一:概念
LinkedBlockingQueue是一个用链表实现的有界阻塞队列。此队列的默认和最大长度为 Integer.MAX_VALUE。此队列按照先进先出的原则对元素进行排序。
与ArrayBlockingQueue的异同:
ArrayBlockingQueue: 必须设置长度容量 底层数组结构 单锁控制
LinkedBlockingQueue:默认Integer最大值 底层链表结构 双锁
二:LinkedBlockingQueue源码实现
不设置容量,默认为Integer的最大值

也支持设置容量

也支持预先将集合设置入队列

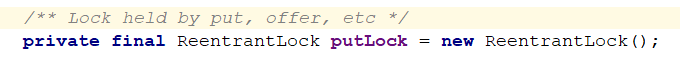
两把锁,一个take锁,控制消费者并发,一个put锁,控制生产者并发:

内部维护单向链表结构:

来看一下主要方法:offer与poll
offer方法:
如果e为null或者对列已满,返回false, 然后加锁,其他的生产者会被阻塞,再次判断如果对列里面元素数量小于容量,那么入队,对列的数量也自加,
如果这时对列仍然有空间,会唤醒正在等待的其他生产者,向对列里面放数据。
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == capacity)
return false;
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() < capacity) {
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
return c >= 0;
}
入队方法:
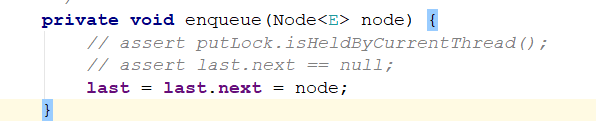
如果是第一次放入数据,效果图:

主要是建立两个连接,让最后一个元素last指向新来的元素,然后将last指针指向新来的。
再来看一下poll方法:取数据
如果对列为空,返回null ,然后加锁,其他想取数据的消费者线程会被阻塞, 如果没有数据释放锁,返回null,对列有数据,则出队,对列自减,
如果出队后对列中还有数据,那么会唤醒正在等待的其他消费者线程来取数据。
public E poll() {
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == 0)
return null;
E x = null;
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() > 0) {
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}
出队方法:
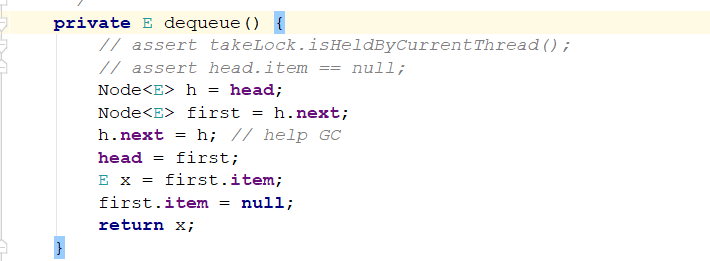
返回first的item元素,这个链表的头结点维护的都是空节点,效果图如下:
出队前:

出队后:

add 和remove:
add方法: 直接使用父类AbstractQueue的方法:
在offer的基础上进行了保证,成功返回true,false的时候返回异常。
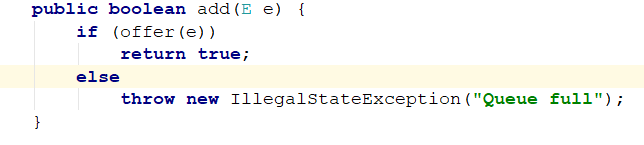
remove方法:
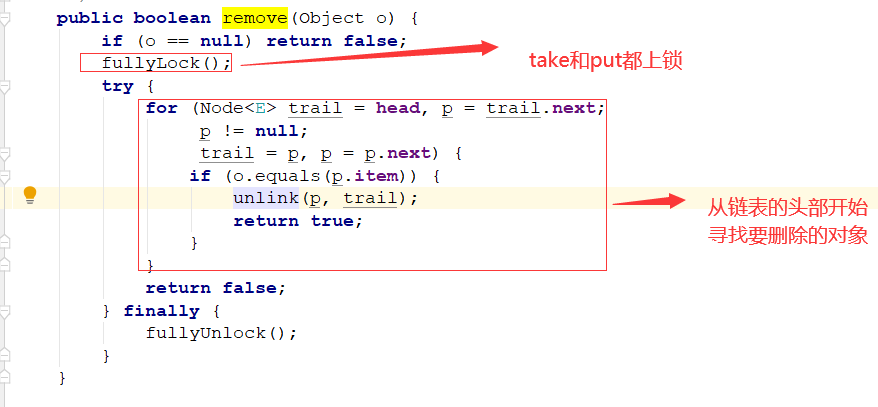
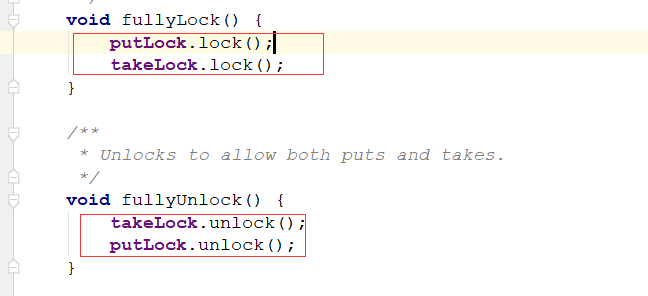
两把锁同时上锁,两把锁同时解锁:
来看一下删除元素的动作:因为数据结构是链表,所以只需要把指向该节点的上一个节点的next变量不指向该节点即可,然后
gc的时候就会把该节点回收掉:
trial.next = p.next 的作用就是让p节点的前一个元素直接指向p的后一个元素,而数组结构就是把该下标置为null object[takeIndex] == null

put和take方法:
put方法:
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset local var
// holding count negative to indicate failure unless set.
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
/*
* Note that count is used in wait guard even though it is
* not protected by lock. This works because count can
* only decrease at this point (all other puts are shut
* out by lock), and we (or some other waiting put) are
* signalled if it ever changes from capacity. Similarly
* for all other uses of count in other wait guards.
*/
while (count.get() == capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
}
take方法:
take方法的判断逻辑与poll基本相同,唯一区别是,如果对列没有元素,take为阻塞消费者线程,而poll会返回false。
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
signalNotFull();
return x;
}