1、在上一篇博客中我们构建度为二的因子分解机模型,这篇博客对这个模型进行实践
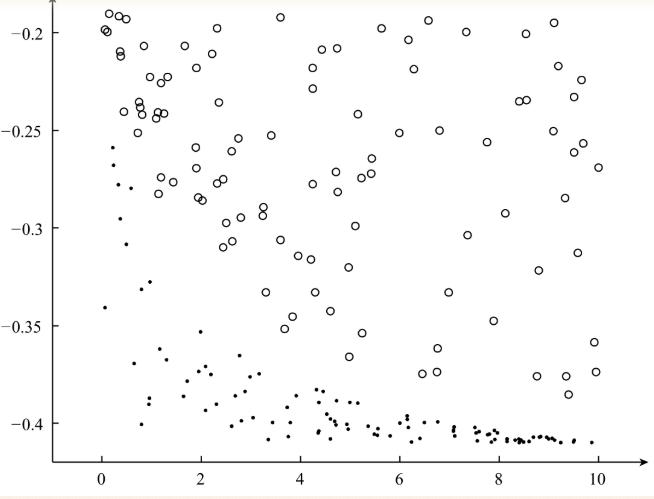
下图为准备的数据集:
完整代码为:

1 # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- 2 # date:2018/6/6 3 # User:WangHong 4 import numpy as np 5 from random import normalvariate # 正态分布 6 7 def loadDataSet(data): 8 '''导入训练数据 9 input: data(string)训练数据 10 output: dataMat(list)特征 11 labelMat(list)标签 12 ''' 13 dataMat = [] 14 labelMat = [] 15 fr = open(data) # 打开文件 16 for line in fr.readlines(): 17 lines = line.strip().split(" ") 18 lineArr = [] 19 20 for i in range(len(lines) - 1): 21 lineArr.append(float(lines[i])) 22 dataMat.append(lineArr) 23 24 labelMat.append(float(lines[-1]) * 2 - 1) # 转换成{-1,1} 25 fr.close() 26 return dataMat, labelMat 27 28 def sigmoid(inx): 29 return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inx)) 30 31 def initialize_v(n, k): 32 '''初始化交叉项 33 input: n(int)特征的个数 34 k(int)FM模型的超参数 35 output: v(mat):交叉项的系数权重 36 ''' 37 v = np.mat(np.zeros((n, k))) 38 39 for i in range(n): 40 for j in range(k): 41 # 利用正态分布生成每一个权重 42 v[i, j] = normalvariate(0, 0.2) 43 return v 44 45 def stocGradAscent(dataMatrix, classLabels, k, max_iter, alpha): 46 '''利用随机梯度下降法训练FM模型 47 input: dataMatrix(mat)特征 48 classLabels(mat)标签 49 k(int)v的维数 50 max_iter(int)最大迭代次数 51 alpha(float)学习率 52 output: w0(float),w(mat),v(mat):权重 53 ''' 54 m, n = np.shape(dataMatrix) 55 # 1、初始化参数 56 w = np.zeros((n, 1)) # 其中n是特征的个数 57 w0 = 0 # 偏置项 58 v = initialize_v(n, k) # 初始化V 59 60 # 2、训练 61 for it in range(max_iter): 62 for x in range(m): # 随机优化,对每一个样本而言的 63 inter_1 = dataMatrix[x] * v 64 inter_2 = np.multiply(dataMatrix[x], dataMatrix[x]) * 65 np.multiply(v, v) # multiply对应元素相乘 66 # 完成交叉项 67 interaction = np.sum(np.multiply(inter_1, inter_1) - inter_2) / 2. 68 p = w0 + dataMatrix[x] * w + interaction # 计算预测的输出 69 loss = sigmoid(classLabels[x] * p[0, 0]) - 1 70 71 w0 = w0 - alpha * loss * classLabels[x] 72 for i in range(n): 73 if dataMatrix[x, i] != 0: 74 w[i, 0] = w[i, 0] - alpha * loss * classLabels[x] * dataMatrix[x, i] 75 76 for j in range(k): 77 v[i, j] = v[i, j] - alpha * loss * classLabels[x] * 78 (dataMatrix[x, i] * inter_1[0, j] - 79 v[i, j] * dataMatrix[x, i] * dataMatrix[x, i]) 80 81 # 计算损失函数的值 82 if it % 1000 == 0: 83 print (" ------- iter: ", it, " , cost: ", 84 getCost(getPrediction(np.mat(dataMatrix), w0, w, v), classLabels)) 85 86 # 3、返回最终的FM模型的参数 87 return w0, w, v 88 89 def getCost(predict, classLabels): 90 '''计算预测准确性 91 input: predict(list)预测值 92 classLabels(list)标签 93 output: error(float)计算损失函数的值 94 ''' 95 m = len(predict) 96 error = 0.0 97 for i in range(m): 98 error -= np.log(sigmoid(predict[i] * classLabels[i] )) 99 return error 100 101 def getPrediction(dataMatrix, w0, w, v): 102 '''得到预测值 103 input: dataMatrix(mat)特征 104 w(int)常数项权重 105 w0(int)一次项权重 106 v(float)交叉项权重 107 output: result(list)预测的结果 108 ''' 109 m = np.shape(dataMatrix)[0] 110 result = [] 111 for x in range(m): 112 113 inter_1 = dataMatrix[x] * v 114 inter_2 = np.multiply(dataMatrix[x], dataMatrix[x]) * 115 np.multiply(v, v) # multiply对应元素相乘 116 # 完成交叉项 117 interaction = np.sum(np.multiply(inter_1, inter_1) - inter_2) / 2. 118 p = w0 + dataMatrix[x] * w + interaction # 计算预测的输出 119 pre = sigmoid(p[0, 0]) 120 result.append(pre) 121 return result 122 123 def getAccuracy(predict, classLabels): 124 '''计算预测准确性 125 input: predict(list)预测值 126 classLabels(list)标签 127 output: float(error) / allItem(float)错误率 128 ''' 129 m = len(predict) 130 allItem = 0 131 error = 0 132 for i in range(m): 133 allItem += 1 134 if float(predict[i]) < 0.5 and classLabels[i] == 1.0: 135 error += 1 136 elif float(predict[i]) >= 0.5 and classLabels[i] == -1.0: 137 error += 1 138 else: 139 continue 140 return float(error) / allItem 141 142 def save_model(file_name, w0, w, v): 143 '''保存训练好的FM模型 144 input: file_name(string):保存的文件名 145 w0(float):偏置项 146 w(mat):一次项的权重 147 v(mat):交叉项的权重 148 ''' 149 f = open(file_name, "w") 150 # 1、保存w0 151 f.write(str(w0) + " ") 152 # 2、保存一次项的权重 153 w_array = [] 154 m = np.shape(w)[0] 155 for i in range(m): 156 w_array.append(str(w[i, 0])) 157 f.write(" ".join(w_array) + " ") 158 # 3、保存交叉项的权重 159 m1 , n1 = np.shape(v) 160 for i in range(m1): 161 v_tmp = [] 162 for j in range(n1): 163 v_tmp.append(str(v[i, j])) 164 f.write(" ".join(v_tmp) + " ") 165 f.close() 166 167 168 if __name__ == "__main__": 169 # 1、导入训练数据 170 print ("---------- 1.load data ---------") 171 dataTrain, labelTrain = loadDataSet("data_1.txt") 172 print( "---------- 2.learning ---------") 173 # 2、利用随机梯度训练FM模型 174 w0, w, v = stocGradAscent(np.mat(dataTrain), labelTrain, 3, 10000, 0.01) 175 predict_result = getPrediction(np.mat(dataTrain), w0, w, v) # 得到训练的准确性 176 print( "----------training accuracy: %f" % (1 - getAccuracy(predict_result, labelTrain))) 177 print ("---------- 3.save result ---------") 178 # 3、保存训练好的FM模型 179 save_model("weights", w0, w, v)
最终训练过程为:
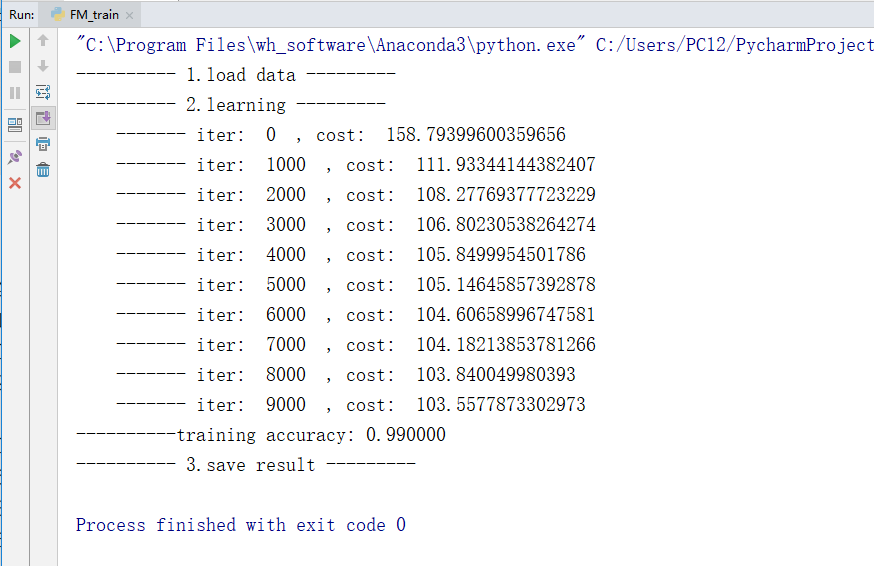
训练的过程比较慢,我用来将近有一分半
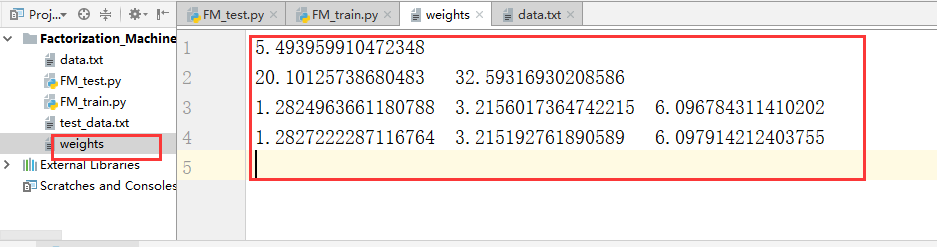
得到的权值文件为:
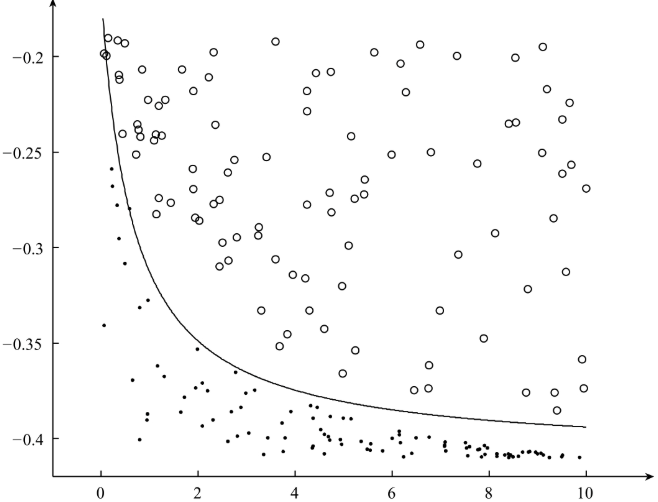
最终分隔得到的超平面为:
2、对新的数据进行预测:
预测的全部代码为:

1 # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- 2 # date:2018/6/6 3 # User:WangHong 4 5 import numpy as np 6 7 from FM_train import getPrediction 8 9 def loadDataSet(data): 10 '''导入测试数据集 11 input: data(string)测试数据 12 output: dataMat(list)特征 13 ''' 14 dataMat = [] 15 fr = open(data) # 打开文件 16 for line in fr.readlines(): 17 lines = line.strip().split(" ") 18 lineArr = [] 19 20 for i in range(len(lines)): 21 lineArr.append(float(lines[i])) 22 dataMat.append(lineArr) 23 24 fr.close() 25 return dataMat 26 27 def loadModel(model_file): 28 '''导入FM模型 29 input: model_file(string)FM模型 30 output: w0, np.mat(w).T, np.mat(v)FM模型的参数 31 ''' 32 f = open(model_file) 33 line_index = 0 34 w0 = 0.0 35 w = [] 36 v = [] 37 for line in f.readlines(): 38 lines = line.strip().split(" ") 39 if line_index == 0: # w0 40 w0 = float(lines[0].strip()) 41 elif line_index == 1: # w 42 for x in lines: 43 w.append(float(x.strip())) 44 else: 45 v_tmp = [] 46 for x in lines: 47 v_tmp.append(float(x.strip())) 48 v.append(v_tmp) 49 line_index += 1 50 f.close() 51 return w0, np.mat(w).T, np.mat(v) 52 53 def save_result(file_name, result): 54 '''保存最终的预测结果 55 input: file_name(string)需要保存的文件名 56 result(mat):对测试数据的预测结果 57 ''' 58 f = open(file_name, "w") 59 f.write(" ".join(str(x) for x in result)) 60 f.close() 61 62 if __name__ == "__main__": 63 # 1、导入测试数据 64 dataTest = loadDataSet("test_data.txt") 65 # 2、导入FM模型 66 w0, w , v = loadModel("weights") 67 # 3、预测 68 result = getPrediction(dataTest, w0, w, v) 69 # 4、保存最终的预测结果 70 save_result("predict_result", result) 71 72
最终测试结果得到一个predict_result.txt文件