item in student: print(item) for i in range(len(student)): print(i,student[i])