如何统计对象中某个成员变量的访问次数?
解法:

这里我们只能满足普通对象的访问统计,那么const对象呢?
完善解法,使得能统计只读对象的访问次数:


使用了mutable之后,只读对象名存实亡。
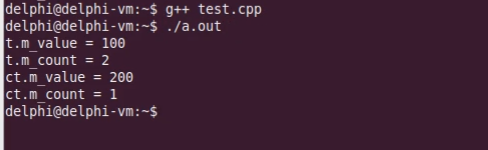
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Test 7 { 8 int m_value; 9 int * const m_pCount; 10 /* mutable int m_count; */ 11 public: 12 Test(int value = 0) : m_pCount(new int(0)) 13 { 14 m_value = value; 15 /* m_count = 0; */ 16 } 17 18 int getValue() const 19 { 20 /* m_count++; */ 21 *m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1; 22 return m_value; 23 } 24 25 void setValue(int value) 26 { 27 /* m_count++; */ 28 *m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1; 29 m_value = value; 30 } 31 32 int getCount() const 33 { 34 /* return m_count; */ 35 return *m_pCount; 36 } 37 38 ~Test() 39 { 40 delete m_pCount; 41 } 42 }; 43 44 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 45 { 46 Test t; 47 48 t.setValue(100); 49 50 cout << "t.m_value = " << t.getValue() << endl; 51 cout << "t.m_count = " << t.getCount() << endl; 52 53 const Test ct(200); 54 55 cout << "ct.m_value = " << ct.getValue() << endl; 56 cout << "ct.m_count = " << ct.getCount() << endl; 57 58 return 0; 59 }
使用mutable可以完成const对象的访问统计,但是不使用mutable也可以完成这个需求。
使用指针常量完成这个需求,不改变指针的值,但是可以改变指针指向的值。
运行结果如下:
实际工程中,mutable使用比较少。最好不要使用。
问题2:
new关键字创建出来的对象位于什么地方?
被忽略的事实:

我们通过一些方法可以是new出来的对象位于静态存储区。
new是关键字,也是操作符,因此,可以重载new和delete。

工程中不建议全局重载new。

通过函数来对这两个操作符进行重载,一般情况下都是针对具体的类进行重载,所以new和delete的重载函数就是类的成员函数,并且这两个重载函数默认为静态成员函数,写不写static都是静态的。
静态存储区中创建动态对象:
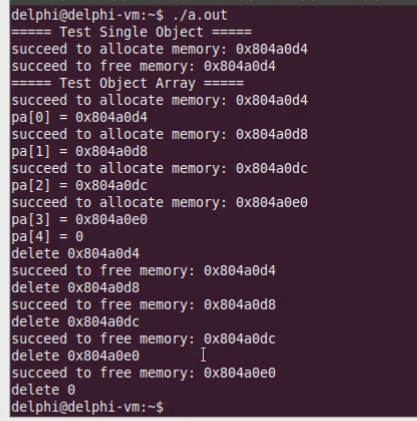
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Test 7 { 8 static const unsigned int COUNT = 4; 9 static char c_buffer[]; 10 static char c_map[]; 11 12 int m_value; 13 public: 14 void* operator new (unsigned int size) 15 { 16 void* ret = NULL; 17 18 for(int i=0; i<COUNT; i++) 19 { 20 if( !c_map[i] ) 21 { 22 c_map[i] = 1; 23 24 ret = c_buffer + i * sizeof(Test); 25 26 cout << "succeed to allocate memory: " << ret << endl; 27 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 32 return ret; 33 } 34 35 void operator delete (void* p) 36 { 37 if( p != NULL ) 38 { 39 char* mem = reinterpret_cast<char*>(p); 40 int index = (mem - c_buffer) / sizeof(Test); 41 int flag = (mem - c_buffer) % sizeof(Test); 42 43 if( (flag == 0) && (0 <= index) && (index < COUNT) ) 44 { 45 c_map[index] = 0; 46 47 cout << "succeed to free memory: " << p << endl; 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 }; 52 53 char Test::c_buffer[sizeof(Test) * Test::COUNT] = {0}; 54 char Test::c_map[Test::COUNT] = {0}; 55 56 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 57 { 58 cout << "===== Test Single Object =====" << endl; 59 60 Test* pt = new Test; 61 62 delete pt; 63 64 cout << "===== Test Object Array =====" << endl; 65 66 Test* pa[5] = {0}; 67 68 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) 69 { 70 pa[i] = new Test; 71 72 cout << "pa[" << i << "] = " << pa[i] << endl; 73 } 74 75 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) 76 { 77 cout << "delete " << pa[i] << endl; 78 79 delete pa[i]; 80 } 81 82 return 0; 83 }
第53行定义静态存储空间。
运行结果如下:
我们可以使用这种方法结合二阶构造法,可以限制一个类最多产生多少个对象。
单例模式仅仅是使一个创建一个对象,而在静态存储区创建类结合二阶构造模式可以完成n例模式。
问题3:
如何在指定的地址上创建C++对象?

自定义对象的存储空间示例程序:
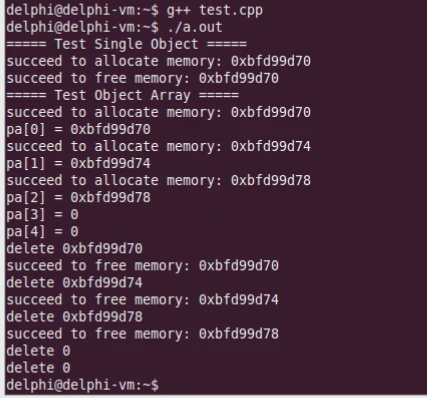
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Test 8 { 9 static unsigned int c_count; 10 static char* c_buffer; 11 static char* c_map; 12 13 int m_value; 14 public: 15 static bool SetMemorySource(char* memory, unsigned int size) 16 { 17 bool ret = false; 18 19 c_count = size / sizeof(Test); 20 21 ret = (c_count && (c_map = reinterpret_cast<char*>(calloc(c_count, sizeof(char))))); 22 23 if( ret ) 24 { 25 c_buffer = memory; 26 } 27 else 28 { 29 free(c_map); 30 31 c_map = NULL; 32 c_buffer = NULL; 33 c_count = 0; 34 } 35 36 return ret; 37 } 38 39 void* operator new (unsigned int size) 40 { 41 void* ret = NULL; 42 43 if( c_count > 0 ) 44 { 45 for(int i=0; i<c_count; i++) 46 { 47 if( !c_map[i] ) 48 { 49 c_map[i] = 1; 50 51 ret = c_buffer + i * sizeof(Test); 52 53 cout << "succeed to allocate memory: " << ret << endl; 54 55 break; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 else 60 { 61 ret = malloc(size); 62 } 63 64 return ret; 65 } 66 67 void operator delete (void* p) 68 { 69 if( p != NULL ) 70 { 71 if( c_count > 0 ) 72 { 73 char* mem = reinterpret_cast<char*>(p); 74 int index = (mem - c_buffer) / sizeof(Test); 75 int flag = (mem - c_buffer) % sizeof(Test); 76 77 if( (flag == 0) && (0 <= index) && (index < c_count) ) 78 { 79 c_map[index] = 0; 80 81 cout << "succeed to free memory: " << p << endl; 82 } 83 } 84 else 85 { 86 free(p); 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 }; 91 92 unsigned int Test::c_count = 0; 93 char* Test::c_buffer = NULL; 94 char* Test::c_map = NULL; 95 96 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 97 { 98 char buffer[12] = {0}; 99 100 Test::SetMemorySource(buffer, sizeof(buffer)); 101 102 cout << "===== Test Single Object =====" << endl; 103 104 Test* pt = new Test; 105 106 delete pt; 107 108 cout << "===== Test Object Array =====" << endl; 109 110 Test* pa[5] = {0}; 111 112 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) 113 { 114 pa[i] = new Test; 115 116 cout << "pa[" << i << "] = " << pa[i] << endl; 117 } 118 119 for(int i=0; i<5; i++) 120 { 121 cout << "delete " << pa[i] << endl; 122 123 delete pa[i]; 124 } 125 126 return 0; 127 }
15行的函数用于动态设置创建对象的地址。
结果如下:
被忽略的事实:


new[]和delete[]是新的操作符,不同于new和delete。

动态数组的内存管理:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Test 8 { 9 int m_value; 10 public: 11 Test() 12 { 13 m_value = 0; 14 } 15 16 ~Test() 17 { 18 } 19 20 void* operator new (unsigned int size) 21 { 22 cout << "operator new: " << size << endl; 23 24 return malloc(size); 25 } 26 27 void operator delete (void* p) 28 { 29 cout << "operator delete: " << p << endl; 30 31 free(p); 32 } 33 34 void* operator new[] (unsigned int size) 35 { 36 cout << "operator new[]: " << size << endl; 37 38 return malloc(size); 39 } 40 41 void operator delete[] (void* p) 42 { 43 cout << "operator delete[]: " << p << endl; 44 45 free(p); 46 } 47 }; 48 49 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 50 { 51 Test* pt = NULL; 52 53 pt = new Test; 54 55 delete pt; 56 57 pt = new Test[5]; 58 59 delete[] pt; 60 61 return 0; 62 }
运行结果如下:

我们通过重载的方式说明了new 和new[]的不同,第57行的new调用的是34行的new[]重载,第57行5个元素占用20个字节,但是结果中却打印出了24个字节,这就是额外的空间记录数组的长度信息。这个长度信息用于记录调用析构函数的次数。
new[]和delete[]的使用必须匹配,不能和new、delete交叉使用。 例如new[]在栈上分配空间时,使用delete释放到堆上,这样就可能崩溃。或者使用delete只会调用一次析构函数。
小结:
