YAML 语言(发音 /ˈjæməl/ )的设计目标,就是方便人类读写。它实质上是一种通用的数据串行化格式。
它的基本语法规则如下。
• 大小写敏感
• 使用缩进表示层级关系
• 缩进时不允许使用Tab键,只允许使用空格。
• 缩进的空格数目不重要,只要相同层级的元素左侧对齐即可
• yaml文件以"---"作为文档的开始,"..."作为文档的结束
#表示注释,从这个字符一直到行尾,都会被解析器忽略。
YAML 支持的数据结构有三种。
• 对象:键值对的集合,又称为映射(mapping)/ 哈希(hashes) / 字典(dictionary)
• 数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列(sequence) / 列表(list)
• 纯量(scalars):单个的、不可再分的值
对象
对象的一组键值对,使用冒号结构表示。
job: Developer
列表
--- fruits: - Apple - Orange - Strawberry - Mango
转换为python格式
{'fruits': ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Strawberry', 'Mango']}
可以使用行内表示法
--- fruits: ['Apple', 'Orange', 'Strawberry', 'Mango']
字典
--- martin: name: Martin D'vloper job: Developer skill: Elite
转换为python格式
{'martin': {'job': 'Developer', 'name': "Martin D'vloper", 'skill': 'Elite'}}
可以使用行业内表示法
---
martin: {name: Martin D'vloper, job: Developer, skill: Elite}
复合结构
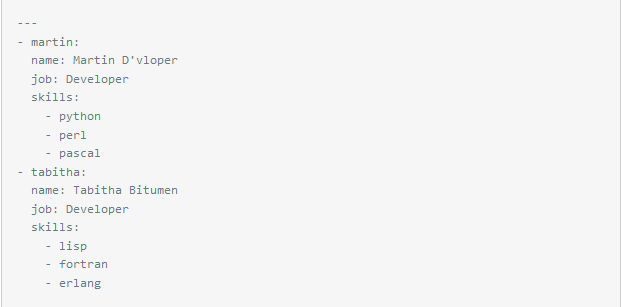
转换为python格式
[{'martin': {'job': 'Developer','name': "Martin D'vloper",'skills': ['python', 'perl', 'pascal']}},{'tabitha': {'job': 'Developer', 'name': 'Tabitha Bitumen','skills': ['lisp', 'fortran', 'erlang']}}]
纯量
数值
number: 12 float:12.30
转换为python格式
{'float': 12.300000000000001, 'number': 12}
布尔值
表示true的值
true, True, TRUE, yes, Yes, YES, on, On, ON, y, Y
表示false的值
false, False, FALSE, no, No, NO, off, Off, OFF, n, N
转换数据类型
e: !!str 123 f: !!str true
转换为python格式
{'e': '123', 'f': 'true'}
字符串
# 字符串默认不使用引号表示。
str: 这是一行字符串
# 转换为python格式
{'str': '这是一行字符串'}
# 单引号和双引号都可以使用,双引号不会对特殊字符转义。
# 如果字符串之中包含空格或特殊字符,需要放在引号之中。
str: '内容: 字符串'
# 转换为python格式
{'str': '内容: 字符串'}
s1: '内容
字符串'
s2: "内容
字符串"
# 转换为python格式
{'s1': '内容\n字符串','s2': '内容
字符串'}
# 单引号之中如果还有单引号,必须连续使用两个单引号转义。
str: 'labor''s day'
# 转换为python格式
{'str': "labor's day"}
# 字符串可以写成多行,从第二行开始,必须有一个单空格缩进。换行符会被转为空格。
str: 这是一段
多行
字符串
# 转换为python格式
{'str': '这是一段 多行 字符串'}
# 多行字符串可以使用|保留换行符,也可以使用>折叠换行。
this: |
Foo
Bar
that: >
Foo
Bar
# 转换为python格式
{'that': 'Foo Bar', 'this': 'Foo
Bar
'}
# +表示保留文字块末尾的换行,-表示删除字符串末尾的换行。
s1: |
Foo
s2: |+
Foo
s3: |-
Foo
# 转换为python格式
{'s1': 'Foo
', 's2': 'Foo
', 's3': 'Foo'}
# 字符串之中可以插入 HTML 标记。
message: |
<p style="color: red">
段落
</p>
# 转换为python格式
{'message': '
<p style="color: red">
段落
</p>'}
引用
# 锚点&和别名*,可以用来引用。
# &用来建立锚点(defaults),<<表示合并到当前数据,*用来引用锚点。
defaults: &defaults
adapter: postgres
host: localhost
development:
database: myapp_development
<<: *defaults
test:
database: myapp_test
<<: *defaults
# 等同于下面的代码。
defaults:
adapter: postgres
host: localhost
development:
database: myapp_development
adapter: postgres
host: localhost
test:
database: myapp_
test adapter: postgres
host: localhost
# 转换为python格式
{'defaults': {'adapter': 'postgres', 'host': 'localhost'}, 'development': {'adapter': 'postgres', 'database': 'myapp_development', 'host': 'localhost'}, 'test': {'adapter': 'postgres', 'database': 'myapp_test', 'host': 'localhost'}}
# 下面是另一个例子。
- &showell Steve
- Clark
- Brian
- Oren
- *showell
# 转换为python格式
['Steve', 'Clark', 'Brian', 'Oren', 'Steve']
yaml中引用变量
foo: "{{ variable }}"
高级YAML语法
!unsafe使用
# 变量值中保存的数据应被视为不安全的,防止不安全的字符子集和信息披露。
---
hosts: all
vars:
my_unsafe_variable: !unsafe 'unsafe value'
tasks:
...