这两个占位符,#预编译后设置参数,#{}会被参数替换,$ 是sql与参数直接拼接,容易sql注入。
变量直接替换一般使用$,例如in(${xxx}),下面看一下源码层面怎么实现的。
一:#{}的替换
#{} 的替换就是jdbc预编译后的替换占位符 ?
/**
* 执行查询操作
*
* @param sql
* @param list
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void executeQuery(String sql, List<Integer> list) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = getPreparedStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, list.get(0));
preparedStatement.setInt(2, list.get(1));
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
}

下面来看看mybatis是如何替换的,第一步,把#{} 替换 为 ?
这是解析mapper.xml文件中解析select|update|delete|insert 元素的方法
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? new Jdbc3KeyGenerator() : new NoKeyGenerator();
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
解析sqlSource的部分:


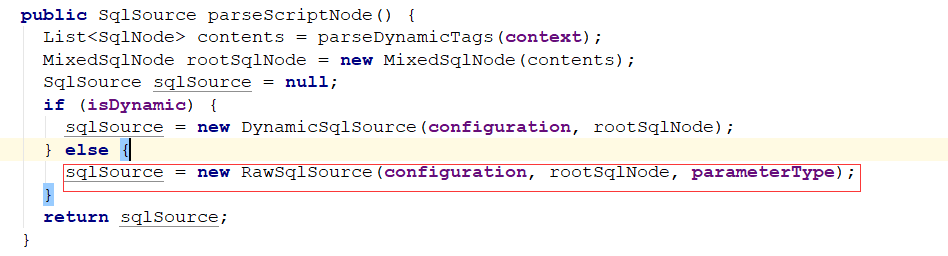


一路跟下来之后,会发现这里的GenericTokenParser解析器就是把#{} 符合 替换 为 ?占位符,具体替换工作在parse方法中进行。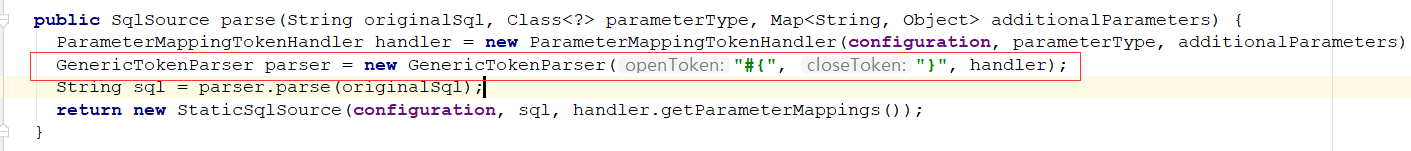
第二步是把 占位符 ? 替换为 具体的参数:
这时simpleExecutor类的doQuery方法:
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
创建PrepareStatement语句:
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
PrepareStatementHandler的parameter方法:
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
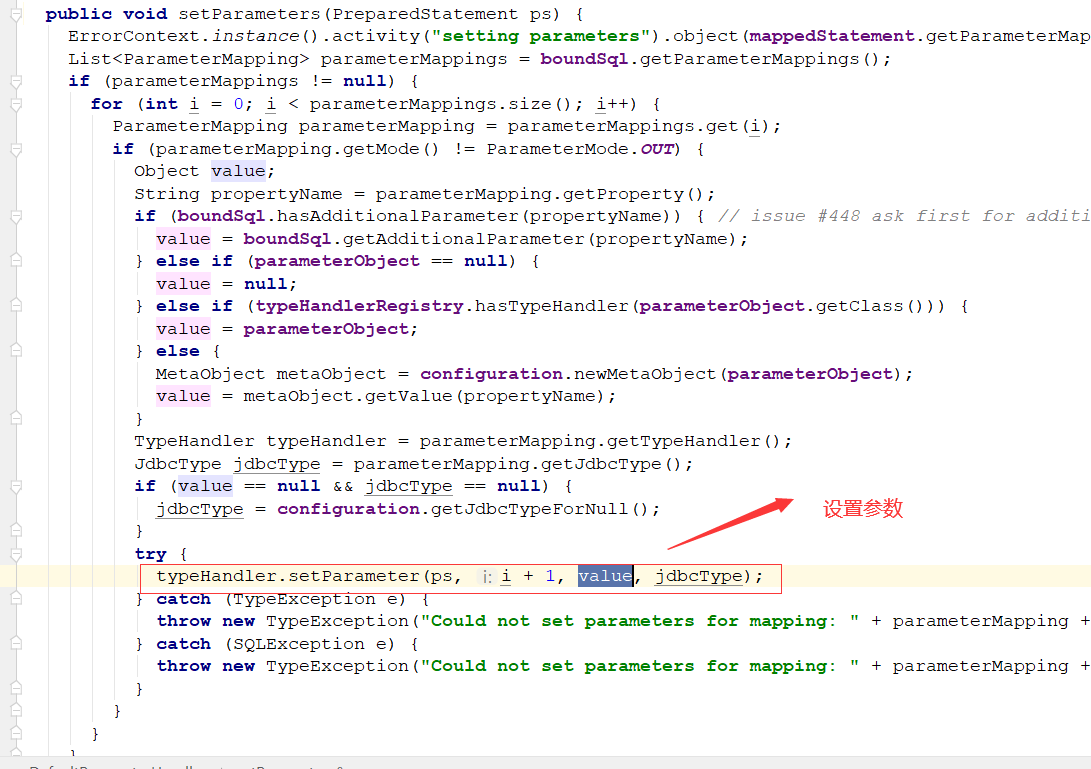
设置非空参数:
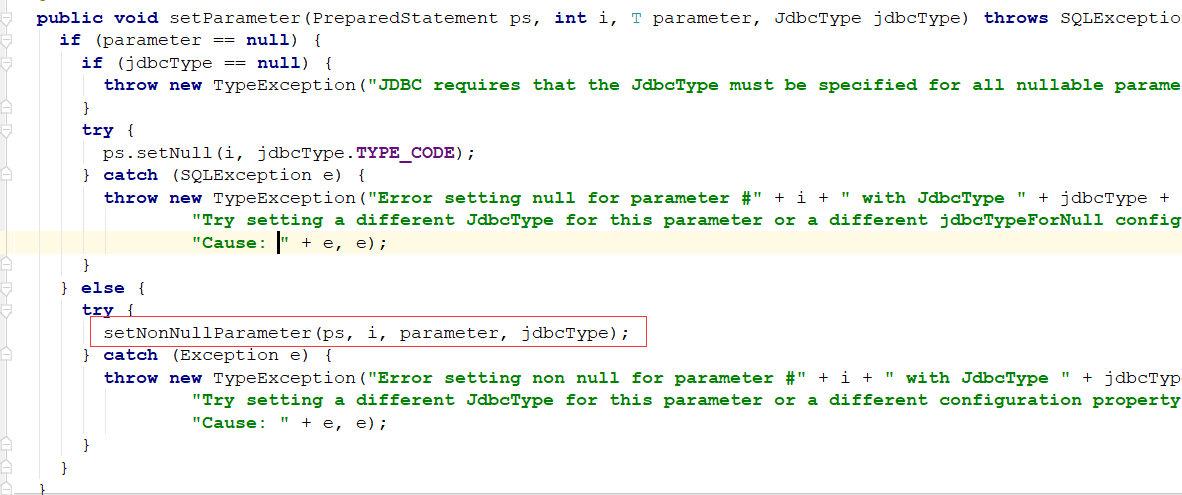
和上面jdbc设置参数的方式是一样的:

上面就是#{} 的工作原理,下面来看一下${} 是怎么替换的
CacheExecutor的query接口:

DynamicBoundSql类的getBoundSql:

MixedSqlNode:

创建一个替换 ${} 的解析器,然后在parse中解析

到这里就完成了${} 解析的分析了
总结:#{} 在解析mapper.xml 生成 mappedStatement的时候,就会把 #{} 替换为 ?,然后在创建preparedStatemnt后,执行前,需要
设置参数,将占位符替换为参数,${} 是在查询开始前,获取boundSql的时候 把 ${} 替换为了参数。